Many dacha growers suffer from the fact that the subsoil water is too high on the plot. Excessive soil moisture is not suitable for all plants, and many plants develop poorly or die. The problem can be solved by making high beds. With such an organization of planting there is an opportunity to control the degree of moisture. And a pleasant bonus to this solution will be an earlier maturation period and a much larger harvest.
Raksta saturs
Priekšrocības un trūkumi
In addition to solving problems with overwatering, high beds in the vegetable garden allow you to sow or plant plants 2-3 weeks earlier: raised above the ground they warm up more actively due to the fact that the sun warms the walls. Decomposition processes occurring in plant waste, which makes up a significant part of the backfill, also contribute to this. This is why such beds are called warm beds. If you put on such a bed arcs and cover with spunbonod or other similar material, then the harvest can be collected even earlier.
More problematic is the device in regions with a hot climate. The task in this case is not to better heat the ground, but to keep it from overheating. But even this can be solved: use materials with poor thermal conductivity, for example, wood, to fence high beds. For a better effect, you can make double walls, between which to pour, for example, sawdust, lay foam, and you can leave an air layer – the best thermal insulation. In hot climates it is better to paint the outer wall with white paint or whitewash. It is known that light-colored surfaces are less heated. In this case, it will be possible to save the root system from overheating: in the south, the earth sometimes heats up very strongly and the higher the plant is, the cooler it will be. And you can also stretch the same covering material over the beds. It not only preserves heat, but also protects from overheating.
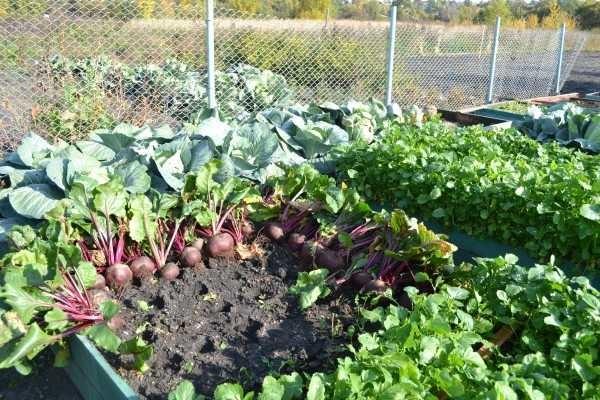

High beds can be a good solution and on infertile land. It is more convenient to spread the soil over the beds rather than spreading it over the whole plot. The compost layer, which is underneath the soil layer, helps to maintain fertility.
The problem of arid regions is also solved. In this case, the fence for a high bed from the inside is covered with bituminous mastic or lined with film, laid on the bottom (on the grid) roll waterproofing material (roofing felt will quickly rot, so it is better something from the modern type of hydroisol). Full waterproofing will not be achieved, but to keep moisture inside in sufficient quantity – yes.
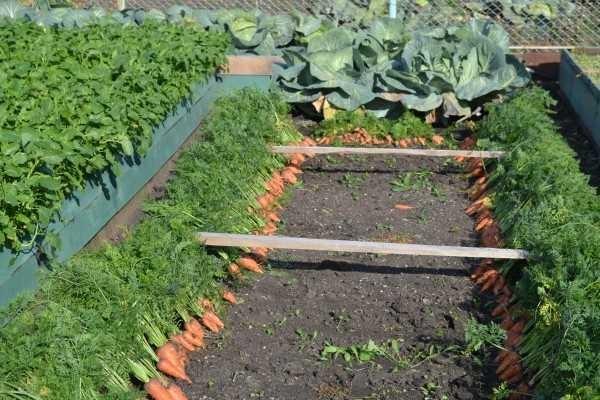

