Gas is still the cheapest type of fuel, but the cost of connection is sometimes very high because many people want to assess in advance how economically justified such costs. To do this, you need to know the gas consumption for heating, then you can estimate the total cost and compare it with other fuels.
Innehåll i artikeln
Calculation methodology for natural gas
Approximate gas consumption for heating is calculated on the basis of half the capacity of the installed boiler. The whole point is that when determining the capacity of the gas boiler, the lowest temperature is laid down. This is understandable – even when it is very cold outside, the house should be warm.

But to count the gas consumption for heating on this maximum figure is completely wrong – because in general the temperature is much higher, which means that the fuel is burned much less. That is why it is accepted to count the average fuel consumption for heating – about 50% of the heat loss or boiler capacity.
Calculating gas consumption by heat loss
If there is no boiler yet, and you estimate the cost of heating in different ways, you can count from the total heat loss of the building. They, most likely, you know. The methodology is as follows: take 50% of the total heat loss, add 10% for the provision of DHW and 10% for the heat outflow during ventilation. The result is the average consumption in kilowatts per hour.
Then you can find out the fuel consumption per day (multiplied by 24 hours), per month (by 30 days), if desired – for the entire heating season (multiplied by the number of months during which the heating works). All these figures can be converted into cubic meters (knowing the specific heat of combustion of gas), and then multiply the cubic meters by the price of gas and thus find out the cost of heating.
| Name of fuel | Unit of measurement | Specific heat of combustion in kCal | Specific heat of combustion in kW | Specific heat of combustion in MJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural gas | 1 м 3 | 8000 kCal | 9.2 kW | 33.5 MJ |
| Liquefied gas | 1 kg | 10800 kCal | 12.5 kW | 45.2 MJ |
| Hard coal (W=10%) | 1 kg | 6450 kCal | 7.5 kW | 27 MJ |
| Wood pellet | 1 kg | 4100 kCal | 4.7 kW | 17.17 MJ |
| Dried wood (W=20%) | 1 kg | 3400 kCal | 3.9 kW | 14.24 MJ |
Example of heat loss calculation
Let the heat loss of a house be 16 kWh. Let’s start calculating:
Convert to cubic meters. If we use natural gas, we divide the gas consumption for heating per hour: 11.2 kWh / 9.3 kW = 1.2 m3/h. In the calculations, the figure 9.3 kW is the specific heat capacity of combustion of natural gas (available in the table).
By the way, you can also calculate the required amount of any type of fuel – you only need to take the heat capacity for the required fuel.
Since the boiler has not 100% efficiency, but 88-92%, you will have to make more corrections to this – add about 10% of the obtained figure. Total gas consumption for heating per hour – 1.32 cubic meters per hour. Then you can calculate:
- consumption per day: 1.32 m3 * 24 hours = 28.8 m3/day
- demand per month: 28,8 m3/day * 30 days = 864 m3/month.
The average consumption for the heating season depends on its duration – multiply by the number of months, while the heating season lasts.
This calculation is approximate. In some month gas consumption will be much less, in the coldest – more, but the average figure will be about the same.
Calculation by boiler output
Calculations will be a little easier if there is a calculated boiler output – here all the necessary reserves (for DHW and ventilation) are already taken into account. Therefore, simply take 50% of the design capacity and then count the consumption per day, month, per season.
For example, the design capacity of the boiler – 24 kW. To calculate the gas consumption for heating, we take half of it: 12 kW. This will be the average heat demand per hour. To determine the fuel consumption per hour, divide by the calorific value, we get 12 kW / hour / 9.3 k / W = 1.3 m3. Then everything is calculated as in the example above:
Then add 10% for the non-ideality of the boiler, we get that for this case the consumption will be a little more than 1000 cubic meters per month (1029.3 cubic meters). As you can see, in this case it is even simpler – fewer numbers, but the principle is the same.
By square meter
Even more approximate calculations can be obtained by the square footage of the house. There are two ways:
- You can calculate according to SNiPov norms – for heating one square meter in the Middle Belt of Russia on average requires 80 W/m2 . This figure can be applied if your house is built according to all requirements and has good insulation.
