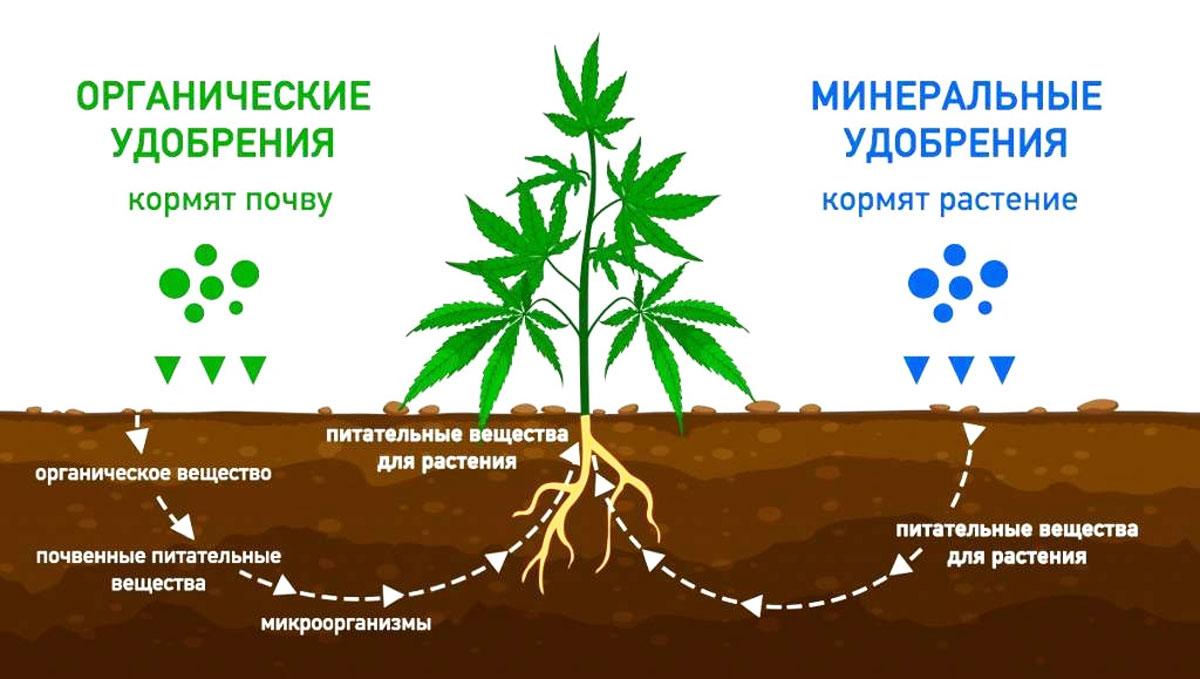
Spring is the time of nature’s awakening and the best time to start caring for plants in the garden, vegetable garden or flower bed. Knowing what fertilizers for the garden or vegetable garden in spring is the best way to apply to the soil, you can make full use of the potential of the land and the crops grown on it.

After the winter stagnation comes the period of plant activation. But the melted snow leaches useful elements from the soil, thus impoverishing it. And after all, the intensity of their development, the density of flowering and future harvest depends on the saturation of the soil with the necessary substances, as well as on the full nutrition of plants. But before we list the types of fertilizers for effective growth, let us remind a couple of golden rules for their introduction in spring:
- Fertilizers are not applied in the snow, as useful microelements for plants will “float away” together with melt water;
- do not exceed the recommended dose, because in this case more does not mean better, because the excess of this or that element will lead to the opposite effect – the plant will begin to wither and wither, and the rich harvest can be forgotten.
Vsebina članka
The importance of additional nutritional elements for plants
To the nutrient elements of first importance in spring, nitrogen is first of all. It is thanks to him that the green part of plants is actively gaining strength. But later in the period of flowering and fruit setting it is necessary to reduce the flow of nitrogen into the soil, otherwise all the vitality of the plant will go into the haulm. At that time, potassium-phosphorus fertilizers become relevant.