As you can see, with a balanced approach, you can solve almost any problem. The disadvantages of high beds are few, but not without them:
- In most cases, you have to make a fence, and this is an expense.
- Labor-intensive process. Again, it takes time to make fences, and still move a decent amount of earth and plant residue, and this is hard labor.
- In decaying leaves, branches, bark feel great bears and other similar animals. You have to fight them.
- Fertility has to be maintained, renewing or completely replacing the “stuffing”.
These are all the disadvantages. If you decide to arrange high beds, be prepared for a considerable amount of work. But the harvest will be many times more. For a trial you can make one or two beds. And then decide whether you need them or not.
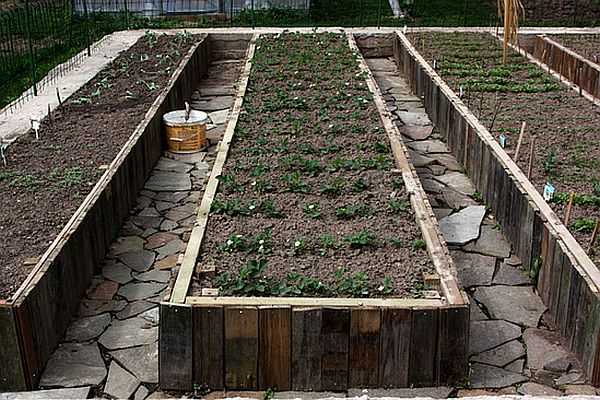
Size
There are no strict recommendations on this matter, and there can not be: very different conditions in the country, and people too. There are sizes that many people consider optimal.

So, the dimensions of high beds:
- Height – from 20 cm to 50-60 cm. Here look what a difficult task turns out. The higher the raised bed, the easier it is to process it – bend less. But the earth and all the other “stuffing” will require more. One more thing: if a small height bed can be under the snow and will be covered from severe frosts, the high bed will freeze through: the sides are also open. For those beds, where sown annuals it does not play any role, but for perennial strawberries, say, it is a problem. Therefore, choose the height still based on these considerations. According to the experience of many dachniki for strawberries optimal height – 20 cm. Then you can hope that it will not freeze.
- Width – from 60 cm to 1.2 m. You choose such a distance that it was convenient for you to process the bed. The distance of 60-70 cm is chosen if the approach to the bed is only from one side. If you can get to it from both sides, you can make a meter and more. It is important that the middle is also processed without much strain.
- Length. Here everyone chooses based on the configuration of the site or his desire. There are no recommendations at all.
So that the bed was not too high, part of it can be buried: bury at 20-30 cm, and from above already put the walls. Removed soil will go to backfill (the land is often simply not enough), and the substrate of the lower coarse layers can be made thicker. And to minimize the cost of maintaining such a bed, you can make drip irrigation.
What can be used to enclose high beds
You can use anything that can hold the soil. The most durable borders are made of brick, stone and concrete.

But brick costs a lot, with concrete it takes a long time to fiddle. Concrete fence is made according to all the rules: first formwork, in which the reinforcement is laid, then pour concrete and wait until it is seized. But the service life is impressive – dozens of years.
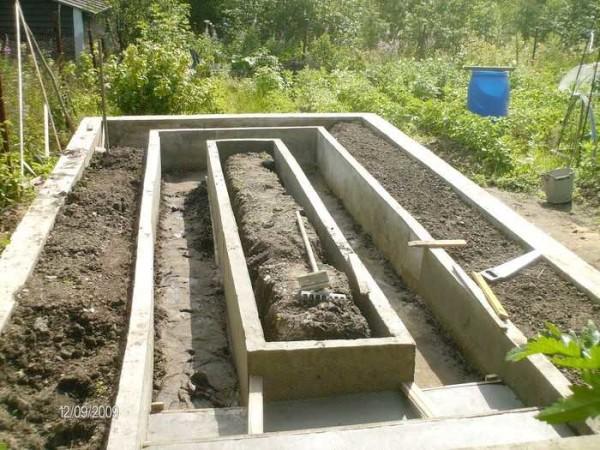

Brick and stone fences are also laid according to all the rules: on the mortar with dressing. To reduce brick consumption, the walls are laid in half a brick. And so that the earth did not move it, the rows are reinforced with a mesh.
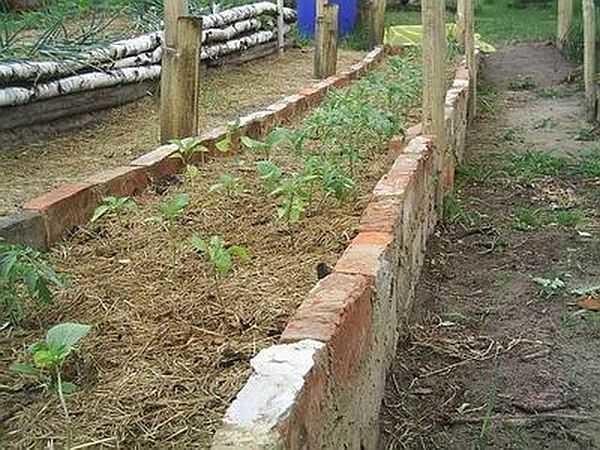

