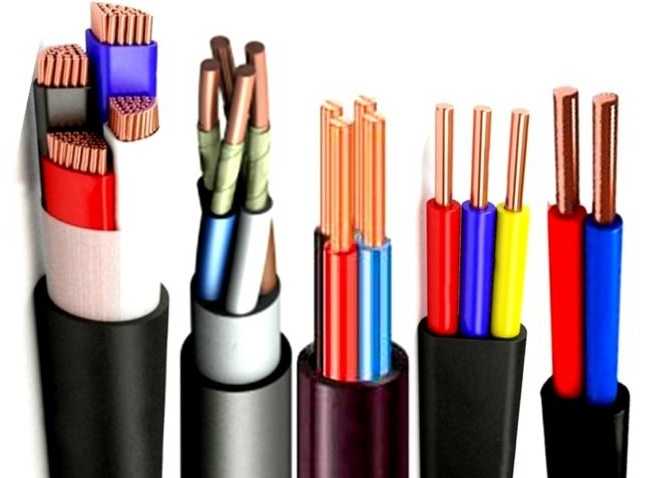
Today it is almost impossible to live without electricity. More and more we depend on the availability of electricity, so power grids accompany us everywhere – at enterprises, in public institutions, in houses and apartments, at summer houses. Literally everywhere where a person spends at least some more or less long period of time. And most often for laying wiring is used cable VVG and its modifications.
Contents of the article
VVG cable: area of application
When laying/replacing wiring, other works on the part of electricity in private homes and apartments most often use cable VVG. This is due to the wide area of application and relatively low price. It can be used in electrical networks with voltage not exceeding 1000 V and frequency of 50 Hz (special types up to 100 Hz). That is, it is suitable for single-phase and three-phase networks. It can be installed indoors and outdoors. In case of outdoor installation it needs additional protection. It is laid in HDPE pipes, cable trays, etc.

It is not recommended to use its laying in the ground, as it has no armor, because of which it quickly fails. If desired, it can be laid in the ground, but in an additional protective sheath (goforotube) and / or in the cable sewer.
The area of application depends largely on the modification: the type of material from which the sheaths of the cores and the cable itself. We will talk about it in detail a little further.
Decoding and modifications
To understand what the difference between different types of this cable, you need to know the decoding of the name. Then you can already decide which of the species you are more satisfied with.
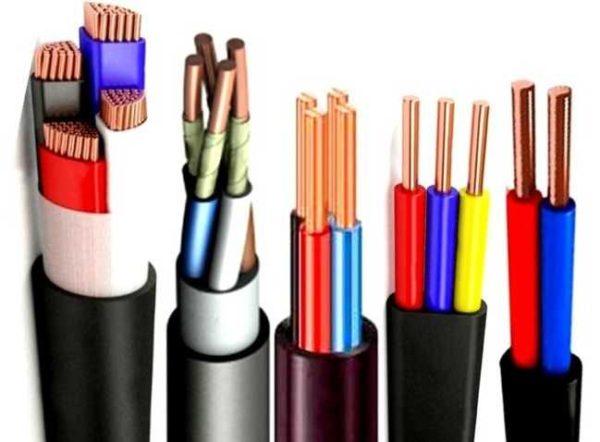

Ordinary VVG
The deciphering of the basic abbreviation – VVG – is not difficult:
- the absence of the letter A in front indicates that the cores are copper;
- the first letter “B” indicates the insulation material of the cores – PVC (polyvinyl chloride);
- the second letter “B” – the material of cable insulation – also PVC;
- “G” – indicates the absence of additional protection (armor or other protective sheaths).
That is, the cable VVG – consists of several copper conductors and PVC insulation. Each of the wires has its own color (read about color marking here). Conductors are twisted in one plane, protected by PVC sheath. Conductors can be stranded or single-core (in the abbreviation OJ is added).
