The arrangement and layout of the site provides for the creation of paths. And the requirements for them are quite serious: they must be reliable, comfortable, functional, functional, beautiful and very desirable – inexpensive. On how to make garden paths with their own hands with little expense will talk in this article.
Contents of the article
What to make paths of
The covering of the path is solid or bulk. To create a solid coating, the following materials are used:
- Concrete. Concretized paths are not just an ordinary gray tape. In addition to the fact that there are dyes and it can be colored if desired. There are also molds for pouring immediately on the spot. It turns out homemade paving tiles. Another option is to pour yourself small concrete slabs of the desired size, then lay them on the backfill. Examples of design see in the photo.
- Plitnjak. This is a natural stone that is sawn into plates. It is laid on the prepared base (about this further), the gaps are filled with backfill. It turns out beautiful, reliable, non-slip. It is not without reason that stone paths of flagstone are so loved by landscape designers.
- Backfill – one of the important elements that form the appearance
- In this form of flagstone path does not break the lawn, and it is comfortable to walk on
- The color of the stone can be any
- Brick. Ordinary ceramic brick – a beautiful material, but not for paths. It absorbs moisture, if then wet freezes, it breaks into pieces. If you are going to make a path of broken bricks, then more or less normally walk on it can only be a couple of years. Then you will have to redo it. The resulting gaps will need to be filled with coarse sand or fine crushed stone. Much longer on the path will serve clinker brick, but this option low-cost can not be called: the cost of one piece of several tens of rubles.
- Quite pretty paths from the old brick. And if the backfill is made on the sides and in the seams, it will be a beauty in general
- These are two types of brick – ceramic and chipped from granite
- A path from clinker brick – beautiful, nothing to say…. but maybe too beautiful for a garden?
- Wood. Such a seemingly unsuitable material, but with proper processing it can serve for a long time. Moreover, many made with their own hands paths made of wood, can be classified as low-cost. For example, invented to use stumps and tree trimmings as curbs or cover. Also make decking from well-treated boards – better terraced, but if not, it will fit and from the old floor.
- Plastic. There are tiles for garden paths exactly from plastic – polyethylene or polypropylene. It has a square shape and a system of locks, which is attached one to another. It can be laid directly on top of the lawn or previously trampled on the dacha or on the site paths. This option is fast and cheap. It can definitely be called “low-cost”. It is better, of course, to make a crushed stone and sand backfill according to the rules, and lay plastic elements on top. This is already a little longer and more expensive. There is still immodest, but very beautiful option of plastic tiles for paths. There is also a “garden parquet”. These are plates or boards made of wood-polymer composite – WPC (they are on the photo, looking exactly like a parquet). This material has appeared relatively recently. It looks and feels like wood, but in fact it is a mixture of wood flour and polymer. This is a very beautiful coating, but here is the cost of their cost is not modest. Although not fabulous.
- Pebbles. These are rounded natural stones that can be found on the banks of rivers or lakes. For the manufacture of paths is more suitable more flat pebbles. They come in different shades of gray, black, white, sometimes you can find maroon. From these stones, stacked one to another closely, get an amazing beauty of mosaic paths. But this is an activity for the diligent and persistent. Those who do not have enough patience, can find large flat boulders or large pebbles and lay them in the sand. This is not so luxurious, but no less reliable. You can also do the same with granite or other similar stones. It is important that at least one edge be relatively flat. This flat part and put up, the rest is buried. Work is not easy, but the path will be possible not only to walk, but also to drive.
- Different types of paths from pebbles
- Large pebbles do not require so much time for laying
- Beautiful pebble paths in the garden.
- From a large natural stone, you can pave pretty good corners
- Handy materials. Dacha paths are made of old tires and bottles.
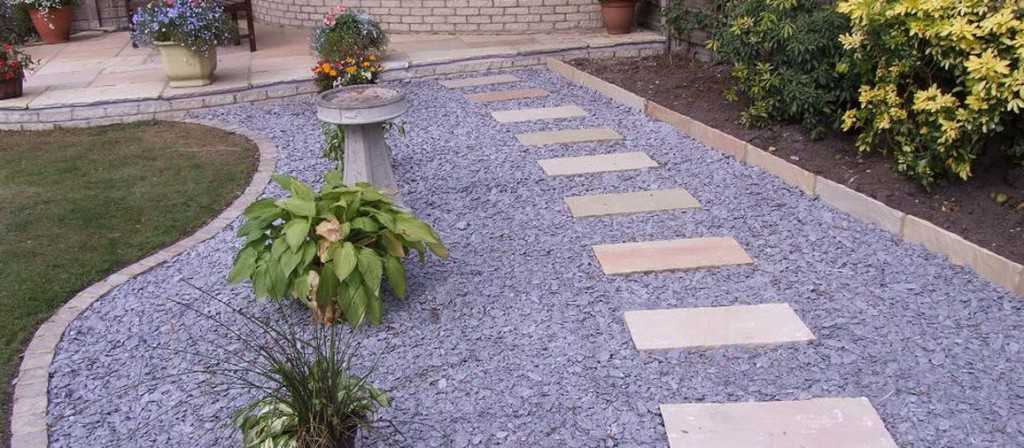
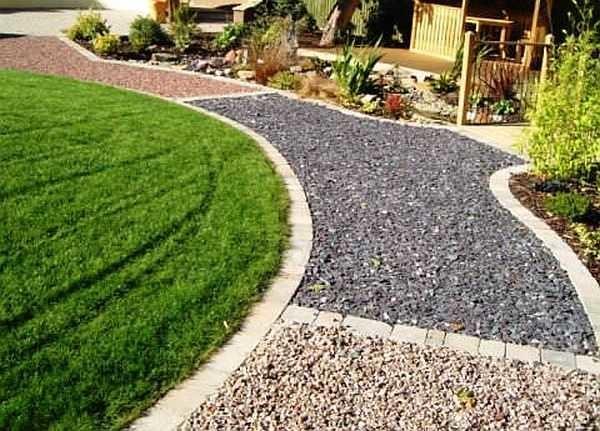
There are also paths with a poured surface: these are gravel or crushed stone. Their peculiarity is that with a small layer of 2-3 cm and with sufficient compaction, it is convenient to walk on them. If the layer is a little more, unevenness is formed when walking, and such walking is tiresome. Therefore, as you have seen in many photos, gravel and crushed stone are used as backfill, in which rigid elements of other materials are laid. If done properly, this is convenient: gravel conducts water well and puddles are not formed. Those who do not like the gray color, you can advise to paint it: many designers do so when organizing rockeries.