But even in this variant it will be necessary to install support posts after a meter. If your soil is viscous, heavy and often overwatered, such walls may squeeze out. Therefore, put wooden or metal supports that will fix the long walls or make small beds, as for an ornamental vegetable garden.

Well-proven fences from expanded clay blocks. Even voids in them can be filled with soil and plants with a small root system can be planted there too, e.g. some types of herbs and salads.

Also make fences for high beds from galvanized metal and slate. Slate can be used second-hand, you can buy new, wave or smooth – no difference. Cut the sheets into strips of the necessary width. Fear that it is harmful is not worth it. Slate contains asbestos in a bound state, and it is not dissolved by water. It is harmful when it is sawed: the dust rises and through the respiratory tract gets into the body. To reduce the harm, work in a respirator and also wet the cutting areas.
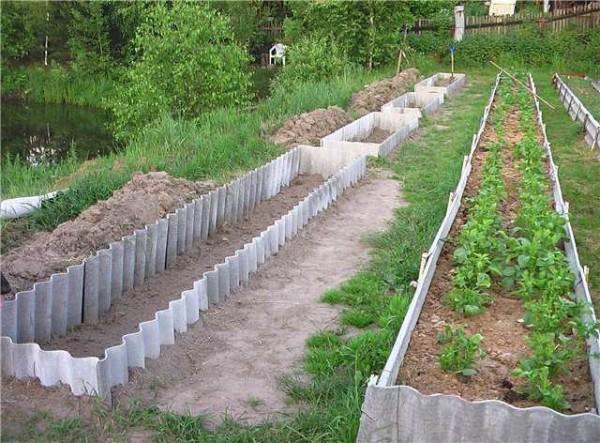

Make fences for beds from plastic. Changed your siding? Use it. There are old plastic panels – they are in business. But plastic requires a rigid base. It is made of metal mesh from thick wire.

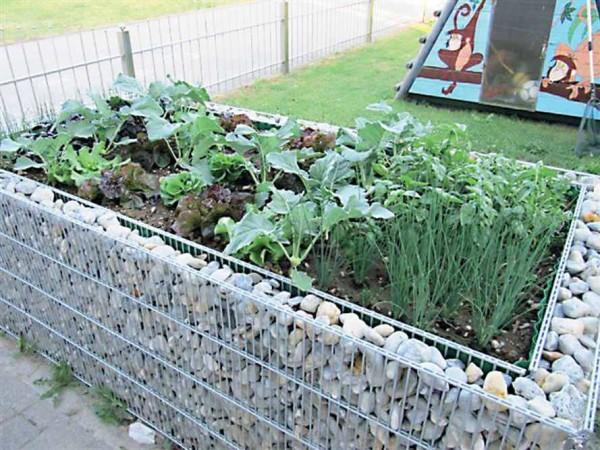
Grids can become the basis for pebbles or pellets. Only in this case, a double frame is needed, inside which stones or some other material is poured. Such a technique is called “gabion” and from it they make not only fences for beds and beds, but also fences. But to prevent water from seeping through the walls of the gabion beds, the inside of the box is lined with a dense film.

The most popular fence is made of wood. You can use planks, beams, logs. Wood is good for everything, except that it rots.