All of the above elements can be applied as both organic and mineral fertilizers. Many experienced plant breeders give preference to universal fertilizers for the vegetable garden, since the composition of such preparations includes the entire set of necessary macro- and microelements, balanced in their quantitative content. Spring complex feeding allows you to reduce the number of treatments and eventually get a rich harvest.
When to apply fertilizers
There are a number of recommendations that regulate the timing of the introduction of nutrients in the spring:
- The first time feeding is carried out immediately after the snowfall. This applies only to mineral fertilizers.
- Effective is considered the introduction of substances when preparing the soil for sowing. In this case, useful substances reach the root system, where they immediately begin to work.
- Feeding during planting requires strict adherence to the dosage, which can be difficult to achieve. This method is justified for those gardeners and gardeners who use sowing and planting equipment.
| Calendar of fertilizing plants in the garden (per 1m2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Apple, pear | Apricot, plum, cherry | Gooseberry, currant | Raspberry | Strawberry, strawberry |
| April | 30-50 grams of urea | 30-50 grams of urea | 30 grams of urea | 40 grams of urea | 5-7 grams of urea |
| May | 150 grams of ash and 20 grams of ammophoska. Spraying with humic fertilizer. | 150 grams of ash and 20 grams of ammophoska. You can replace the infusion of cow dung with ash: 1 bucket of manure on 1-1.5 kg of ash pour 5-6 buckets of water and insist 4-6 days. Apply ½ bucket under the tree. The first feeding immediately after flowering, the second – after 2 weeks. | Do spraying with humic fertilizer. If the leaves lighten, it means that there is a lack of nitrogen. In this case, additionally make liquid nitrogen fertilizer or humus 10-15 kg per bush | You can do without fertilizer. If necessary, you can make ash 150 g per 1m2 and spray with a solution of urea 1 tbsp. spoon per 10 liters of water. | Infusion of cowslip 0,5 liters under the bush or complex fertilizer according to the instructions. |
Thus, in the spring, fertilizers are better to make three times, and the full dose is crushed, so as not to harm the plants. In addition, feeding crops, it is important to pay attention to what part of the plants will be consumed.
Types of fertilizer to be applied
Feeding in the springtime is made by 2 types of fertilizers: organic and mineral fertilizers.
Organics, in turn, are divided into vegetable and animal. The first type includes: ashes, peat, compost, onion husks, food waste, siderates, herbal infusions, sawdust, silt. Organic fertilizers of the animal type include: manure, poultry manure, bone meal. This is an excellent source of nitrogen, increasing the quality of the soil, its oxygen permeability, the content of useful substances.
But the introduction of organic matter also carries with it the possibility of getting into the soil weed seeds, insect larvae, toxic inclusions. Therefore, it is important to know the origin of the manure used. It is best to prepare it yourself or purchase manure in pellets.
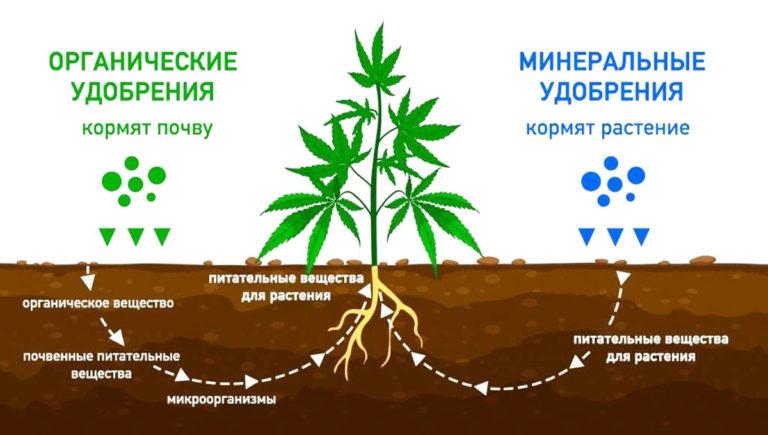
Mineral fertilizers, unlike organics, do not affect the soil, supplying the necessary macro- and microelements directly to the plants. These include nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. It is optimal to apply mineral fertilizers to the soil every year in the proportions shown in the table.
| Ime elementa | Name of fertilizer | Application rate |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | ammonium nitrate, urea | 30-35 g per sq. m. |
| Fosfor | superphosphate, ammophos | 25 g per square meter. |
| Potassium | potassium sulfate, kalimagnesia, kalimag | 20 g per square meter. |
For the most part, the mineral additives under consideration are presented in a convenient format of granules, but liquid mineral fertilizers are also popular with gardeners. Both allow a more rational approach to plant nutrition, achieving excellent yields.
