Even if the house has a centralized water supply, a well will not be superfluous: it is too expensive to water the vegetable garden or flowerbeds with water from the tap, and in case of disconnection it will be very useful. At the dacha, it is in general, the main and only source of life-giving moisture. So its value is difficult to overestimate. Build a well with your own hands is not easy, but you can. Even if you decide to hire a brigade (it is hard to do it physically), you will need to control them. Not everyone does it the way it should be done. More often, as easier and faster. That’s what you need to know how it should be.
Contents of the article
How to choose a place
The most reliable way is to order hydrogeologic studies. You will get the exact place where you need to dig with an analysis of the water that will be there. But this service is not cheap and justifies itself if you plan to use the water as drinking water, that is, near the house of permanent residence. At the dacha you need it mostly for technical needs, and to drinking water can be purified only the part that goes into the house.
If you do not order a study, orient yourself immediately on several notes:
- the position of wells on neighboring plots;
- analysis of growing plants;
- observations of insects and animals;
- folk methods.
All these methods are only ways to approximate the place where aquifers may lie. None of them gives no guarantees, but if as a result of several methods you get more or less specific place, it makes sense to try to dig a well here.
Wells on neighboring plots
You probably know that rock strata lie quite unevenly, as well as aquifers. If your neighbors have water at a distance of 6 meters, it does not mean that you will have it exactly the same. It may be higher or lower, or it may go sharply somewhere to the side. So this is only a rough “shooting” on the ground.
Plants
This method is suitable if the site has not yet been plowed. You examine the “local” vegetation, identifying islands of characteristic grass. Not single plants (they may be accidentally introduced), but islands, glades, etc.

Observations of wildlife and nature
The best predictors are small midges. In the warm season, in windless weather, in the evening, before sunset, look at the site. If there are places where gnats “hang” pillars, most likely in this place, and quite close, there is water.
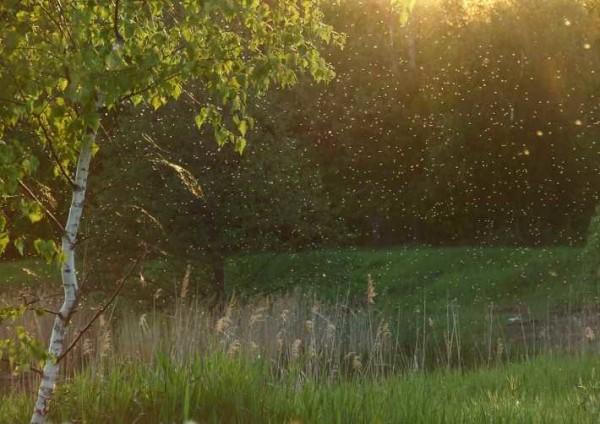

To be sure of this, you can observe this place in the morning. If the water is really close, there will be a fog.

Folk methods
Find an earthenware bowl. Preferably not glazed. But it is difficult to find such now, so any jug or pot will do. No such thing? You can also use an ordinary pot, only with a wide.
In the dishes pour oven-dried silica gel. Don’t have it, don’t know where to get it? You take ceramic bricks, break them to the state of fine crumbs (not flour, but crumbs), dry them for a couple hours in the oven. Pour into a bowl up to the top, tie with a dry cotton cloth. Only so that it does not come undone. Weigh and record the result.
In the proposed place/places of water dig a hole 1-1,5 meters deep, put the pot in it and cover it with earth. Leave it for 24 hours. Then dig it up and weigh it again. The more the mass has changed, the more water is in this place (or closer to the surface it is).
Best time
There are two periods when digging a well is best: it is the second half of August and the middle of winter – after two weeks of frost. At this time, the water table is the lowest, there is almost no water table. So it will be easy to work and you will not miss with the definition of the debit – it at this time is minimal and suffer from lack of water in detail you will not have to.