And since in high beds there are all the conditions for the activation of this process, the destruction occurs quite quickly. Slow down the process somewhat by painting the boards or impregnating them with a bioprotective composition. But there is still no guarantee against destruction.
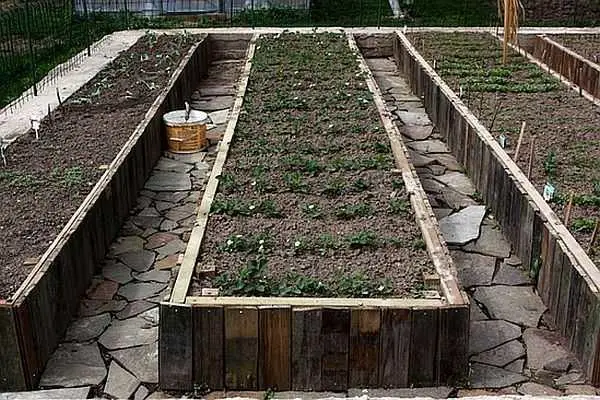

But the material can be used cheap, and sometimes, so even throwaway: leftovers after construction, humpback, old logs, pallets, etc. If desired, you can even make a fence from branches. Only it is desirable to remove the bark: under it there are many larvae and woodworms. Although… they will also recycle the woody residues that you lay at the bottom of the backfill. But you don’t want too many of them either, so it’s probably best to remove the bark after all.
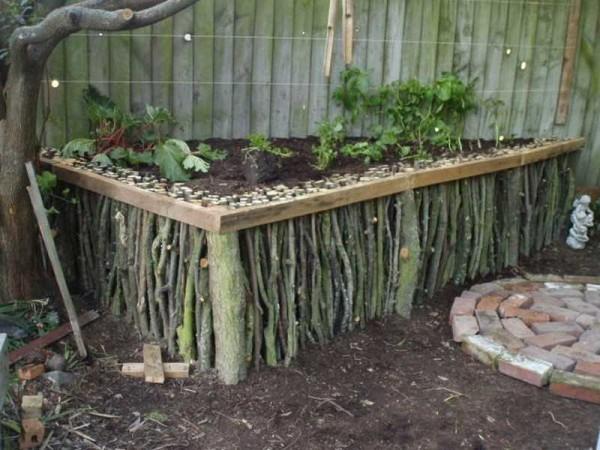

From the same branches, only freshly cut, you can make a wicker fence. And it will also need to be lined with a film from the inside: to keep water and soil inside.
On how to make wicker read here.

Even straw can be used. It is tied in small bundles, which are connected to each other with wire. Cheaper simply can not be cheaper, and water and temperature holds well. The only disadvantage of this option – such a fence will serve a maximum of two seasons, but more likely – one. But it can then be used as one of the layers.

Bulk beds
There are high beds without a fence: so-called bulk beds. The soil is poured into them in the form of hills.
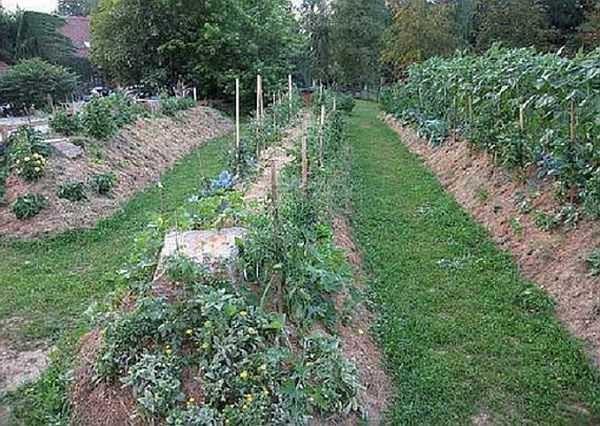

To improve drainage, branches are placed inside the bed. To reduce the height of the bed (e.g. for tomatoes), it is slightly deepened by tilting the soil to the side. After laying the branches, it is backfilled from above, there is often a need for additional imported soil. If it is not possible to deeply select the inter-row rows.
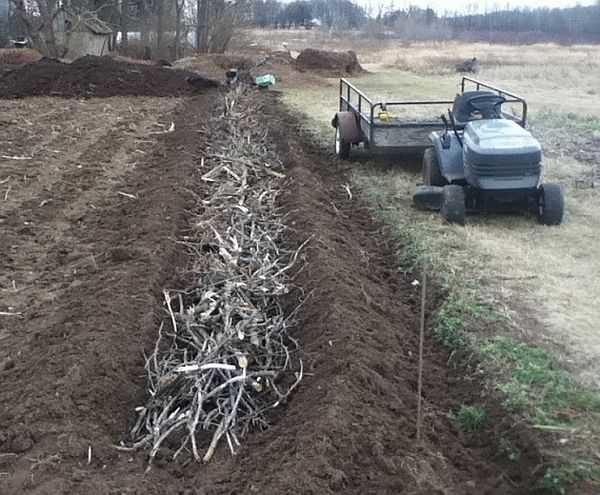