Complex fertilizers include several useful elements balanced by percentage content. The use of complex water-soluble fertilizers, for example, allows you to reduce the frequency of additives, effectively increasing yields. They are designed both for individual plants and for several types of crops. Popular complex fertilizers include preparations “Kalimag”, “Aquarin”, “Stimul”, “Ammophos”, “Kemira”, “Azofoska” and others.
Folk ways of feeding are also in demand among plant breeders. Among them:
- eggshells and bone meal – enrich the soil with calcium and produce the effect of deoxidizing the soil;
- bark and sawdust improve soil air permeability, making the soil softer and looser;
- siderates (clover, mustard, oats, rye) saturate the soil with nitrogen;
- onion husks – the number one way to sanitize the soil and get rid of pests;
- silt – an unambiguous leader in nitrogen content, on this indicator it is ahead of manure 4 times.

Garden feeding
Spring feeding of the garden is necessary to help crops to please with rich fruiting. To understand what to fertilize the garden in the spring, continue with our overview. We have tried to conveniently structure all useful information by crop type.
Spring fertilization of trees
The ideal time for fertilizing garden trees in spring is 2-3 weeks before flowering. Perennial fruit trees in spring are in dire need of nitrogen fertilization. To compensate for the deficiency of this important element will help the application of the following solution: 5% solution of ammonium nitrate, urea and litter. The composition is watered into the soil in the bordering circle. Application rate: half a bucket (5 liters) per m².
In addition to such root fertilization, foliar fertilization is successfully used, produced by spraying. For example, an excellent fertilizer for apple trees will be 0.3% urea solution, for pears such a composition is taken in a dosage of 0.1-0.2%, for stone plantings (cherries, cherries, quince, peaches, apricots) – 0.5-0.6%.

Quite popular preparation “Healthy Garden”, which is a unique biocomplex that increases yield and safety of fruits in storage.
Shrub feeding
If the soil on the site from the fall was treated with organics, the need for spring fertilization is eliminated.
The first application should coincide with the moment when the earth completely thaws, and buds begin to swell. Use a nitrogen-containing fertilizer: ammonium nitrate (25-30 g per square meter) or ammonium sulfate (40-50 g per square meter).
The second time fertilizing shrubs is made at the end of May. Then gooseberries, raspberries, currants are fertilized foliar – 1-2% solution of superphosphate and potassium sulfate. Together should be fertilized with microelements: 0,01-0,055% – boric acid and 0,1-0,5% – manganese sulfate.

In the case of shrubs, it is also recommended to start with nitrogen and phosphate compositions that develop the green mass of the plant. And potassium fertilizers are introduced later to support flowering and fruiting.
Fertilizing the vegetable garden
Fertilizers should be introduced into the vegetable garden beds 3-4 weeks before sowing. At this time it is advisable to use organics – compost or over-ripe manure at the rate of 1 bucket per 1 square meter. In general, manure is universal as a vegetable garden fertilizer, suitable for the absolute majority of crops.
