Gas prices are constantly rising, but so far heating with this type of fuel remains one of the most inexpensive. But we are talking about monthly expenses – modern boilers have a high efficiency – 95-98%, which reduces costs. Also adds popularity to the high degree of automation – you can leave the house for quite long periods without much risk (if the electricity is not cut off). This is why many people consider gas heating of a private house in the first place.

Vsebina članka
What can be gas heating
For heating can be used two types of gas – main and liquefied. Trunk gas under a certain pressure is supplied through pipes to consumers. It is a single centralized system. Liquefied gas can be supplied in cylinders of different capacities, but usually in 50-liter cylinders. It is also poured into gas holders – special hermetically sealed tanks for storing this type of fuel.
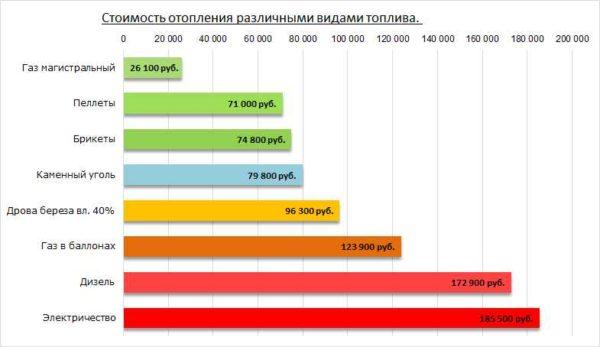
Cheaper heating – with the use of main gas (not counting the connection), the use of liquefied gas is only slightly cheaper than the use of liquid fuels. This is a general statistic, but it is necessary to calculate specifically for each region – prices differ significantly.
Water heating
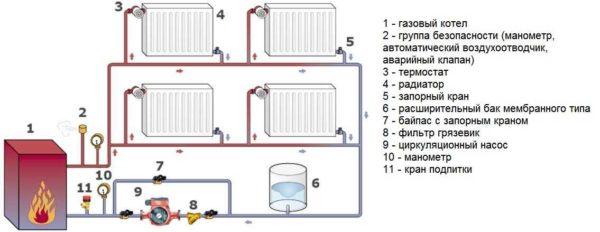
Traditionally in private houses make a water heating system. It consists of:
This is the most general description of the system of water gas heating of a private house, because there are many additional elements that ensure performance and safety. But schematically – these are the main components. In these systems, heating boilers can be on natural or liquefied gas. Some models of floor boilers can work with these two types of fuel, and there are some that do not even require replacement of the burner.
Air (convector) heating
In addition, liquefied gas can also be used as fuel for special convectors. In this case, the premises are heated with heated air, respectively, heating – air. Not so long ago, convectors that can work with liquefied gas have appeared on the market. They require readjustment, but can work on this type of fuel.
Gas convectors are good if you need to quickly raise the temperature in the room. They start heating the room as soon as they are turned on, but they stop heating as soon as they are turned off. Another disadvantage is that they dry the air and burn oxygen. Therefore, the room requires good ventilation, but there is no need to put radiators and build a pipeline. So this option also has its advantages.
Vrste plinskih kotlov
According to the type of installation, there are two types of gas boilers: floor and wall-mounted. Wall-mounted can work only with natural gas, floor – with two types of blue fuel. The advantage of wall-mounted gas boilers is that they can be installed in kitchens – they are automated and safe. Some floor standing ones can also be installed in the kitchen (up to 60 kW), but this room must meet certain requirements. Read more about how and where gas boilers can be installed here.

Types of wall-mounted boilers for heating the house
First of all, it is worth dividing gas heating equipment by functionality: it will be used only for heating or still for the preparation of hot water for technical needs. If it is supposed to heat water, you need a two-circuit boiler, only for heating works single-circuit.