If a team is working, they can cope in a few days: two or three, occasionally – more. If you plan to work alone, there may not be enough time in August. This is the “border” zone – before the rains. Then you should start work earlier. Maybe from the beginning of August. At this time, there is already a small amount of top water, and by the middle of the month (even if you work alone in the evenings) you will already be near the aquifer. In general, try to calculate so that the exit to the aquifer came to the most “waterless” time. It is desirable to finish the waterproofing of the walls.
Type and structure
If the place you have decided, it remains to choose what exactly you will make your mine. Digging can only mine well, and Abyssinian – drill. The technique here is quite different, so further we will talk specifically about the shaft well.
Type of well shaft
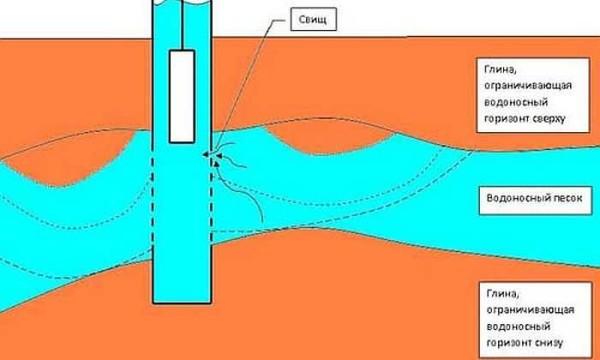
The most common today is a well made of concrete rings. Widespread – because it is the easiest. But it has serious disadvantages: the joints are not airtight at all and through them into the water gets rainwater, melt water, and with it what is dissolved in it, and what has sunk.
Joints of rings, of course, try to seal, but those methods that will be effective will not apply: the water should be suitable at least for irrigation. And just putty the joints with mortar – very short-term and ineffective. Slots are constantly increasing, and then through them not only rain or melt water enters, but also animals, insects, worms, etc.
There are rings with a lock. Between them, they say, you can put rubber gaskets, which will ensure airtightness. There are rings with locks, but they cost more. But the gaskets are practically not found, as well as wells with them.
The same “disease” suffers and the mine from logs, only the gaps are even more. Yes, our grandfathers did so. But they, first of all, had no other way, and secondly, they did not use so much chemistry in the fields.
From this point of view, a mine made of monolithic concrete is better. It’s cast right on the spot with removable formwork. A ring is poured, buried, the formwork is put up again, rebar is stuck in, another one is poured. We waited for the concrete to “set”, removed the formwork again, we dig.
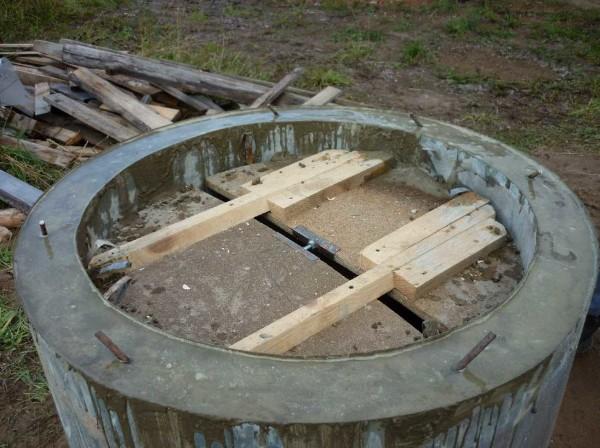