The turn of introduction of mineral compositions comes just before planting, or before loosening the soil. Let us specify what should be applied in the spring under digging for vegetable crops:
- Nitrogen compositions (ammonium nitrate, urea) at the rate of 30-35 g per square meter;
- potassium compositions (potassium sulfate, calimagnesia, calimag) – 20 g per sq. m.;
- phosphorus compositions (ammophos, superphosphate) – 25 g per square meter. m.
| Vegetable | Phases and signs | 1st, consumption per 10 liters of water | Phases and signs | 2nd, consumption per 10 liters of water Phases and signs | Phases and signs | 3rd, consumption per 10 liters | Dose, liters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KAPUSTA | 10-15 days after planting | Infusion of cowpea, or 10 g of urea. 20 g superphosphate, 10 g potassium sulfate | 10-15 days after 1 fertilization | Infusion of cowpea, or 10 g urea. 20 g superphosphate, 10 g potassium sulfate | 20-25 days after 2 fertilizing | For 10 liters of cowdung infusion 30 g superphosphate | 0.5 |
| CARTOPHELLE | If leaves are thin and yellowing | 15-20 g ammonium nitrate | Bud emergence phase | 20 g potassium superphosphate, 20 g wood ash | Tuber formation phase | 20 g superphosphate | 1,5, 1, 0,5 |
| ONION | Phase 1-3 leaves | 30 g superphosphate, 20 g potassium sulfate, 10-15 g ammonium nitrate | 10-15 days after 1 top dressing | 60 g superphosphate, 40 g potassium sulfate | – | One month before harvest do not water and do not feed | 0.2 |
| MORCOW | 20 days from sprouting | 25 g urea, 10 g superphosphate, 30 g potassium sulfate | 20-25 days after 1 feeding | 35 g nitrophoska | 20-25 days after 2 fertilizing | 30 g superphosphate, 30 g potassium sulfate | 0.1 |
| CUCUMBERS | Phase of 3 true leaves | 10 g urea, 10 g superphosphate, 10 g potassium sulfate | 15-20 days after 1 fertilization in the flowering phase | 20 g urea, 20 g superphosphate, 20 g potassium sulfate + trace elements | – | – | 0,7-1 |
| PERTS | 14-15 days after planting | Liquid cow dung or poultry manure | 14-15 days after flowering | For 10 liters of slurry 15-20 g of urea, 30 g of superphosphate, 30 g of potassium sulfate. | From the beginning of the first fruit harvest | Per 10 liters of slurry infusion, 15-20 g urea, 30 g superphosphate, 30 g potassium sulfate | 0.8-1 |
| BEET | Phase of 2-4 true leaves | 15-20 g superphosphate, 50 g potassium sulfate | 14-15 days after 2 top dressings | 2 g boric acid | 14-15 days after 2 fertilizing | 1% table salt solution | 10 liters per 15 linear meters of the bed |
| TOMATES | 5-6 true leaves | Infusion of cowpea, or 15-20 g of urea. 30-50 g superphosphate, 10-15 g potassium sulfate | Flowering phase, fruit appearance | 40-50 g superphosphate, 10-15 g potassium sulfate | Fruit appearance on lateral shoots | 40-50 g of superphosphate, 10-15 g of potassium sulfate | 0,5-0,8 |
| GARLIC | If the leaves are yellowing, but there is enough water | 10 g urea | Spruce heads are small | 60 g superphosphate, 40 g potassium sulfate | – | – | 0.2 |
You can also successfully apply complex fertilizers for vegetables, carefully observing the norms of application. To make it easier to navigate in the choice of the type of fertilizer and its dosage, we offer recommendations for specific crops:
- Potatoes are fertilized by applying manure or humus in a continuous way, as well as using a more labor-intensive, but economically advantageous spot method, when in each well half a shovel of humus and ¼ shovel of ash is introduced.
- On the beds with garlic, onions, carrots or beets distribute humus, and again by re-compacting the soil 2-3 days before planting.
- With cucumbers will have to do a little bit of work: high beds are made, the bottom layer of which consists of straw, manure and humus, and the upper one of a layer of garden earth. This is done for a specific purpose. When decomposing the organic substrate, heat will be released, so necessary for cucumbers.
- Tomatoes are fertilized when digging with peat and humus, mineral fertilizers are added when transferring seedlings into the soil.
- For strawberries, which is a perennial plant, and due to this depleting the soil, use a mixture of 0.5 infusion of cowdung and a tablespoon of ammonium sulfate, diluted in 10 liters of water.