About the secrets of plot planning, read here.
How to make garden paths with your own hands
It is not enough to know what you can make garden paths with your own hands. You also need to know how to make them correctly, so that it served not one season and not two. Laying different materials can be slightly different, but there are a few rules and actions that are repeated in any technology.
Bufirst rule: when laying or forming the pavement of the path, it is made with a slight slope. If the material allows, a slope of a few centimeters is made on both sides of the center. If, for example, a concrete path is poured, the slope is formed in one direction – away from the house, if it is nearby. The slope is made towards the lower part of the site, if the path is located on a slope.
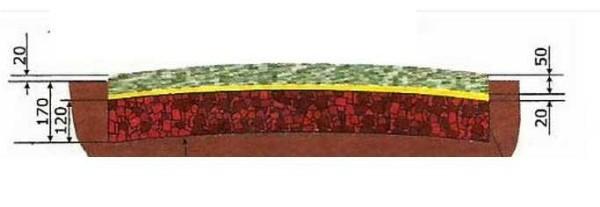
The second rule: under any coating requires preparation of the base. If you lay stones (for example) directly in the clay or loam, the benefit, of course, will be – it will definitely be more comfortable to walk, but the stones after a while “silted”. They will simply sink into the clay. It will take much more time if you make a backfill. And if you make a drainage cushion and curb, water drainage will be even more effective, and everything will look even more beautiful.
The third rule: the level of the pavement should be a couple of centimeters higher than the adjacent area. Then the water will quickly descend, it will be more convenient to clean, and cleaning will be needed less often: will not flow eroded earth neither during rains, nor during the watering of flowerbeds, which are often made along the paths.
On how to make beautiful beds read here.
Step-by-step instructions
Making garden paths with your own hands, start with markings. Ideally, the size and shape should be you put on the site plan, and the marking should take place according to the project. But most often everything is done locally. To view the future path more clearly, its contours can be pre-poured white sand or something similar. If the shape is satisfied, you can hammer in the pegs and stretch twine between them, but you can work on the sprinkling.
Next, to make a path from stone, flagstone, brick, paving stones, pebbles and other similar materials, the actions are as follows:
- Between the two marks, the sod is removed. The depth of the ditch should be about 15-25 cm.
- A curb is dug along the edge, if it is provided.
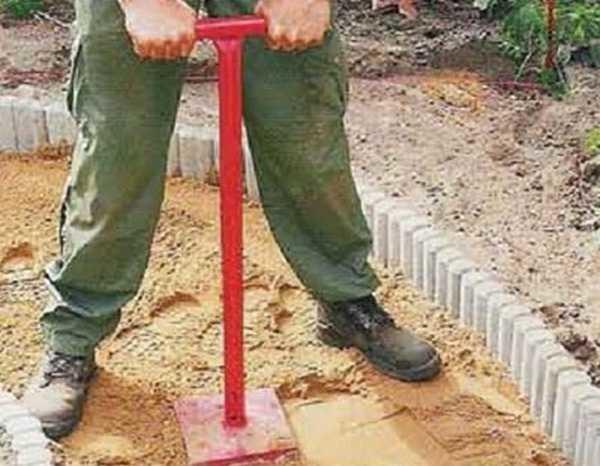
- The bottom of the ditch is leveled by removing roots, stones, eliminating significant holes or hillocks. The bottom is tamped (tamping in the photo below).
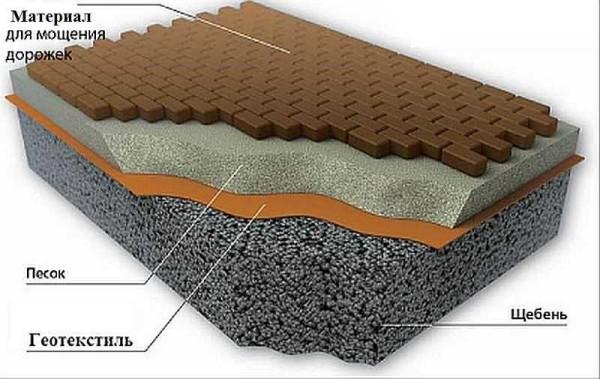
- Pour a layer of crushed stone of coarse or medium fraction. To save the budget, you can pour broken bricks, other large construction debris. If you have a vibratory plate – great, if not, take something similar to the tool in the photo (you can make a large log, to which to nail across the cut handle). Use this tool to level the bottom. If you have filled in the debris, you need to pour a little crushed stone on top and tamp it once again.
- Lay a layer of geotextile on top. Its edges are raised in line with the borders or even a little higher. It is better not to skip this layer. It does not allow the sand to mix, which is usually poured on top of the crushed stone, prevents the roots of plants that destroy the path from sprouting. Very useful thing.
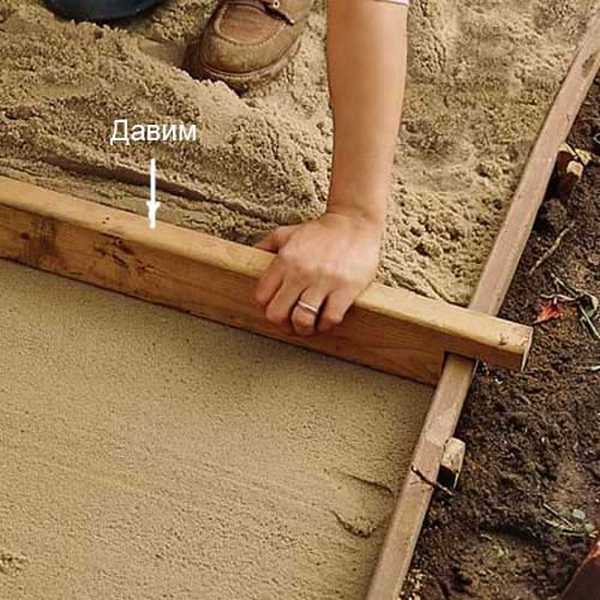
- Sand is poured on the geotextile. Its layer should be such that the laid covering was a little higher than the general level on the site. Sand is first scattered with a shovel, then, evenly distributed, leveled with a rake. Then it is tamped and leveled. To level the sand level, you can use a rule (a construction tool that is often used when pouring a concrete floor) or just take a large ruler, a construction level, a level lath. Sometimes it is necessary to pour, tamp and level several times. It is desirable to achieve a perfect surface.
- In the sand lay stone, pebbles, flagstone, paving stones, bricks, etc. They are put in the right place, then knocked with a rubber mallet: drive deep into the sand.
Along a beautiful path you can place a flower bed or flowerbed. How to make them, read here.
Beautiful path from pebbles with their own hands
If with flagstone, paving stones, bricks, everything is more or less clear – everyone has already seen and not once, how it is done, then how to lay pebbles in patterns is not clear.