The process is very slow. This is the main disadvantage. Otherwise, only pluses. First, it turns out to be quite cheap. Costs only for two sheets of galvanizing, and then on cement, sand, water (proportions 1:3:0,6). It is much cheaper than rings. Secondly, airtight. No seams. Pouring goes about once a day and because of the uneven top edge turns out to be almost a monolith. Just before pouring the next ring scrape off the surface of the risen and almost contracted cement milk (gray dense film).
How to determine the aquifer
According to the technology, the soil is excavated inside and under the ring. As a result, under its own weight, it settles. This is the soil that you take out and will serve as a reference point.
As a rule, water lies between two water-retaining layers. Most often it is clay or limestone. The water-bearing layer is usually sand. It can be fine, like sea sand, or coarse with inclusions of small pebbles. Often there are several such layers. As the sand goes, it means that water will soon appear. As it appeared at the bottom, it is necessary to dig for some more time, taking out the already wet soil. If the water arrives actively, you can stop here. The aquifer may not be too large, so there is a risk of going through it. Then you will have to dig to the next one. Deeper water will be cleaner, but how much deeper – it is unknown.
Next, the well is pumped – throw in a submersible pump and pump out the water. These clean it, slightly deepening, and also determine its flow rate. If the rate of arrival of water you are satisfied, you can stop here. If it is not enough – it is necessary to pass this layer quickly. With the pump running, continue to excavate until they pass this layer. Then dig to the next water carrier.
Bottom filter in the well
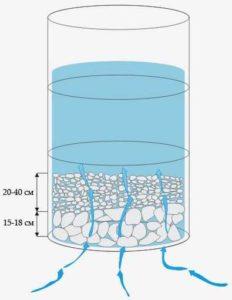
If you are satisfied with the speed of arriving water and its quality, you can make a bottom filter. This is three layers of stones of different fractions, which are laid on the bottom. They are needed in order to get as little silt and sand into the water as possible. To make the bottom filter for the well work, it is necessary to properly lay out the stones:
- At the very bottom put large stones. These should be fairly large cobblestones. But in order not to take away greatly the height of the water column use a flatter shape. Lay out at least two rows, and do not try to make them stand closely, but with gaps.
- The middle fraction is poured in a layer of 10-20 cm. The size is such that stones or pebbles do not fall through the gaps between the bottom layer.
- The upper, finest layer. Pebbles or stones of small size in a layer of 10-15 cm. The sand will settle in them.
With this arrangement of fractions, the water will be cleaner: first, the largest inclusions settle on the large stones, then as you move up, all the smaller ones.
Digging methods
There are two technologies for digging a well. Both methods are used, just at different depths. And both have disadvantages.
The alternate installation of rings
The first ring is placed on the soil, which is gradually removed from the inside and under the edge. Gradually the ring is lowered. Here is a very important point: it is necessary to ensure that it descends strictly downward, without skewing. Otherwise, the shaft will turn out to be inclined and, sooner or later, the draft of the rings will stop.
To avoid misalignment it is necessary to control the verticality of the walls. This is done by tying a plumb line to the bar and placing it on the ring. In addition, you can also control the top with a level.

