A cottage and a vegetable garden instead of a place of rest often become a place of exhausting labor. Watering, weeding, loosening, watering again, weeding, loosening and so on in a circle. And the harvest is not always pleasant. The situation can be changed. There is a special technology – smart vegetable garden. The cultivated area is reduced several times, the amount of water needed for irrigation is reduced, and the yield increases. This is not a fairy tale. Many people have already switched to smart beds, and all of them are satisfied with the result.
Obsah článku
What is a smart vegetable garden or smart beds?
Smart vegetable garden allows you to get maximum yields with minimal labor. How? There are several basic rules and techniques: proper planting planning, turnover of planted plants, special cultivation techniques (in high beds, trenches), drip irrigation, mulching or the use of covering material. All this has been known for a long time and many are already used. But it is in the complex all these measures give what is called a smart vegetable garden. Because everything on the plot is done intelligently.
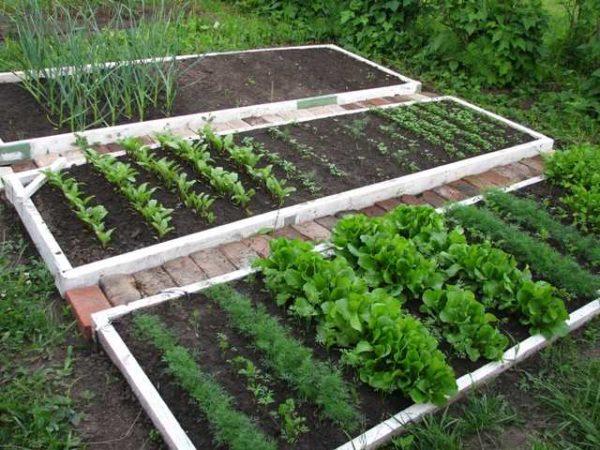

The main task of this technology, to make everything so that the work at the dacha was not a drudgery. This is possible if you approach the organization of the process with intelligence. And for nothing this technology is called a vegetable garden for the lazy. At the stage of arrangement will have to work hard, but then everything will grow almost by itself, but the first stage requires a shocking effort.
It is worth starting with the planning of the site. It is necessary to choose the location of beds, taking into account the illumination. Then develop a scheme for laying water pipes on the site and lay them. At the same time, you can engage in the arrangement of beds. Approximately in this order. All this requires time, considerable effort and money. Material costs may not be too large.
Planning a vegetable garden
If you already have a dacha or a plot of land near the house, you have probably already faced the situation of an excess of fruits, vegetables and berries. When the harvest has to be distributed to relatives, neighbors, colleagues. And after all, to grow it, you had to put a lot of effort. To avoid such a situation, it is necessary to plan the harvest. Of course, you will not get great accuracy, but close to the planned results are possible.