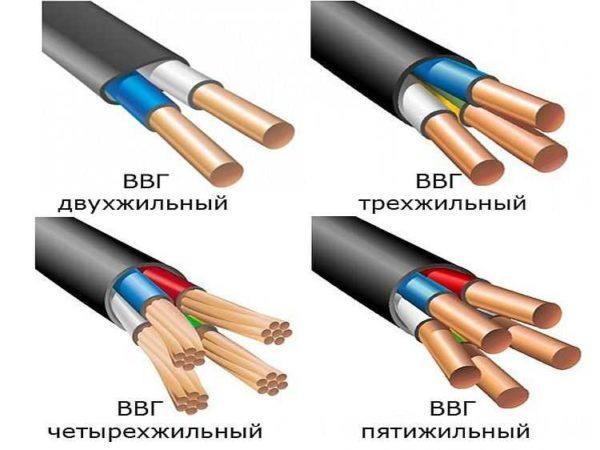
In private houses, single-core cables are more often used. They can have 2, 3, 4 or 5 conductors. The cable can be round or flat cross-section, with a neutral conductor (blue color) and / or with a grounding conductor (yellow-green color).
Non-combustible VVGng
In fire-hazardous premises (wooden houses, baths, etc.) and public buildings (children’s and medical institutions, in particular) cables that do not support combustion are required. In such cases it is possible to use products with reduced flammability – VVGng. Additional letters “ng” just say that the sheath does not support combustion.
There are several other types of cable VVGng:
So, what is the difference between the ordinary cable VVG and VVGng and its varieties? The ordinary VVG conductor does not support combustion when laid alone. Products with the prefix “ng” does not burn even in group laying – in a bundle with other conductors. Other “additions” to the name simply improve the characteristics.
Forms of release
Depending on the number and shape of the cores, the VVG cable can be round, flat, triangular or pentagonal (see photo below).
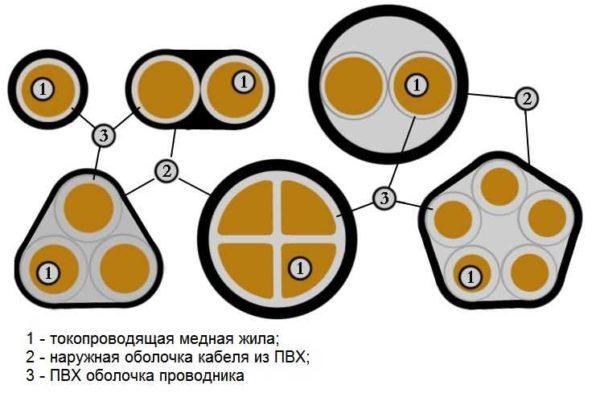
Sheaths are made of polyvinyl chloride of different modifications. The spaces between the cores are filled with the same plasticate. In some variants, a harness made of the same material is used. At small cross-section of conductors – up to 25 mm2 – it is allowed to issue without filling.
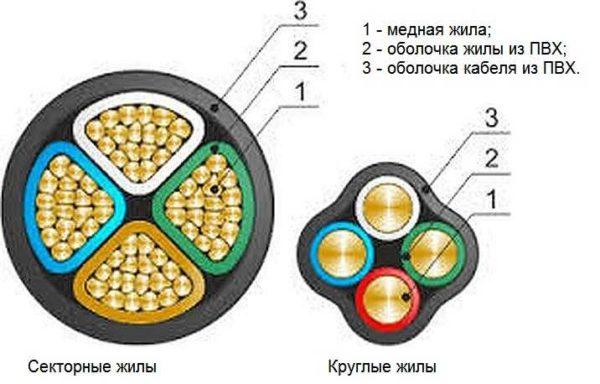
The cores in the cable can be round or sectional. Sectional are usually multicore, round – single core. In any case, their cross-section should correspond to the declared parameters (how to check read here).
Technical characteristics of VVG cable
About the peculiarities of the use of different types of cable VVG told above, and now we will talk about the technical parameters of conductors of this brand.
- It can be laid at temperatures up to -15°C. At lower temperatures it is necessary to heat the cable, which is not easy to organize (the sheath becomes too rigid, it is very difficult to bend).
- The operating temperature range is from -50°C to +50°C. At the same time, in case of outdoor installation, additional protection against ultraviolet radiation is required.