When the upper edge of the ring is level with the ground level, roll the next one. It is placed strictly on top. Work continues. If on the first ring, the soil can be thrown over the side with a shovel with a shortened stem, then on the next ones it is necessary to take out with the help of a gate or tripod and a block. Thus, at least two people have to work, and at least three or even four people are needed to turn the rings. So it is impossible to dig a well on your own, in one hand. Unless you adapt a winch.
So, gradually, the depth of the well increases. When the ring is lowered to a level with the ground, a new one is put on it. For the descent use hammered staples or attached ladders (more correctly – staples).
The advantages of this method of digging a well:
- It is possible to control how tight and level the ring has become.
- You can put the very rubber gaskets that will ensure tightness or put them on the mortar.
- The walls do not crumble.
These are all the pluses. Now about the minuses. Working inside the ring is inconvenient and difficult physically. That’s why this method is mostly dug to a small depth – 7-8 meters. And in the mine work in turn.
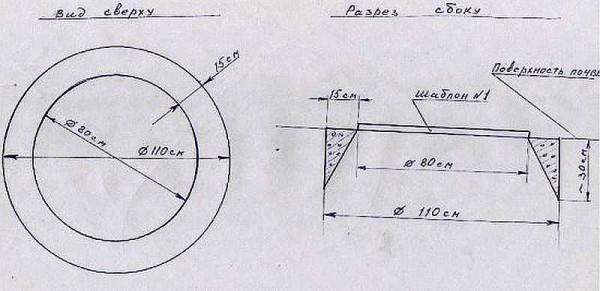
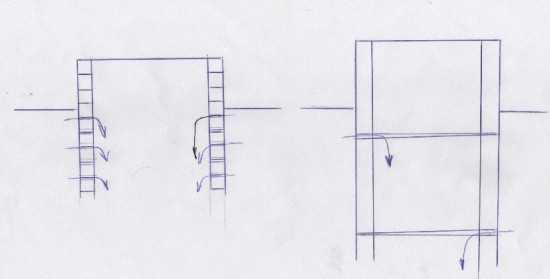
Another point: when digging a well with rings, accelerate the process of settling and facilitate the passage of soil, you can use a knife. It is made of concrete, it is poured into the ground at the very beginning. For its formation, a groove is dug in a circle. In the cross-section, it has a triangular shape (see figure). Its inner diameter coincides with the inner diameter of the rings used, the outer diameter is slightly larger. After the concrete has gained strength, on this ring put the “regular” and start working.
Installation of rings after reaching the aquifer
First, the shaft is dug without rings. At the same time, the walls are monitored. At the first signs of crumbling put rings inside and continue to deepen according to the first method.
If the soil does not crumble throughout the entire length, having reached the aquifer, stop. With the help of a crane or manipulator, the rings are placed in the shaft. Then, deepen a couple more rings according to the first method, increasing the flow rate.
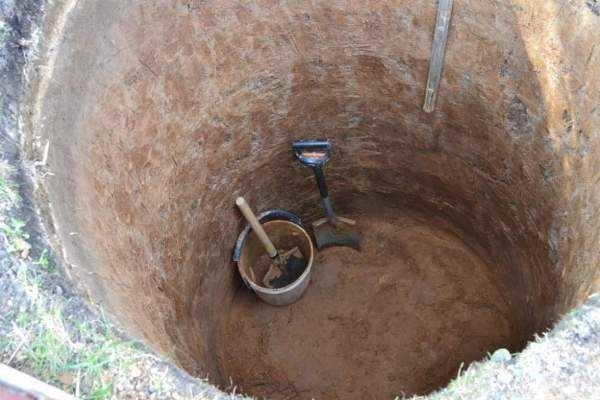

The technique of excavation is the same: as long as the depth allows, it is simply thrown out with a shovel. Then they put a tripod and a gate and lift it in buckets. After installing the rings, the gap between the walls of the shaft and the ring is filled and tamped. The upper few rings can be sealed from the outside (bitumen impregnation, for example, or other grease waterproofing).