- It is possible to estimate by average statistical data:
Each owner can estimate the degree of insulation of his house, accordingly, you can estimate what gas consumption will be in this case. For example, for a house of 100 square meters. m. with average insulation will require 400-500 cubic meters of gas for heating, a house of 150 squares will take 600-750 cubes per month, for heating a house of 200 m2 – 800-100 cubes of blue fuel. All this is very approximate, but the figures are based on many actual data.
Calculation of liquefied gas consumption
Many boilers can work from liquefied gas. How profitable is this? What will be the consumption of LPG for heating? All this can also be calculated. The methodology is the same: you need to know either the heat loss or the boiler capacity. Then the required amount is converted into liters (units of measurement of liquefied gas), and if desired, count the number of cylinders needed.
Let’s look at the calculation by example. Let the boiler capacity is 18 kW, respectively, the average heat demand is 9 kW/hour. When burning 1 kg of liquefied gas, we get 12.5 kW of heat. So, to get 9 kW, 0.72 kg will be needed (9 kW / 12.5 kW = 0.72 kg).
Next, we calculate:
- per day: 0.72 kg * 24 hours = 17.28 kg;
- per month 17.28 kg * 30 days = 518.4 kg.
Let’s add a correction for the boiler efficiency. It is necessary to look at each case, but we will take 90%, that is, add another 10%, it turns out that for a month the consumption will be 570.24 kg.
To calculate the number of cylinders, this figure is divided by 21.2 kg (that’s how many kg of gas is on average in a 50-liter cylinder).
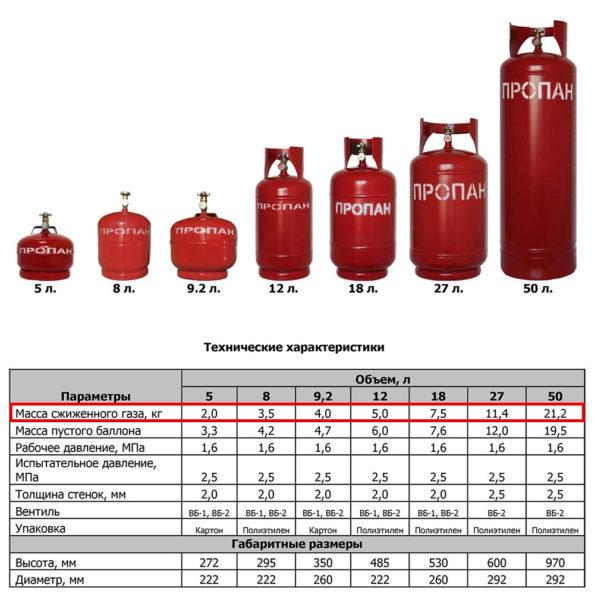
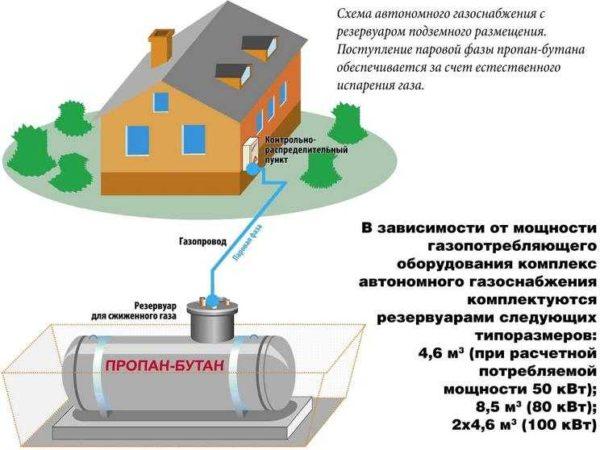
Total, for this boiler will require 27 cylinders of liquefied gas. And the cost count yourself – prices in the regions are different. But do not forget about transportation costs. They, by the way, can be reduced if you make a gas holder – a sealed container for storing liquefied gas, which can be refueled once a month or less often – depends on the volume of storage and the need.
Again, it should be remembered that this is only an approximate figure. In cold months, the gas consumption for heating will be higher, in warm months – much less.
P.S. If it is more convenient for you to count consumption in liters:
- 1 liter of liquefied gas weighs about 0.55 kg and when burned gives about 6500 kW of heat;
- a 50 liter cylinder contains about 42 liters of gas.