Below is a photo report on the process of making a path from pebbles. It shows the main techniques: on the leveled sand, lines are drawn on which the pebbles will be laid out. If these are arcs, they are made with a string and two sticks/nails.
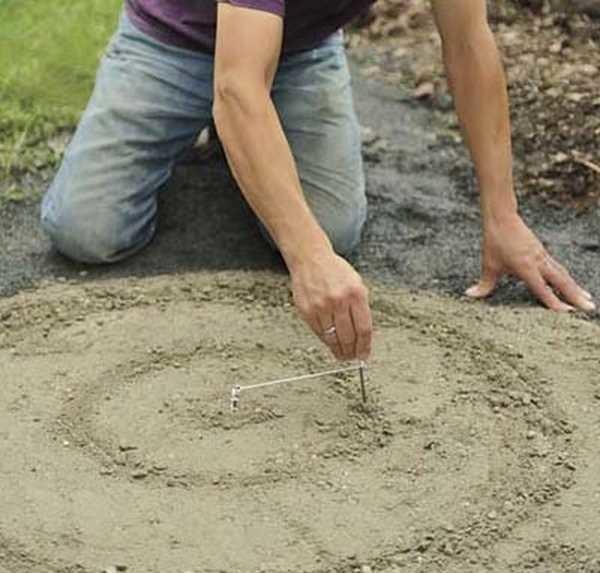