Calculating the area of the beds
The first thing to do is to sit down and think about what and how much you want to grow. The specific quantity is in kilograms. How much you need to eat and to close. Write a list of plants (in a column) and the desired harvest.
Having decided on the list of plants you want to grow, sit down and look at the average yield that can be achieved when growing on smart beds. It is given in the table. Since you are still an inexperienced “lazy gardener”, halve it. Opposite each of the plants put numbers. Record should be written in kilograms per square meter of area.
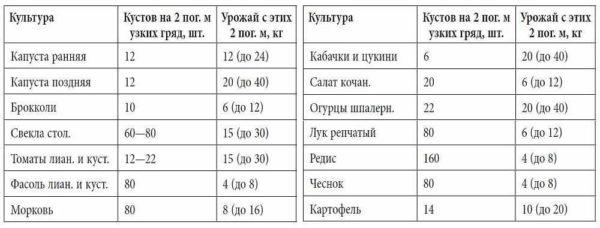
Now it is easy to calculate how much area you need to allocate to each type of plant: the desired yield in kilograms is divided by the average yield for each type of plant. This gives you the square footage of vegetables, berries, herbs, etc. If all these areas are added up, we find out how many beds you need in total. These are the beds that should be placed on your plot.
You are probably surprised at how little space you need for the beds. Several times less than we are used to! You will have very little land to work with. You can use the freed up space for flower beds, rockeries, fountains and other decorations.
Kam umiestniť
Planning smart beds, it is necessary to take into account the degree of illumination. Almost all the plants you need prefer sunny places. In the penumbra, you can grow rhubarb, sorrel, onions (including feather). Perhaps all of them. Horticultural plants that would grow well in shaded places, there are no plants at all. Or rather, they will grow, but the yield will decrease by 3-4 times. Shady areas should be set aside for a recreation area or place a flowerbed with shade-loving plants.
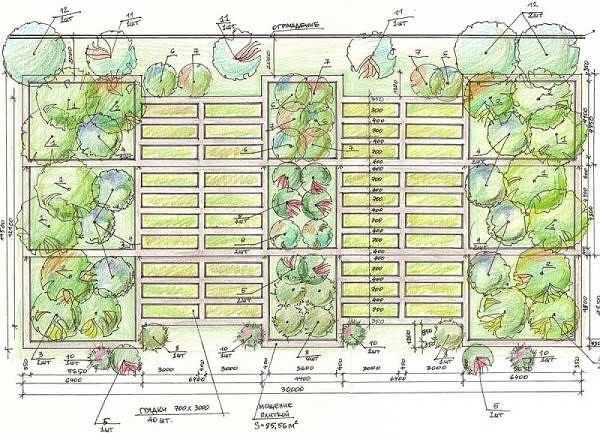
Another principle of bed layout: the more care (read watering) a crop requires, the closer to the entrance to the house it should be placed:
Why place the plants in this way? Because at the beginning of work on watering/weeding, gardeners are full of enthusiasm and plants get more water, weeds are removed more thoroughly. Gradually, the fervor wanes, less water per square meter is available, and the treatment becomes less thorough. And with the approach suggested above, the amount of water will be just right and everything will be fine with soil treatment.
Orientation to the sides of the world and precise positioning
If you want to get a harvest from the entire area of the lazy bed, the location is north-south. Strictly. Only in this way the whole area will be fruitful. Also locate trellises for climbing vegetables. Although they can be planted along the southern and eastern walls of buildings.
To smart vegetable garden was also beautiful, you need to think through where to put the beds. To do this, we take a scale plan of the plot, indicating the north/south direction. On it we draw all the buildings and capital paths, water supply (pay special attention to the position of taps), trees and shrubs. On the plan immediately delineate shadow zones, in them to place vegetables will not be placed, this is the place for flowers, arbors, fountains.
From the paper cut out beds (on the same scale as the site plan). And we make them in the shape we plan: rectangle, square, circle, triangle, etc. The shape is chosen based on the area planned for the culture. And it does not have to be a boring rectangle. Since the free area will be enough (you remember that the beds need much less), then the rationalism goes to the second plan, and the main emphasis is on aesthetics. After all, few people work at the dacha to have something to eat, mostly it is also a pleasure. And what can be more pleasant than the beauty of the cultivated area?
So, each paper, denoting a smart bed, sign – put the name of the culture or cultures (you can grow two or three or more on one ridge). Now we look for a place for each of them, taking into account the rules described above. As you go along, you can change the shape of smart beds: for the sake of beauty or convenience. When you have found the places, outline the contours, transfer the inscriptions. It remains only to realize the conceived.
Watering system
A significant part of the work on the vegetable garden – watering plants. If you use lazy beds, you will have to water much less often. But even in this case, it is better to make the distribution of pipes on the site competently. You already have a plan of location on your vegetable garden beds. Now add there flower beds, bushes and trees. Get a plan for the placement of plants that need to be watered. Now you should think about how to lay water pipes in the vegetable garden, so that up to any “watering object” was no more than 2-3 meters. If you do this, then to each bed will have to pull a small hose, which is much easier.
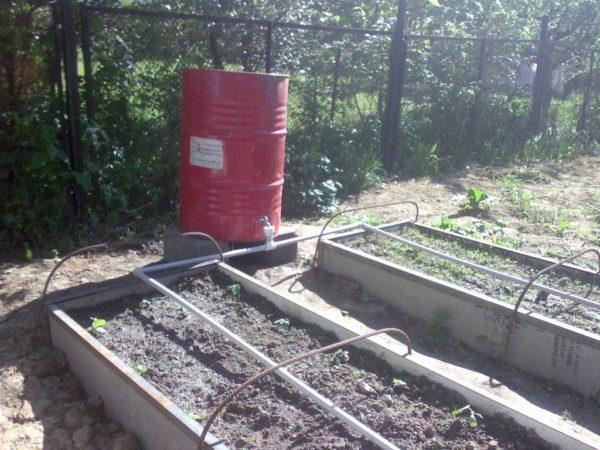

Even better, if a hose for drip irrigation will be laid in the smart bed. This will reduce water consumption and increase the harvest. Yes, at the same time. A hose for drip irrigation is a polyethylene tube with small holes through which water is oozed drop by drop. When planting, plants are planted next to the holes. As a result, water is delivered under the root, the plant receives sufficient moisture, and the spaces between plants remain only slightly moistened (due to redistribution of moisture in the soil).
With drip irrigation, you have very little work to do. You open the faucet, wait for a certain period of time, close the faucet. Hoses for drip irrigation is to connect to the water supply (sold on the meter), there are in the form of sets with a small pump that will pump water from the tank. The difference in prices for hoses for drip irrigation solid – prices differ by several times.
No matter how limited your finances, do not take the cheapest hoses – they will not last more than one season. It is better to slightly overpay for quality goods and use for several years. When choosing kits for drip irrigation should be looked at and irrigated area. But, most likely, it will suit you, since lazy beds are rarely large. Read more about drip irrigation kits and manufacturers here.
How to make smart/ lazy beds
The principle of building smart beds is that you need to create ideal conditions for the development of plants and convenience of processing for yourself. What do plants need? Nutrients, sufficient light, air, moisture and no weeds.