Spring fertilization of flowers
Fertilizers for garden flowers in spring are applied immediately after the snow has fallen. Before fertilizing, the soil should be loosened and mulched. The first to be fertilized are bulbous plants. Here is a list of recommendations for the most popular types of garden flowers:
- Hyacinths are fertilized after the appearance of the first sprouts with 25 g of ammonium nitrate per square meter. m.
- Daffodils will need 2 fertilizers – after sprouting sprouts and after the appearance of peduncles. The recommended fertilizer is nitrofoska – 30 g per square meter. m.
- Krokusi are fed after the appearance of the first leaves. Do this with superphosphate or sulfuric acid potassium in a dosage of 20 g per square meter. m.
- Tulips require fertilizer after the sprouts have germinated, and after the third leaf has emerged. The most popular in this case is the preparation “Kemira”, which is presented on the market as a universal fertilizer for flowers. Take 1 tablespoon per bucket (10 liters) of water.
- Primroses are fertilized only after the formation of the first buds. Fertilization and dosage is similar to that used for tulips – 1 tablespoon of “Kemira” per bucket of water.
To improve rooting and better blooming of indoor flowers, the universal remedy “Rainbow” of the firm “Garden of Miracles” is widely used.
Feeding roses in the spring in the garden is done according to the following scheme:
- For young bushes, there is a feeding with phosphorus compositions that improve flowering. Roses respond well to the introduction of organics – infusion of weed grass, liquid cowpea, bird droppings. It is not recommended to use fresh manure, which can burn the roots of plants. In the course should go only over-prepared manure, the dry mass of which is diluted in water (1:10), insist 7 days, then the resulting infusion is diluted with water (1:2) and watering.
- Mature rose bushes in spring need ammonium nitrate in a dosage of 20-30 g per square meter. m. To already in May to enjoy the sight of the first blossoming buds, it is recommended to feed the plants with a composition of 10 g of potassium sulfate and 10 g of superphosphate, diluted in 10 liters of water.

Popular nutrients
Here we have listed a number of mineral fertilizers that are in demand due to their effective effect. Which of these fertilizers to prefer will depend on the characteristics of the soil, the crop being grown and the desired results.
Urea (urea) contains up to 46% nitrogen. It is applied (foliar and foliar) first of all fertilizers without mixing with them. Urea is processed by bacteria to nitrates and nitrites, which are digested by plants.
Superphosphate is a mineral fertilizer containing phosphorus. There are simple (15-20% phosphorus) and double superphosphate (50% phosphorus). The fertilizer can also be enriched with elements such as nitrogen, boron, sulfur, molybdenum, etc. Superphosphate can not be introduced into the soil together with urea, dolomite flour, lime and ammonium nitrate. In the case of these fertilizers, superphosphate can only be applied after one week. The use of superphosphate in the spring for the garden is justified together with organics.
Potassium sulfate – supplies one of the most important elements responsible for the resistance of plants to diseases and unfavorable external conditions. This fertilizer helps plants assimilate nitrogen and reduces nitrates. Potassium sulphate is versatile and suitable for all plants, especially cruciferous and legumes. It is ideal for use on calcareous and acidic soils.
Humates are natural stimulators of healthy plant growth, which, once in the soil, activate the microorganisms living there, improving the structure of the soil. Once inside plants, humates normalize metabolic processes and the rate of protein synthesis, optimizing rooting.
These preparations are available in liquid and granular form, work well together with nitrogen, potassium and organic fertilizers. But the use of phosphorus fertilizers should be separate from humates.
Complex mineral fertilizers – record-breakers in popularity among gardeners. They contain an optimal amount of nutrients in a balanced dosage, which leads to an excellent stimulation of plant growth.
Azofoska, nitrofoska and ammophoska are used on different types of soils for a wide range of crops and show excellent efficiency in terms of high yields.
Kje kupiti
Quality fertilizers are available everywhere. Fertilizers can be purchased in many specialized stores, as well as marketplaces. An excellent choice will be to make a purchase directly from the manufacturer, placing an order on the official website. This will allow you to save money and get a preparation that meets all the required norms and standards.