The disadvantage of this kind of vegetable garden: when watering and during rains, the top layer of soil is washed away. That’s why they started to make boxes – to avoid soil washing out.
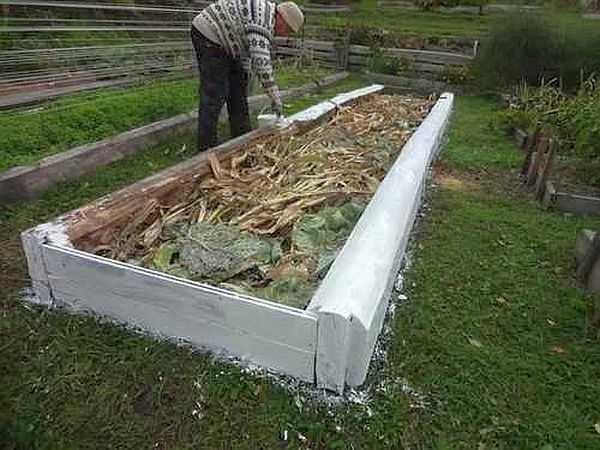
Layers of high beds
Making a frame is only a small part of the work. It is still necessary to fill the resulting box. It should be said right away that the thickness of the layers depends on the height of the bed you have chosen, so if any values are given, they are only approximate. In addition to the size of the bed on the thickness of the layer, for example, fertile, affects the choice of plants: someone will be enough 5 cm, and someone needs much more.
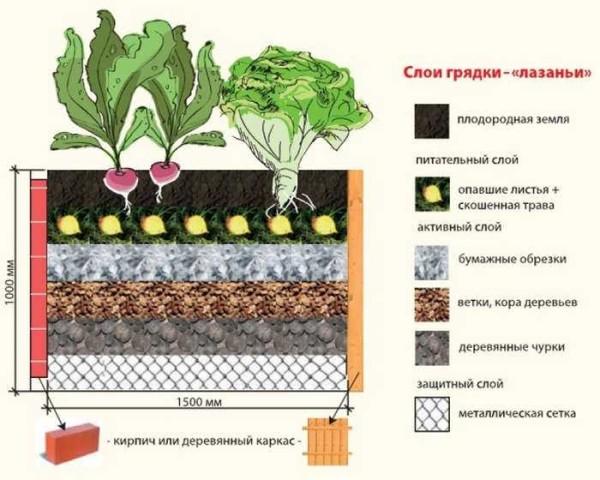
So, what to pour into a high bed – layers from bottom to top:
- At the bottom, a metal mesh with a fine mesh or a layer of geotextile is laid. You can lay cardboard. The mesh and geotextile are protection against rodents and moles. Cardboard plays approximately the same role, but it is less effective.
- Large wood residues: thick branches, twigs, even chunks and logs. This layer serves firstly for drainage, and secondly, moisture accumulates in the wood. The more arid the climate in your region, the more wood there should be. Moreover, the following wood layers too.
- Shredded small branches, bark. Other coarse plant residues will do: corn stalks, straw. Their task is also twofold. They store water, and when decomposing they release heat and nutrients. But when using corn stalks and straw, take into account that the bed will soon sink: these residues quickly rot, but the yield will be high, and you can pour fertile soil on top.
- Paper, thin cardboard. It is usually lined with a thin layer. More often use packing cardboard, because glossy paper is not suitable, as well as newspapers: lead paint base is not what you need to fertilize plants. If there is an old unwanted burlap (natural) you can lay it down.
- A layer of plant residues: leaves, grass, half-decayed sawdust. Be careful with sawdust: they strongly acidify the soil. So pour them under plants that like acidic soil, or neutralize the acidity by sprinkling them with a good layer of ash.
- Fertile soil.
A good portion of mature compost can be added to the last two layers, as can sprinkling deeper layers with it. This will accelerate the “readiness” of the high bed for planting.
About how to make a pond in the dacha with your own hands read here, and in this article it is written how to turn it into a fountain.
When it is better to do and what to plant
Fill the high bed is better from the fall. In this period and “material” will be enough and over the winter the processes inside will gain momentum. In this case, in the spring you can plant plants and hope for a high harvest. You can also do it in spring, but it is unlikely that there will be any significant differences in yield: the processes are just beginning and can not have a noticeable impact on the fertility of the backfill. Although you will definitely feel the difference in the amount of water for irrigation: much less water is required.