Next, it should be determined with the type of smoke extraction. There are gas boilers with atmospheric chimneys and open combustion chambers, there are with turbo (their combustion chamber is closed). Atmospheric require a good chimney and draught in it, oxygen for combustion comes from the room in which the unit is installed, so there must be a channel of air supply and a good chimney (when starting the system all this is checked).
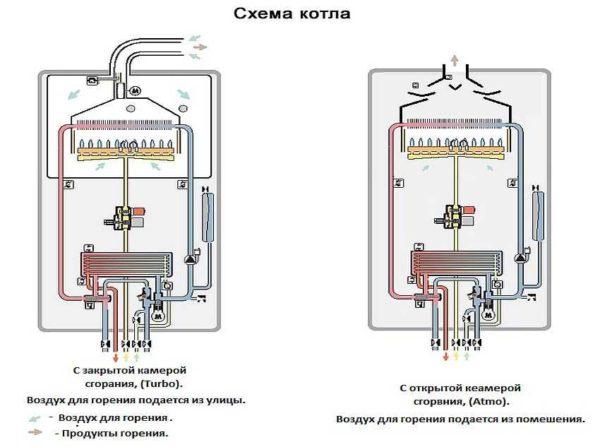
Boilers with forced draught (turbo) can be installed without a chimney. Smoke output of the boiler through a coaxial pipe (also called a pipe in a pipe) can be led directly into the wall. In this case, one pipe exits the smoke (pumped by the turbine), the second receives air for combustion directly into the combustion chamber.
This type of equipment is good for everything, except that in winter the coaxial is overgrown with frost, which worsens the draught. In case of poor draught, the automation switches off the boiler – so that no combustion products enter the room. Switching on is possible only when the draught is restored, i.e. you will have to knock or otherwise remove snow build-up.
There is also a separate type of boiler – condensing boilers. They are characterized by a very high efficiency due to the fact that the heat is taken away from the flue gases (condense vapors). But high efficiency is achieved only when operating in low-temperature mode – in the return pipe the coolant should not have a temperature above +40°C. If the temperature is even lower – even better.
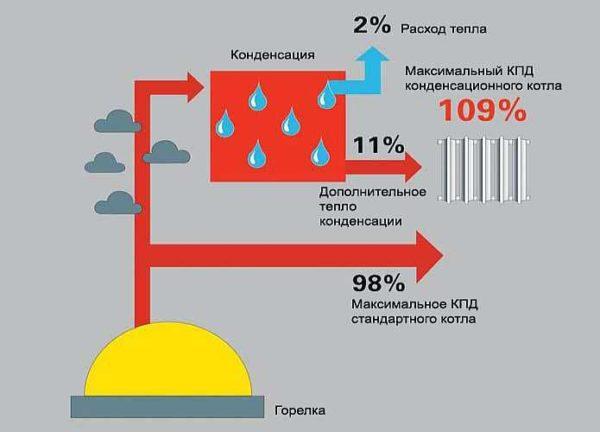
Such conditions are suitable for heating with water underfloor heating. So if you are thinking about such gas heating of a private house – with warm floors, then the condensing boiler is what is required. Minuses it has a little – high price (compared to conventional) and caustic condensate, which makes special demands on the quality of the chimney (of good stainless steel).
Floor-mounted gas boilers
If you need a large capacity, the wall-mounted version is not suitable – they have a maximum output of 40-50 kW. In this case, put a floor boiler. Here they are large capacities, and there are also models that can work in a cascade. So in general you can heat large areas.
Some of the floor boilers can work not only from the main gas, but also from liquefied gas. Some can still work with liquid fuel. So these are quite convenient units. Their body is made of steel, and the heat exchanger can be steel or cast iron. Cast-iron ones weigh and cost more, but have a longer service life – for 10-15 years. Inside the body there is a burner, automation and heat exchanger.