When working, it is also necessary to control the verticality of the walls, but it can be corrected within certain limits. The method of control is similar – a plumb line tied to a bar and lowered into the shaft.
The advantages of this method:
- The shaft is wider, it is more convenient to work in it, which allows you to make deeper wells.
- It is possible to make an external sealing of several upper rings, which minimizes the possibility of the most contaminated water.
There are more disadvantages:
- It is difficult to control the tightness of the joint of the rings: it is forbidden to be in the shaft during installation. It is impossible to turn the already installed ring in it. It weighs hundreds of kilograms.
- You can miss the moment and the shaft will collapse.
- The backfill density of the gap between the shaft wall and the rings remains less than the “native” soil. As a result, melt and rainwater will seep into the depths, where through the gaps will get inside. To avoid this, make around the well a protective circle of waterproof material (waterproofing membrane) with a slope away from the walls of the well.
Commissioning
If you think that you have dug the well and that’s the end of it, not at all. You still have a series of daily exercises to do. Here they can be done with your own hands, without attracting help. First you have to waterproof the walls from the outside, then – clean and wash the walls from the inside and pump out the water – clean the well.
After the well is dug, the rings settle for a couple of days, take their place. During this time, you should not do anything inside, but you can do the external waterproofing.
Waterproofing
If the well was made by the second method – first digging the shaft, then put the rings – this stage is a little easier. You will need to slightly widen the gap to make waterproofing. If you put the rings in at once, you will have to dig a decent ditch around them. At least to the middle of the second ring. When the soil is removed, proceed to waterproofing.
It is best to use sheathing. You can – bitumen mastic, you can – other compositions. In principle, you can clad or glue roll waterproofing, in the most extreme case – to wrap the film. Film is the cheapest, but it will serve no more than two years, and that is if you buy expensive and reinforced.
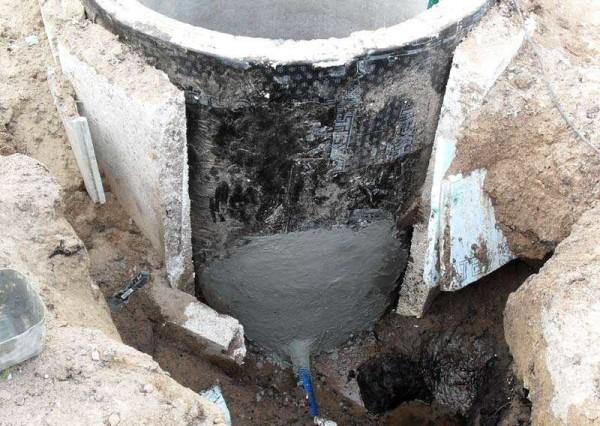