When you pick up the stones, you lay them on the edge close to each other, slightly sinking them into the sand.
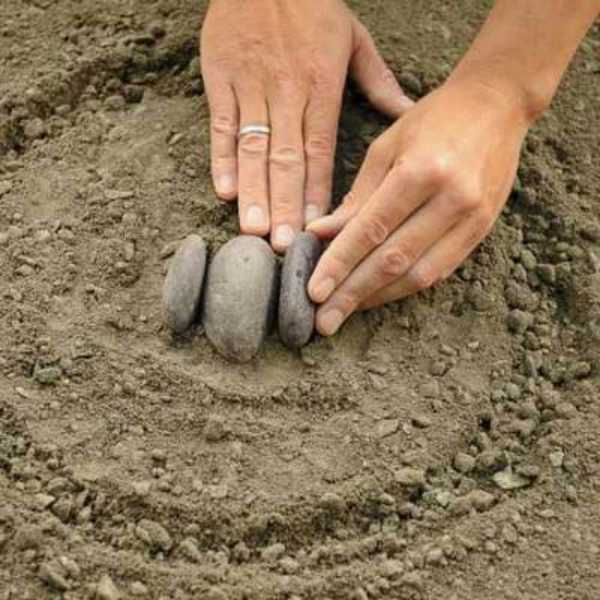