Oxygen and nutrients
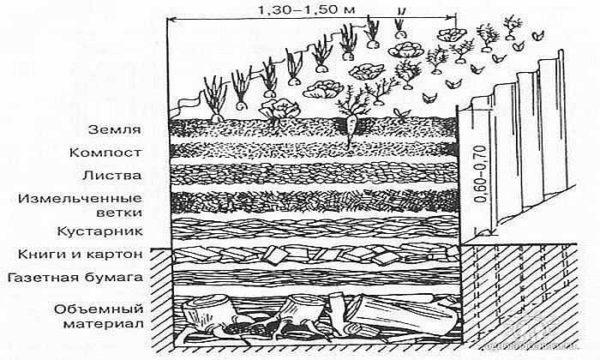
We have provided them with enough sunshine by positioning the beds from north to south. The next task is to provide nutrients and air to the roots. All this is laid down when forming the beds. Depending on the type of soil, we select the components that are lacking in the “source material”. In the Middle Belt of Russia, the main soils are clay and loam, so usually add humus of different degrees of “maturity” (a year, two and three). This is both for fertilizer, and to lighten the soil – for better access of oxygen to the roots. Along with the humus come bacteria and worms, which continue processing, enriching the soil and loosening it instead of you.

If necessary, other fertilizers can also be applied – in the wells when planting or when watering. It depends on the crop or the richness/poverty of the original soil. The most common natural fertilizers are chicken manure, cow dung and ash. If you apply only cow manure, you will be bothered by bears. If you add a little chicken manure, there will be no bears and the soil will be richer.
Moisture retention and weed control
Moisture will partly come from rain and dew, and partly will have to be added by watering. And to require less water, all the space of the bed, not filled with plants, cover with mulch. Mulch, by the way, also reduces the number of weeds – they do not get enough light under it.
As a mulch can be used straw, cut grass, sawdust, fallen needles, special mulch made of wood chips. All this can be used to mulch lazy beds. But all materials are not ideal. Here are their advantages and disadvantages:
There is another good way out: to cover smart/lazy beds with a special covering material of black color. It covers the surface of the beds completely, sometimes in two layers. Small holes are made for the plants. Watering is done directly on the material – it does not retain water and air, does not allow weeds to grow, protects the soil from overheating. In general, everything is good, except that it must be bought.
How to make them
With the general principles of creating a smart vegetable garden sorted out, now specifically understand how to make beds. They can not walk on them, so they must necessarily be fenced – stones, slate, iron, sawed in half logs, boards … It does not matter what, but the beds must be separated from the paths. And since the beds cannot be stepped on, their width should be such that it is possible to work the soil freely.
Now about the width of the smart beds. It depends on the type: they will be of normal height or raised. The beds are made at ground level, their width is 80-100 cm. Sitting squatting or bending over, it is possible to process such a width. If the beds are raised at least half a meter, it will be even more convenient to work. Not only high beds are made. You can use all possible cultivation technologies:
- Barrel beds. Such are especially good for plaited plants: cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins.
- Pit beds and ditches.
- Vertical.
Now about whether the usual height of the beds is better or elevated. For a really lazy vegetable garden is better elevated: when processing the soil will have to strain less. But the device of high beds – a matter troublesome and not quick. So, to begin with, you can get high beds only for the most difficult to care for crops. And you can also use different containers / containers – for greens, salads, spicy plants. Suitable sawed along large barrels, crates. There are plastic containers on sale, which are produced specifically for the smart vegetable garden. They can generally be placed on the paths, near the entrance to the house.
The only culture for which you should not make raised beds is potatoes. It grows perfectly well in trenches, and it is much easier and faster to make them.
Between the beds
The beds in a smart vegetable garden are separated, the distance between them is at least 60 cm (better 90-100 cm or more). A solid distance that needs to be filled with something. Hoeing between the beds is not a good idea. Why bother with separate beds to fight weeds between them? So you can either pave/pave the paths or seed with lawn grass. The best grass for our lawns is Kentucky bluegrass and Kentucky bluegrass. They grow quickly, form dense greens that don’t get trampled on and even tolerate cart work.

The grass will have to be cut, so you will need a lawnmower or trimmer. And the cut grass can be used for mulch. Then, by the way, weeds will come out – they can not withstand frequent mowing.
Some tricks
The technology is called smart vegetable garden for a reason. You can test different approaches, novelties, the experience of colleagues. There are a few tricks that come in the process of operation. One has already been told about – about the covering material. It really greatly simplifies care and mulch is not needed. There are more interesting ideas:
Surely there are more tricks in the processing of a smart vegetable garden. If we learn about them, we will certainly supplement the article.






I love this article! It’s given me so many cool ideas for my garden without all the back-breaking work. Raised beds and smart planting really save time! Can’t wait to try it out this weekend. Thanks for sharing these tips, they’re super helpful!