Summer has passed, the harvest is almost gathered, but it is too early to rest. In September begins the time of important worries to prepare for winter and the next season. Work will require time and serious effort, but you can not be lazy, because the preparation of beds in the fall – a guarantee of future, rich harvest. We tell you how to prepare beds for winter in the vegetable garden and in the greenhouse, improving the soil structure.

Artikkelinnhold
Preparation for winter
The importance of fall tillage cannot be understated, it is the key to what will happen to your harvest next season. Over the year, the land is depleted, pests and pathogenic bacteria multiply. Experienced vegetable gardeners carry out in the first fall month special activities, which necessarily include:
- Cleaning of haulm, plant debris and weeds.
- Digging the beds.
- Treatment from pests and diseases.
- Fertilization and restoration of soil structure.
Although there is a lot of work, but compared to spring, when the planting time is pressing, you can work carefully and not in a hurry. In addition, over the winter the fertilizer will disintegrate and well nourish the soil with useful substances.
Cleaning the area
Preparation for the winter period begins with a thorough cleaning of the vegetable garden from old grass, vegetable haulm, weeds and other plant debris. In the process, you will not only put things in order, but also deal with rodents that like to huddle in “cluttered” places.
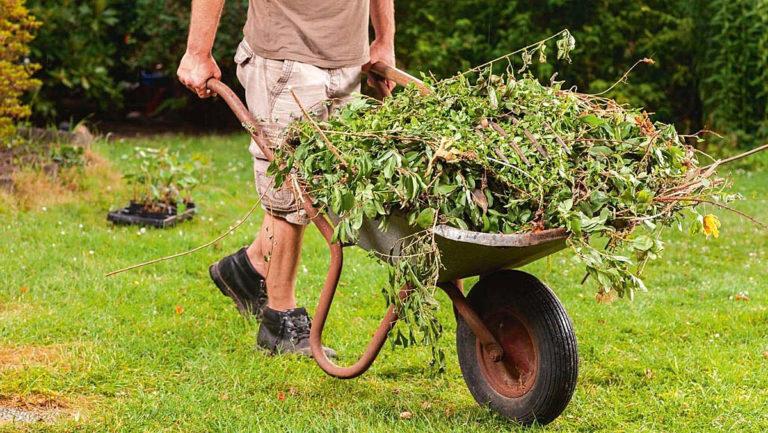

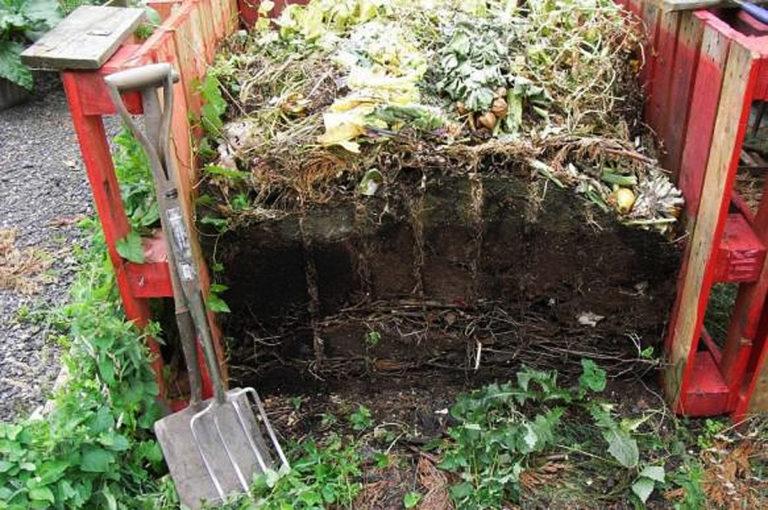
Vegetable waste can either be burned or made into compost. The second method is more labor-intensive, but so you can make with your own hands a good nutritious substrate for feeding the beds.
Digging beds for the winter
In recent years, organic farming trends have been gaining popularity. Their supporters do not recommend fall digging, urging to limit themselves to spreading manure or ash over the site.
However, fall digging is a good way to improve soil structure and should not be neglected. Digging can be done in two ways:
- Moldboard – we turn the earth with a shovel so that the top layer is at the bottom. It is well suited for combating the larvae of pests.
- Bezotvalnym – digging, the land is not turned over, in order to preserve the useful microflora.
In both cases, large clods do not need to be broken. They will help to retain rain and melt water on the site, saturating the soil with moisture and improving the structure.

