In the last few years, closed heating systems have become increasingly popular. Heating equipment is becoming more and more expensive and you want it to last longer. In closed type systems, there is virtually no possibility of free oxygen getting inside, which prolongs the life of the equipment.
Contents of the article
Closed heating system – what is it
As you know, in any heating system of a private house there is an expansion tank. This is a container that contains a certain amount of heat carrier. This tank is necessary to compensate for thermal expansion in different operating modes. By design expansion tanks are open and closed type, respectively, and heating systems are called open and closed.
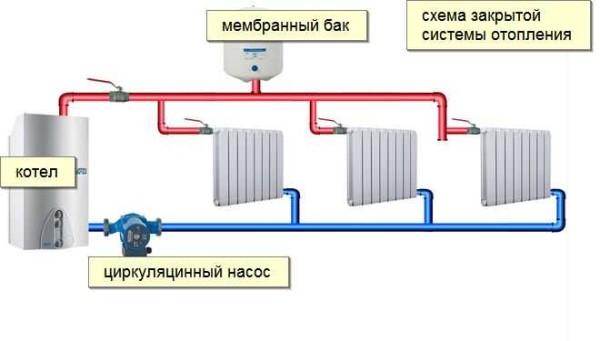
In recent years, it is the closed heating scheme that is becoming more and more popular. First, it is automated and works without human participation for a long time. Secondly, it can use coolant of any type, including antifreeze (from open tanks it evaporates). Thirdly, the pressure is maintained constant, which allows you to use any household appliances in a private house. There are a few more pluses that relate to wiring and operation:
- There is no direct contact of the coolant with air, therefore there is no (or almost no) unbound oxygen, which is a powerful oxidizer. This means that the heating elements will not oxidize, which increases their service life.
- Expansion tank of closed type is placed anywhere, usually not far from the boiler (wall-mounted gas boilers come with expansion tanks). Open-type tank must stand in the attic, and this – additional pipes, as well as insulation measures to ensure that the heat does not “leak” through the roof.
- In the system of the closed type are automatic air vents, so that there is no blowing.
In general, the closed heating system is considered more convenient. Its main disadvantage is energy dependence. The movement of the coolant is provided by a circulation pump (forced circulation), and it does not work without electricity. Natural circulation in closed systems can be organized, but it is difficult – it requires regulation of the flow by means of pipe thickness. This is a rather complex calculation, so it is often assumed that a closed heating system works only with a pump.
To reduce energy dependence and increase the reliability of heating, put uninterruptible power supply units with batteries and / or small generators that will provide emergency power supply.
Components and their purpose
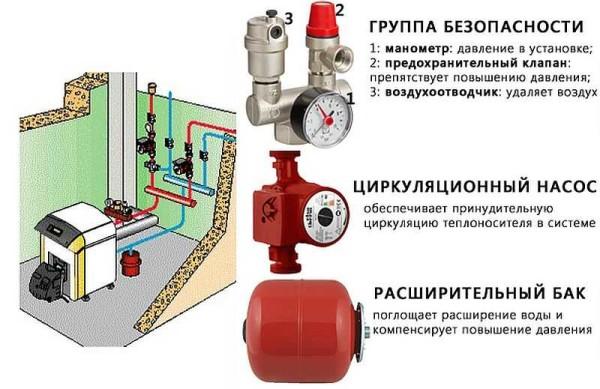
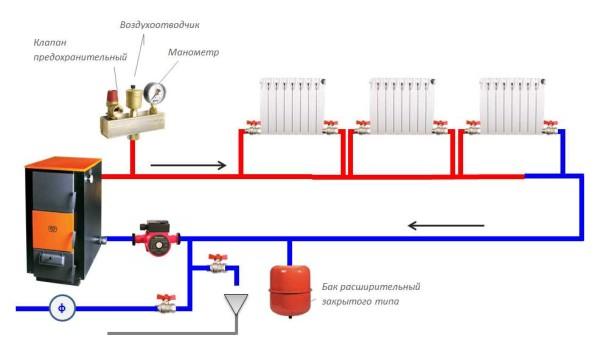
In general, a closed heating system consists of a certain set of elements:
- Boiler with a safety group. There are two options here. First – the safety group is built into the boiler (gas wall-mounted boilers, pellet and some gas-generator on solid fuel). The second – the boiler does not have a safety group, then it is installed at the outlet in the supply pipe.
- Pipes, radiators, water heating floor, convectors.
- Circulation pump. Provides the movement of the coolant. It is installed mainly on the return pipeline (here the temperature is lower and there is less possibility of overheating).