On the folded pattern lay a board, take a rubber mallet and knock on the board, hammering pebbles into the sand. So buried the whole pattern, making sure that the edges of the pebbles were at the same height.
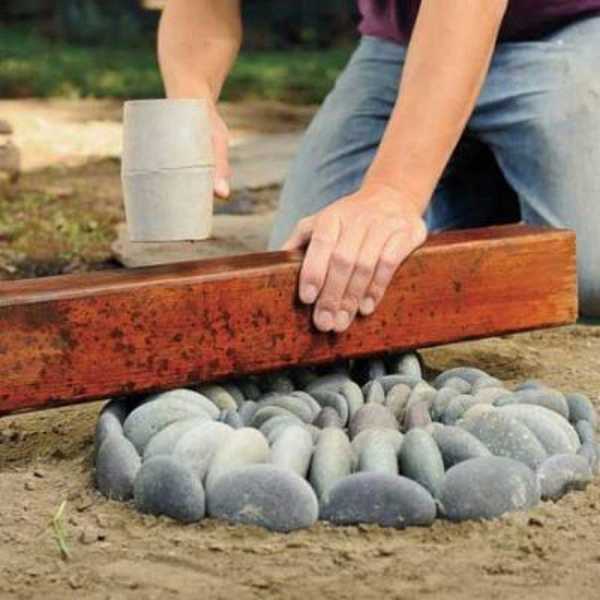

Take a mixture of sand and cement (sand 2 parts, cement 1 part) and fill in the gaps, leveling the layer with a brush.
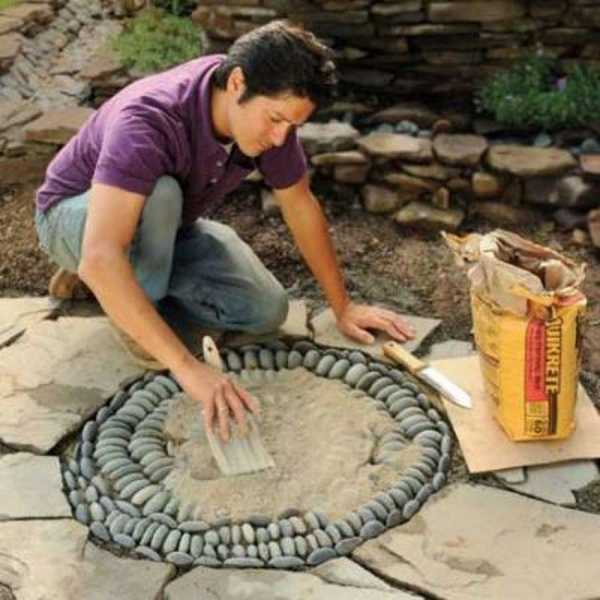

The pebble path fragment is carefully poured with water so that the backfill is not eroded. Wait a few hours for the cement to set a little, then remove the excess with a soft brush.
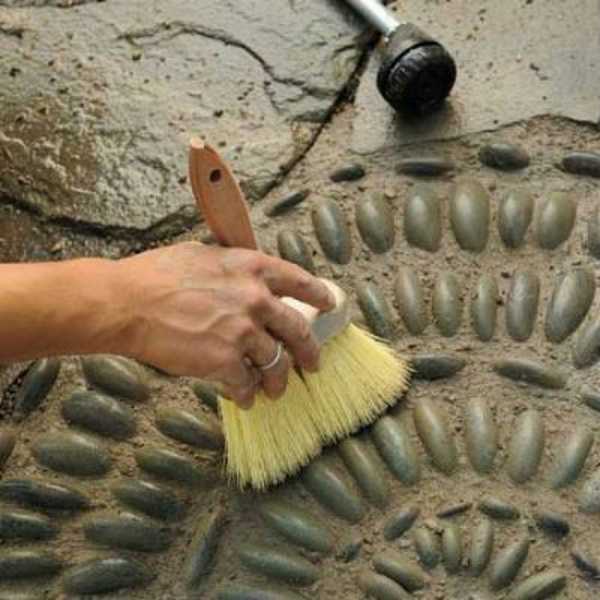