Important! Fall digging is necessary for heavy, clayey, uncultivated soils. For loose and light, a simple loosening is enough, and sandy soil is processed in the spring.
Preparing the soil for winter in the greenhouse
Soil treatment in the fall period is aimed at destroying pathogenic microflora and pests, which quickly multiply in old haulm and shriveled grass. Decontamination is a labor-intensive process, but it should never be neglected, otherwise during spring planting the seedlings will suffer from diseases and pests in the first few days.
Pathogens, parasite larvae and fungal spores overwinter at a depth of 7-10 cm. Therefore, the best option is to remove this layer of soil with a shovel and replace it with fresh soil. It is not worth taking soil from the vegetable garden, as it can also be infected. Prepare the soil with your own hands, using organic matter, wood ash, sawdust or sand.
| Bacteria | Shelf life in soil | |
|---|---|---|
| average | maximum | |
| Salmonella typhi | 0.5 | 12 |
| Cholera vibrios | 0.5 | 4 |
| Brucellae | 0.5 | 2 |
| Tularemia pathogens | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| Dysentery bacillus | 1 | 2 |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 3 | 7 |
As a side note! Allocate a special place for the soil from the greenhouse. Sprinkle the layers with a small amount of lime. After a year it can be used in the beds again.
The resulting soil is evenly distributed over the area of the beds. Treat it with a solution of manganese or copper sulfate to prevent microbes and mold. Then cover the beds with organic mulch – soil preparation for winter is complete.
Important! Treatment with copper sulfate should not be carried out more than once every 5 years (the solution increases the acidity of the soil).
In cases where it is impossible to remove the soil layer for some reason, you can get rid of harmful microorganisms in one of the ways described below.
Pour steep boiling water on the beds and cover them with a film for 24 hours. After removing the film, loosen the soil. Then do the procedure two more times. Keep in mind that after steaming die and useful microorganisms, so after completing disinfection, be sure to water the beds with a solution of biopreparations.
- Mulching the soil in the greenhouse
- Digging over the soil in the greenhouse is effective in combating pests
Their chemical compositions, which are used to spill the soil for disinfection, are well-proven:
- manganese solution (1 teaspoon per liter of water);
- copper sulfate solution (1-2 tbsp. l. per 10 liters of water);
- formalin solution (200 g per 10 liters of water) at the rate of 10 liters per 1 square meter;
- sprinkling the ground with bleach (100-200 g/sq.m.) with subsequent digging of the soil;
- special biopreparations – Phytocide, Phytosporin, etc.
Do not forget about the toxicity of some chemicals. Soil treatment should be carried out in a gas mask.
Important! A very popular method is the burning of sulfur a checkers. However, fumigation requires special precautions, and is also not suitable for greenhouses and greenhouses with a metal frame, since it promotes metal corrosion.
Land treatment in the fall from pests and diseases: a mild alternative
Chemical compositions for disinfection – a thing effective both in greenhouses and on vegetable plots. But they have a disadvantage – at the slightest miscalculation in the dosage turn into serious trouble. In addition, they kill both pathogenic and useful microflora.
There are milder, but effective methods to improve and sanitize the soil in the vegetable garden in the fall:
Fertilizing the vegetable garden in the fall: the choice of fertilizer
Experienced dacha growers and gardeners are sure to make fertilizers in the fall under the digging of the vegetable garden. This is an effective way to increase the fertility of the soil, restoring the balance of nutrients that have been depleted during the season, and also do not allow it to freeze in the winter.
In September-October, mineral and organic fertilizers are applied. Nitrogen fertilizers should be abandoned, as they stimulate the growth of plants, which will die at the first frosts.
The use of fertilizers in the process of digging provides better penetration of useful components into the root system of seedlings, which significantly increases their endurance and yield. Spread fertilizer over the surface of the cultivated area and dig over the soil, evenly smelling fertilizer to a depth of about 15 cm.
The choice of fall fertilizer and its amount depends on the crops you intend to grow. For example, composted organic matter has a beneficial effect on vegetable seedlings and seeds. All types of compost and humus will do. For each linear meter – 1-2 buckets.

Fresh organic matter is recommended to be used exclusively for the pumpkin family of vegetables. For 1 m² – 1 bucket of manure and 1 bucket of litter.
From mineral fertilizers for summer-autumn soil treatment, choose complex and mono fertilizers. They contain phosphorus salts and potassium (kalimagnesia, simple and double superphosphate, potassium salt, etc.). The rate of application of mineral fertilizers is calculated in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
What to treat the soil in the fall at the dacha to improve its structure
Choose a solution based on the type of soil. Heavy soils absorb moisture poorly and need frequent loosening. You can improve the structure by adding washed river sand – 1-2 kg per 1 m².
The problem with sandy loam is its low water holding capacity. It can be increased by systematically fertilizing with compost, over-ripened sawdust or leaf humus.
Neutralize the acidity of the soil will help lime or vegetable ash. Their use will increase the friability of the soil, its air permeability and moisture permeability. In case of high acidity, the amount of ash applied will be high. This will have a harmful effect on the soil, so it is better to use lime. The rate of application of quicklime is calculated based on the chemical parameters of the soil.
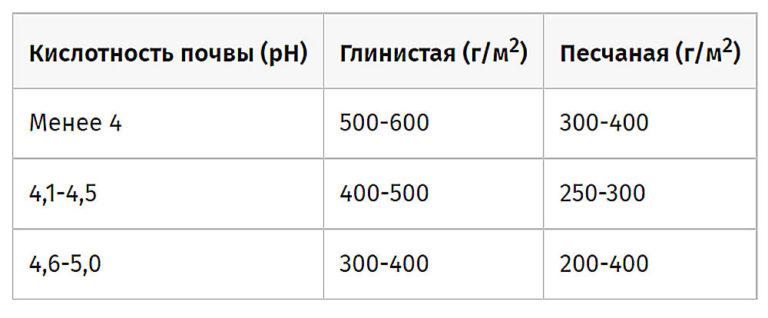
The pH of the soil is checked with litmus paper. To accurately determine pH, take samples from different locations and different depths.
Also a proven method of remediation is sowing siderates. They are recommended when preparing tall beds for winter. Siderates allow you to loosen heavy soil well, disinfect from pathogenic diseases, increase fertility.
Do not use gel or foam balls, as well as foam glass for structuring the earth as loosening agents. Having little chemical resistance, they can react with fertilizers and insecticides. Pellets are even more dangerous for birds. After pecking a large number of balls, they die.
Konklusjon
Properly prepare the vegetable garden for winter, and next season the land will definitely thank you with an abundant, tasty harvest!