Since you all the same, dug the well, insulate it. Let as long as you do not appear at the dacha in winter, but maybe later you will come and cold weather. So take care of the availability of water in advance.
Cleaning the walls and internal sealing of the seams
A couple of days after the well is dug and the “glass sat down”, you go down inside with a broom, sweep the walls. Then you wash the walls: you drench them, sweep them with a clean broom. You pour again, then – with a broom. The water is pumped out, drained away. The next day you repeat the procedure. So – for five-seven-ten days. Until the interior and water will not be clean.
One more thing. Not all crews immediately lubricate the joints of the rings. Then after the first cleaning you need to lubricate the joints with a solution (cement:sand in a proportion of 1:3). To improve the effect, you can add PVA or liquid glass (instead of some water, or dilute PVA with water). It is also desirable to insure against horizontal shifts of the rings. Especially if they are without locks. To do this, neighboring rings are fastened with metal plates, which are attached to anchors. This measure is strictly necessary on unstable loose or strongly pudgy soils.

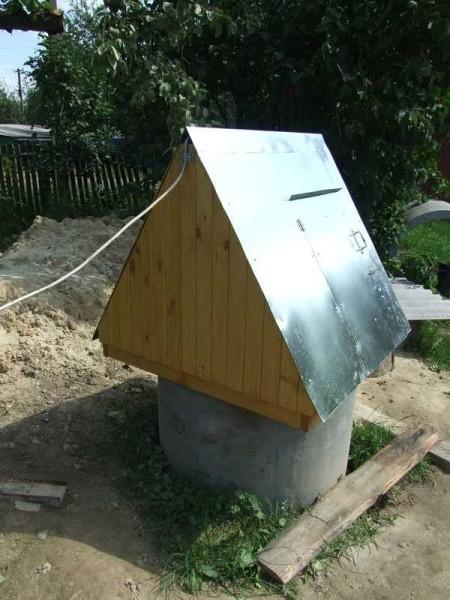
After the walls are washed, the water is pumped several times, you can use water. But in order that nothing attacked inside, it is necessary to close it. About how to make a house for a well, read here.
About some features of digging wells and its cleaning, see in the video.
Safety when working
Digging a well (with your own hands or a team) – the work is hard and dangerous, especially after the first three rings are dug. Buckets have to be pulled out with a winch, a gate or with the help of a block, and it is heavy. It can break – either the rope or the handle can fail. That’s why safety rules need to be followed:
Believe me, precautions are not unnecessary. It’s better to be over-insured.
How to dig a well: photo report
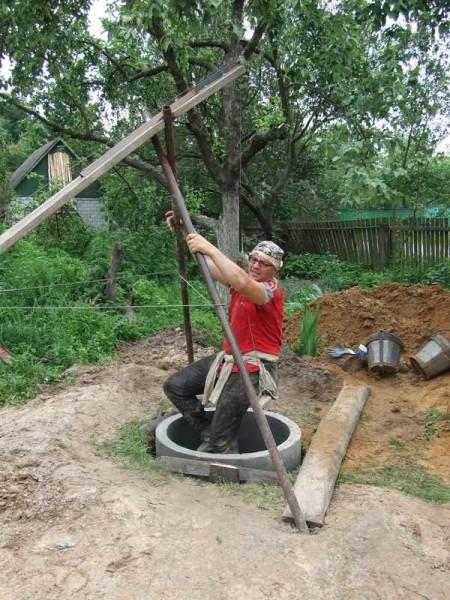
We dug by the first method – immediately put the rings. Three people worked, alternately changing: no one stayed inside longer than for “one ring”. These are briefly all the nuances. The rest – as we go along.
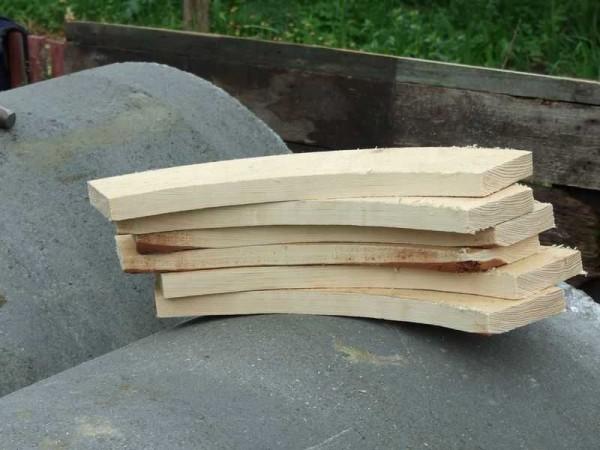
First, the rings were brought in and laid out on the plot. From wooden planks of a special shape assembled the knife.
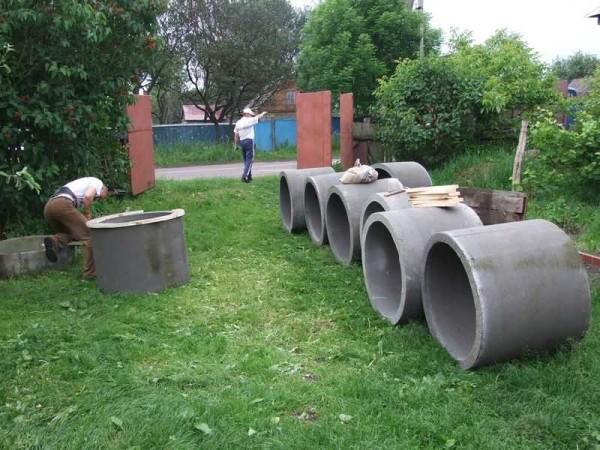