It is important not to miss the point: the mortar should not get dirty, but it should not become a stone either. If you pick it up with your finger, it should crumble. It’s time to scrape off the excess.
On how to grow a green hedge, read the article “Fence hedge: how to grow and form”
A path from wooden stumps and crushed stone: video
Old logs or trees can be turned into a beautiful path. They are sawn into chunks of the required length, the front cut is sanded, the whole wood is treated first with a composition of bioprotection (you can impregnate with waste oil). After drying dip in Kuzbass varnish and dry again. Then cover the face parts of the stumps with paint of the required color – which will protrude outside. Once again drying and only then put in the sand.
The process is described in detail in the video. It explains step by step how to make garden paths with your own hands from stumps or logs.
Independently make a concrete walkway
The process is generally similar to the one described in the beginning. There are some differences, about which we will talk.
After the trench is dug and the bottom is leveled, a formwork is installed along it from both sides. These are boards of 25 mm thickness (thicker is possible, thinner is undesirable, you can use plywood with a thickness of 16-18 mm, chipboard). Their height is the height of the path. If you will form a slope, the boards should be set with it in mind – one side is slightly higher, the other – slightly lower.

To make the formwork, pegs are hammered into the ground with a spacing of no more than 60 cm. Boards are nailed to them. The inner surface of the formwork is better to smear with waste oil or other oil: to remove easily. Next, crushed stone is poured on the bottom and tamped. But tamping should be carefully: if you walk on the bottom, traces should not be visible.
Further, in order that the track does not crack, a metal reinforcing mesh is laid on the crushed stone. The thickness of the rod is 4-6 mm, the step is 5-10 cm. It is sold in pieces, they should be tied together with steel wire.

Then to compensate for the expansion in the winter period, you need to put wooden strips with a thickness of 1,5-2 cm. They are placed across the path, set so that the height of the strips was in line with the planks of the formwork. Compensation strips are placed at least every 2 meters. More often is possible, less often is not. Why do it more often? For beauty. Squares look better than long rectangles.
In the ready-made frame poured concrete mortar grade not lower than M-250 (about concrete grades and its preparation read here). For it take 1 part of cement, 3 parts of sand, 4 parts of crushed stone. Everything is mixed into a mortar of medium fluidity (thick sour cream) and poured into the formwork. When pouring it is necessary to make sure that there are no air bubbles. To remove them, the mortar is pierced with a pin, slightly rocking it – poking. Ideally, if there is a surface vibator for concrete – it quickly compacts the mortar, creating a perfectly flat surface. If it is not, you will have to level with a rule, using the edges of the formwork as beacons.
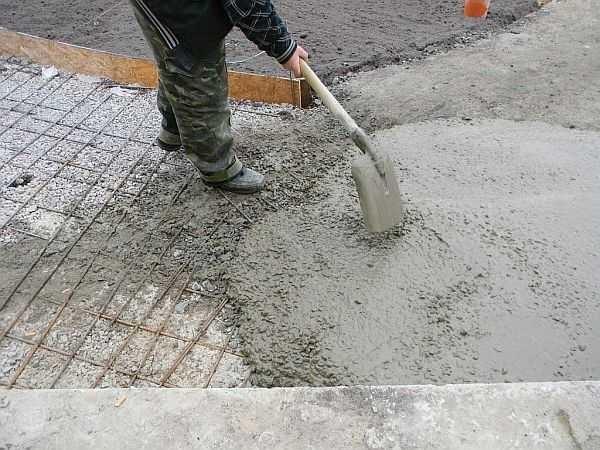