When choosing it is necessary to pay attention to the functionality of the automatics. In addition to the standard set – control of the presence of gas, flame and draught there are many more useful functions:
- maintenance of the set temperature,
- the ability to program modes by day or hour,
- compatibility with room thermostats;
- adjusting the boiler operation to the weather,
- summer mode – work on water heating without heating;
- the possibility of working in parallel with solar panels or other alternative heat sources, etc.
The wider the functionality of the automation, the more expensive the boiler and its maintenance. But also many programs allow you to save fuel, which is not less important. In general, choose you.
Schemes of gas heating of the house
We will talk about water heating with the use of gas. Immediately it is worth determining the type of circulation of the coolant. It can be natural (such systems are also called gravity) or forced (with a mandatory pump).
Gravity systems require the installation of large diameter rubbers, that is, the coolant in the system is obtained a lot. The second point – due to the fact that the coolant moves through the pipes at a low speed, the efficiency of heating is not very high. Distant radiators in long branches can be cold. This is about the disadvantages. There are many of them, but there is one big plus – systems with natural circulation do not depend on electricity. This is important in those regions where the light is often cut off.
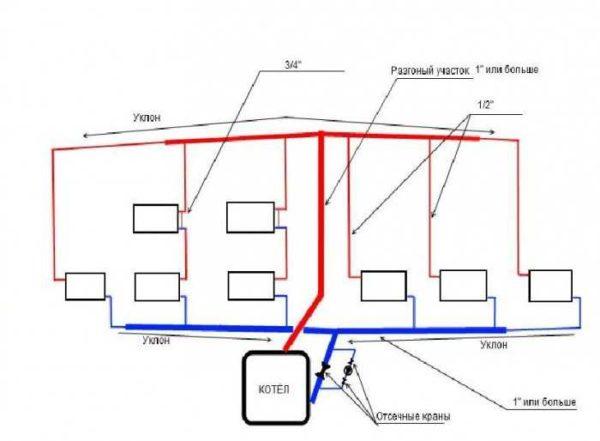
Now a little about systems with forced circulation. They are more efficient – the coolant moves at a given speed, delivering heat to all corners of the system. The presence of a pump allows the use of small diameter pipes. This means that there is not much coolant in the system and it warms up quickly. In general, they provide a greater level of comfort, but have a serious disadvantage – to work, electricity is required, that is, a backup power supply is required. If the light is rarely cut off, it is enough to install an uninterruptible power supply unit with several batteries. They can provide the work of the boiler for dozens of hours. If the light is cut off often and for a long time, you will have to build in the system and a generator. In any case, this is an additional cost and not insignificant.
There are still systems combined – they are designed as gravity, but have a built-in circulation pump. Such a solution can be called ideal in terms of practicality: while there is light, heating works as forced, as soon as the power supply is lost, everything works as a gravity system. In general, not a bad option, except that the pipes will be large and too much in plain sight.
Method of wiring
There are three types of systems – one-pipe, two-pipe and radiant. In single-pipe systems, radiators are connected in series to a single pipe. This method of distribution is economical – less pipes are required, but it is difficult to compensate – it is difficult to achieve the same heat output from the radiators. The whole point is that the coolant enters the first radiator in the branch hot – immediately from the boiler. It passes through it, cools down a little, gets to the next one, cools down a little more. So all along the branch.
It turns out that the last radiator comes coolant much colder than the first. The only way out – to take into account this phenomenon in the design of the system and increase the number of sections in the radiator as you move away from the boiler. But the last radiators will still be the coldest.
It is more or less easy to balance the system shown in the photo above. In it on each radiator there are thermostats – devices that allow you to change the amount of coolant passing through the radiator. In order not to “choke” the circulation in the whole system, a bypass is placed under each radiator – a jumper, which carries the coolant that did not go through the radiator.
In a two-pipe system radiators are connected in parallel – to the supply and return pipes. In this system, the flow of pipes is much greater, since two strings are pulled simultaneously. But in this case, each heater is supplied with the same temperature coolant, so the heat output of the radiators will be the same (if you put the same radiators).
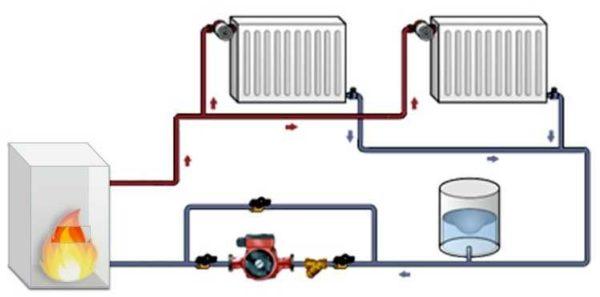
In this scheme it is also possible to put thermostats, but it does not require bypasses – only the flow to one radiator is regulated. So despite the higher pipe consumption, two-pipe systems are more popular.
The radial method of distribution is the most expensive in terms of the number of tubes. In them to each radiator goes separately supply and return pipe. It is connected to a manifold – a device with one inlet and several outlets. In this case, regulation is possible both on the manifold and on the radiator by means of a thermostat.
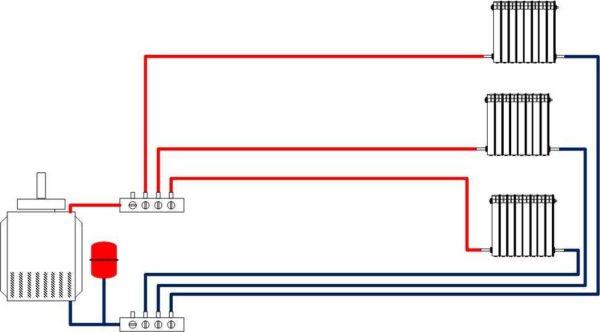
Gas heating of a private house made by this scheme will be the most reliable: if one of the pipelines is damaged, all the rest will work. Therefore, this method is often chosen if the pipes are hidden in the screed.



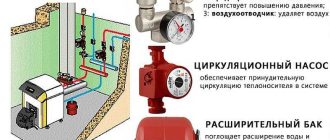


I recently switched to a gas heating system, and it’s been a game changer! It heats up the house super fast and cuts down on my energy bills. Plus, I love how cozy it feels in winter. Totally recommend it for anyone looking to upgrade their heating!
As a homeowner, I’ve seen how gas heating systems can transform your space. They’re super efficient and bring warmth fast, especially during freezing winters. Plus, the cost savings on your energy bill are no joke! If you’re thinking about upgrades, definitely consider gas—it makes a world of difference!