We got a ring, according to the dimensions of which we began to dig the chosen place.
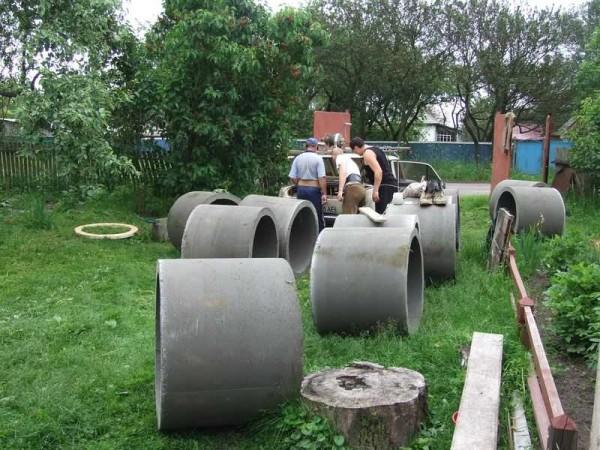
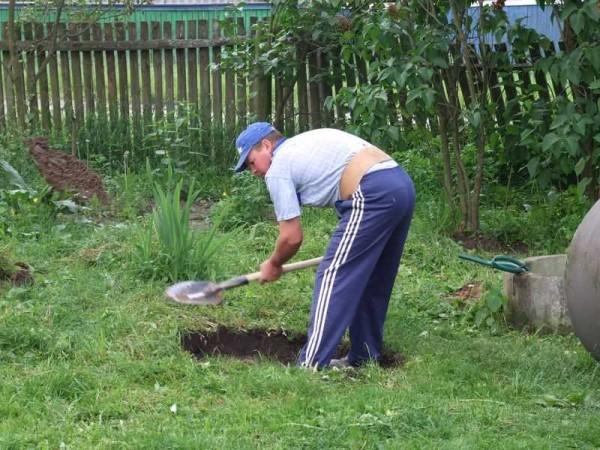


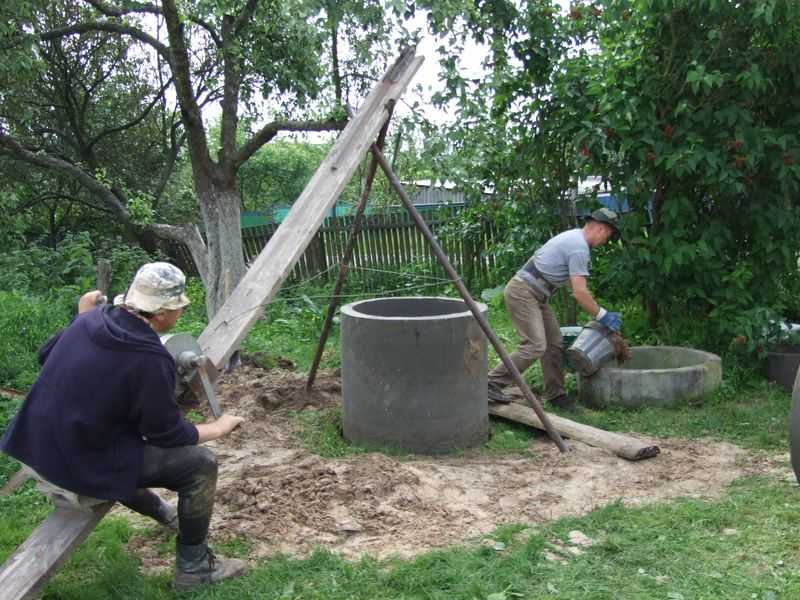
The first concrete ring was laid on this ring. The soil was first only thrown away – as long as the depth allowed.
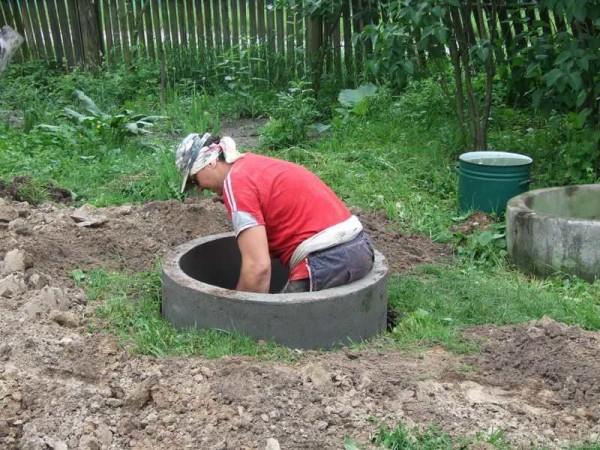