Plant rotation
In the year of the high bed, you can plant plants that require high fertility: cucumbers, zucchini, zucchini, pumpkin, any kind of cabbage, eggplants, tomatoes, sweet peppers. Another year you can plant herbs – spicy-aromatic and leafy. Root crops feel good in the second year.
After the second harvest, it is necessary to restore fertility. If the contents of the bed sagged, in the fall dopyryu good earth mixed with mature compost. If there is nowhere to sprinkle, you remove part of the top layer (on a compost heap or in another box as part of the backfill) and replace it with fresh soil with fertilizers.
High bed for strawberries
It differs only in the fact that on top of the finished “pie” spread a covering material. In it, holes are made, in which plants are planted. This option leads to the fact that moisture evaporates in minimal quantities, and also in the inter-row do not grow weeds. The second option – mulching the ground also works well, but evaporation is more intense.

The peculiarities of strawberries are that their roots are located mainly on the surface. Therefore, the fertile layer can be small. But the same feature leads to the fact that in case of severe frosts it can die. Although inside the high bed and there is a decomposition process that heats the soil, if the bed is without snow and not covered for the winter, the root system can freeze.
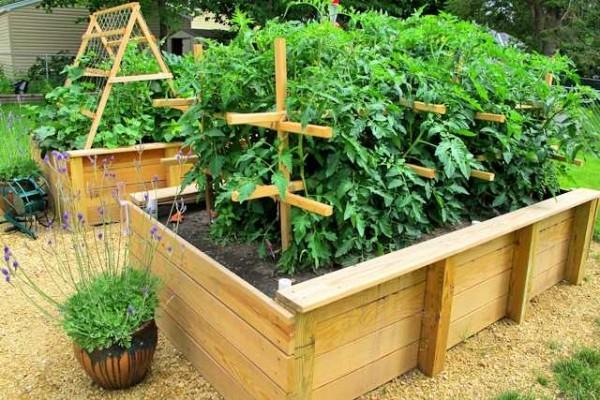
High bed for cucumbers and tomatoes
According to its device, it is no different. Except for the fact that you need posts and crossbars or stretched wire on the edges to be able to tie tomato bushes or cucumber branches.

About the organization of auto irrigation of the vegetable garden or plot can be read here.
High beds with their own hands
Most often, questions arise not when laying layers in high beds, but when making a box. Since the vegetable garden is often-generously engaged in women, up to the manufacture of fences for beds, they may not understand many points. To clarify the most difficult, we give photo reports of making a box of boards and slate – the most common fences.
From boards
Several variants of how you can make high beds from boards, were in the photo above. The main catch is usually in the connection in the corners. It is easiest to make them overlapping: just stick one to the other at 90 ° and knock nails through. But there are aesthetes who want to do everything right. And the right way is to saw two boards at an angle of 45° and so connect them. This is the variant that will be demonstrated in the photo.

To make it convenient to fix the fence on the ground, with a step of 1.2-1.5 m nail vertical bars or pieces of board, the length of which is about 20 cm more than the chosen height of the bed.

The lower end of the bar or board should be pointed – so it will be easier to hammer the fence into the ground. Then take a chisel or a circular saw, and cut the edges at an angle of 45 °. Putting the two boards together we get a perfect 90° angle.

For a strong connection on the inside of the corner, we install a bar, to which we nail the boards.

Fencing for high beds from wood to make not long, but even easier, connect the boards butt to butt, and for strength nail metal corners (on the photo below).

From logs
It is not more difficult to make a similar box from trimmed logs. For example, this option: the two long sides are made of logs, and the short sides are made of pieces of boards.

Whitewash the finished fence: both protection from pests and a more attractive look.