After a few hours, after the concrete has set, you can work on the surface. It can be left as it is, you can run a stiff brush over it, making transverse strips, you can finally lay pebbles, stones, flagstones, etc. in the not quite hardened mortar. This is not very economical, but it is reliable. After a couple of days, the formwork can be removed, and you can already walk on the path.
About what fences are and how to make them is written here.
Budget path from the tire
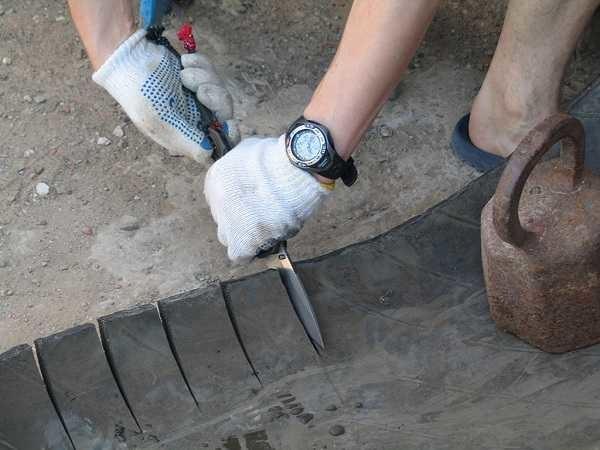
What only do not do from tires: flowerbeds, swings, ponds and…paths. It’s simple: you need to cut off the sides of an old tire, leaving only the tread. What can be cut off with? A bolt cutter. Someone manages with a knife, but this is only if the cord is not metal.
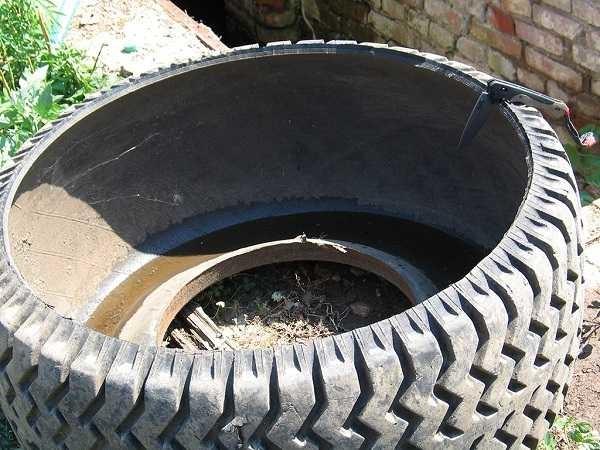

The projector is cut across to make a track. Then on the sides make cuts on the centimeters of 15 centimeters – depending on the diameter of the tire. They will give the opportunity to unfold the rubber.

In this form, it can already be laid on the beds. It will serve for many years. This one is exactly garden paths with low costs.
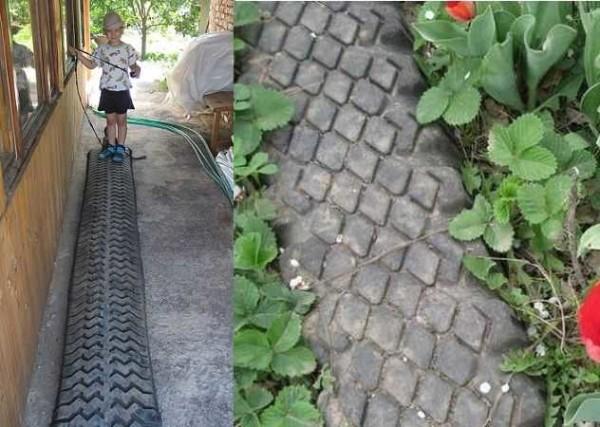

As you realized, there are a lot of options on how to make garden paths with your own hands. It is impossible to tell and describe about all of them, but we try to…
About making a playground with your own hands is written here.




