We put the second one, smeared the joints inside and outside, went to dig further.
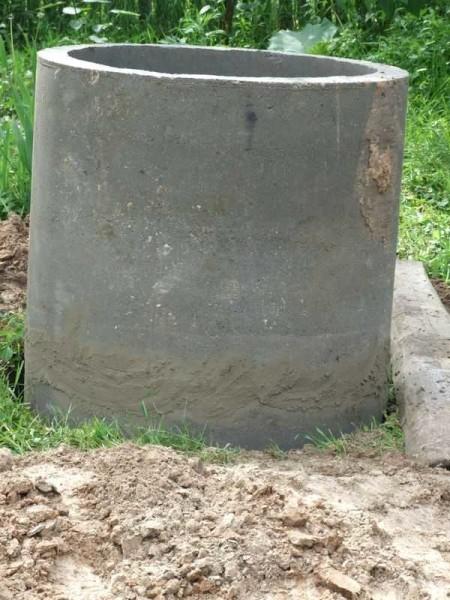

When the second one was level with the ground, we put a tripod with a winch and a block. That’s how we raised and lowered the digger and buckets of rock.
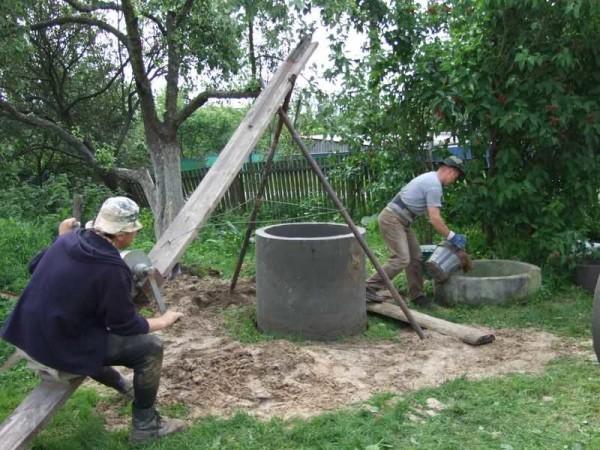

Now: one is digging, the second one is “spinning” on the winch, the third one is dumping the soil. On the same winch lowered into the shaft of the well.

Buried the sixth ring and after that there was water. If you look at the soil, it turned out like this: black earth, sand, clay, water-bearing sand. It means that the layer where water flows through is separated by clay, which conducts water poorly. This is very good – the water should be good, as it turned out later.

After that, three more rings were installed. One left for the end of August, when the water will be lower, we will lower the well another meter. then the procedure is standard – wash the walls, pump out the water. So six – seven times. After saddled head on the well and installed all the stuffing – the gate, pulled out of the house cable, put a socket. The plan is to bring water into the house.








Digging a well at the dacha was a game changer! We used a shovel and a bucket—classic tools, right? It was hard work, but when we hit water, it felt like winning the lottery. Now we’ve got fresh water for our garden and the kids love splashing around!
Totally feel you on that! We dug a trench once for a mini pond, and when we hit that clay layer, it was like “Yes!” The kids turned it into a mud pit—best summer ever! Fresh water makes all the difference for fun and garden blooms!
Haha, that sounds epic! We had a similar vibe when we started a little garden – hit a rock layer instead, though! The kids ended up making a messy splash zone instead of planting. Fresh water really makes it all pop; so worth it for those summer memories!
Haha, I feel you! When I tried gardening, I hit a gopher’s burrow and it turned into a mini mud pit. The kids went all in, splashing everywhere! But those laughter-filled moments? Totally priceless. Fresh water really does magic! Garden plans are a wild ride, right?
Digging a well at the dacha can be a real game-changer, especially for watering those summer veggies. I remember when we did ours, it took some sweat but the fresh water made it all worth it. Just make sure to check local regs before you start!