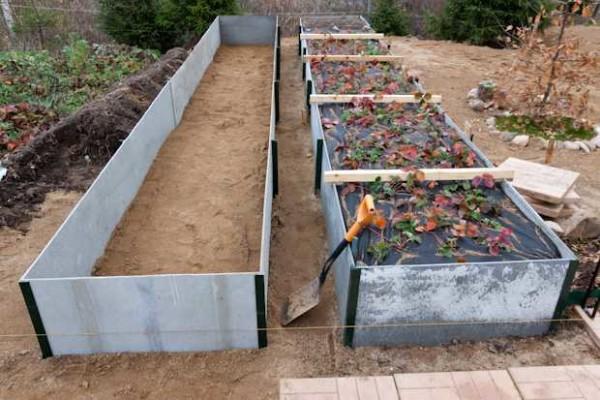
Slate
When making beds from flat or wave slate, there are also questions about how to fix it. The easiest way is to dig in. But it is not economical: you will have to make the strips wider by at least 10 cm, and still there is no guarantee that the slate will not “float” in the spring. In the deoxidized soil it will simply squeeze out the mass. You can correct it, but it is unnecessary time and effort.
Therefore, most often on one or both sides of the sheet are hammered corners or pipes that clamp the slate and do not let it deviate much. In the photo, the corners are hammered only on the outside: from the inside will be pressed by the mass of layers of high beds, so that the fence will not fall inside.

The places of connection of the two sheets are insured by a special welded plate. For reliability, they can be bolted to a wooden bar attached to that side.
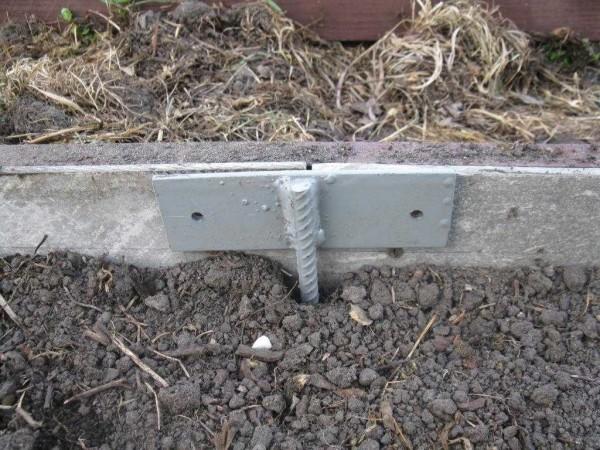

Another option is to make a frame. To similar posts with welded plates to attach a bar or angle – for whom what is cheaper. And to this frame to attach cut into strips of slate (nails in well held, but it is easier with self-tapping screws).
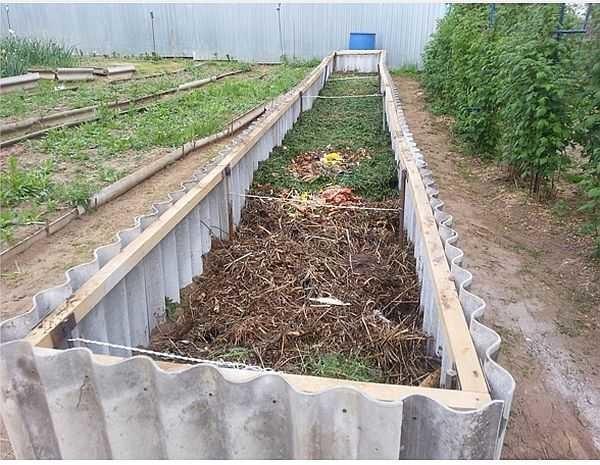

On the same principle – with guides – make beds from plastic panels and other similar materials. As you understand, especially virtuoso skill is not needed here. The main thing is to hold well.






I absolutely love the idea of high beds! I built one myself last summer, and it’s a game changer. The extra storage underneath is so handy, and it just makes my room feel so much cozier. Definitely want to try some new materials next time!
High beds can be a game changer for space! I built mine with some old pallets and a bit of paint. Not only does it look cool, but I can store stuff underneath, too. Just make sure it’s sturdy so you don’t have a surprise drop in the middle of the night!