- Bending is possible with restrictions:
- Permissible heating temperature of conductors:
- During short-circuit at which the conductors retain their serviceability depends on the manufacturer may range from +160°C to +250°C.
- in normal operation +70°C$
- in overload mode +90°C.
- Fire resistance of VVG cables is not less than 180 min.
It should be said that the technical characteristics of VVG cable depend not only on the specific type, but also on the manufacturer. Therefore, before buying, look at the cable passport (you can ask the seller). Above are the parameters common to all brands of VVG cable.
It is not surprising that these conductors are very popular – with good technical indicators they cost relatively little, can be used almost anywhere – both in enterprises and offices, and in houses and apartments.
Cross-section and number of conductors
The cross-section of conductors of any brand of VVG cable can be from 1.5 mm2 to 240 mm2. On sale are usually conductors with cores up to 35 mm2, the rest, larger sizes must be ordered.
As already mentioned, there are VVG cables with 2, 3, 4 and 5 cores. The number of cores is written immediately after the abbreviation: VVG 2 x 3.5; VVGng 4 x 4, etc. The first digit is the number of cores, the second is the cross-section of the conductor.
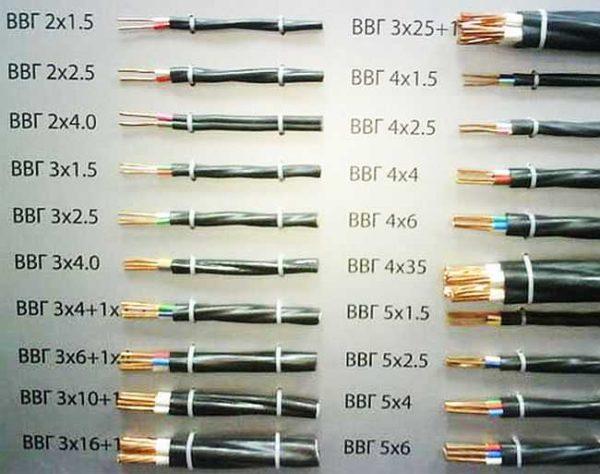

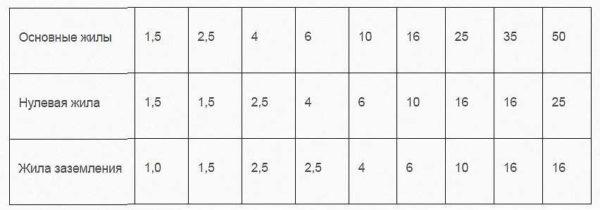
There may be cables VVG with conductors “neutral” and “ground”. And there are variants in which the protective conductors are the same cross-section, there are – with a smaller diameter (to save copper and lower cost). Most often smaller size make “earth” conductor, in some variants a little smaller make and “neutral”. If the protective conductor has a smaller diameter, it is designated as +1. For example, VVGng 4 x 4,0+1 (read as 4 wires with a cross-section of 4 mm2 and 1 step less than 2.5 mm2). Such variants of VVG cable are also standardized, their parameters are shown in the table below.
Long-term allowable current
When selecting the cross-section of the cable, the more correct methodology is by the maximum current. In this regard, such a characteristic as long-term allowable current is normalized. It depends on the number and cross-section of conductors, as well as on the method of laying – open or closed.
| Cross-section of conductors | Long-term allowable current | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| with two main conductors | with three main conductors | with four main conductors | |
| 1,5 mm2 | 24 А | 21 А | 19 А |
| 2,5 mm2 | 33 А | 28 А | 26 А |
| 4 mm2 | 44 А | 37 А | 34 А |
| 6 mm | 56 А | 49 А | 45 А |
| 10 mm | 76 А | 66 А | 61 А |
| 16 mm | 101 А | 87 А | 81 А |
| 25 mm | 134 А | 115 А | 107 А |
| 35 mm | 208 А | 177 А | 165 А |
Two modifications of VVG cables are produced – with rated voltage of 0.66 kW and 1 kW.