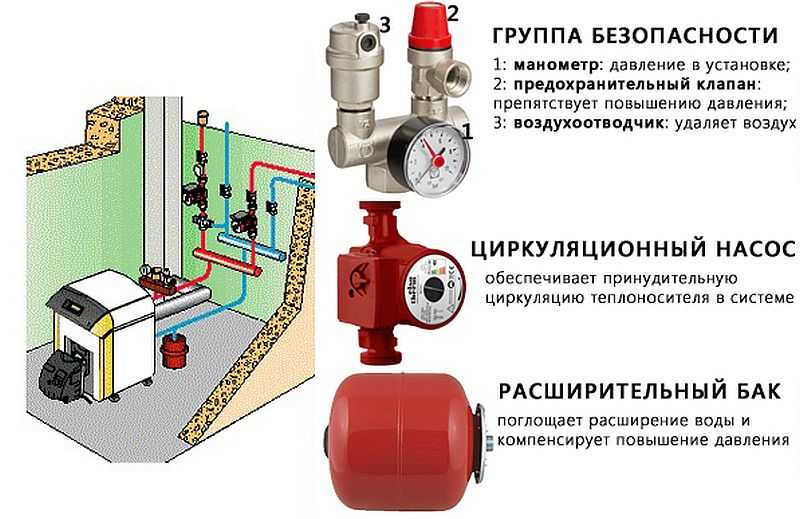
- Expansion tank. Compensates for changes in the volume of coolant, maintaining a stable pressure.
Now more about each element.
Boiler – what to choose
Since the closed heating system of a private house can work in an autonomous mode, it makes sense to install a heating boiler with automation. In this case, having adjusted the parameters, you do not need to return to this. All modes are maintained without human intervention.
The most convenient in this regard are gas boilers. They have the possibility of connecting a room thermostat. The temperature set on it is maintained with an accuracy of one degree. It fell by a degree, the boiler turned on, heating the house. As soon as the thermostat is triggered (the temperature is reached), the work stops. Comfortably convenient, economical.
In some models there is an opportunity to connect weather-dependent automatics – these are external sensors. According to their readings, the boiler corrects the power of the burners. Gas boilers in closed heating systems – good equipment that can provide comfort. It’s only a pity that gas is not everywhere.
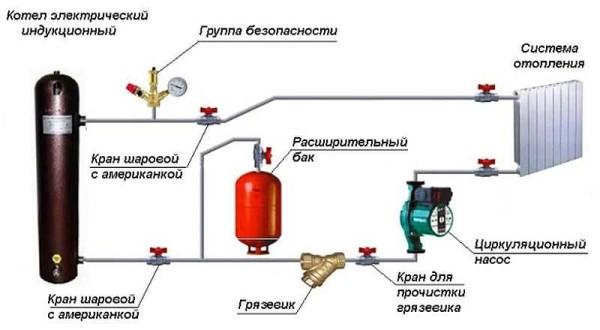
Not a lesser degree of automation can give electric boilers. In addition to traditional units on TENs not so long ago appeared induction and electrode. They are characterized by compact dimensions and low inertia. Many believe that they are more economical than boilers on TENS. But this vidotopilnyh units are not everywhere you can use, as power outages in winter – a frequent phenomenon in many regions of our country. And to provide electricity to the boiler power. in 8-12 kW from the generator – a very difficult matter.
More versatile and independent in this regard boilers on solid or liquid fuel. Important point: for the installation of a boiler on liquid fuel must be a separate room – this is a requirement of the fire department. Solid fuel boilers can stand in the house, but this is inconvenient, since during the furnace from the fuel falls a lot of debris.
Modern boilers on solid fuel, although they remain equipment of periodic action (then heated up during the furnace, from cool down when the tab burned through), but they also have automation, which allows you to maintain a set temperature in the system, regulating the intensity of combustion. Although the degree of automation is not as high as gas or electric boilers, but it is there.
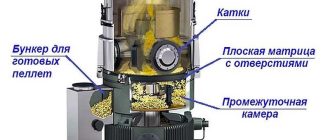
Not very common in our country boilers on pellets. In fact, this is also solid fuel, but boilers of this type work in a continuous mode. Pellets are automatically fed into the furnace (until the stock in the bunker is finished). With good quality fuel, cleaning of ash is required once every few weeks, and all parameters of operation are controlled by automation. Restrains the spread of this equipment only its high price: manufacturers are mainly European, and their prices are corresponding.
A little about calculating the boiler capacity for heating systems of closed type. It is determined by the general principle: 10 square meters of area with normal insulation take 1 kW of boiler power. Only to take “to the brim” is not advised. First, there are abnormally cold periods, in which you may not be enough calculated power. Secondly, working at the limit of power leads to rapid wear and tear equipment. Therefore, it is desirable to take the boiler power for the system with a reserve of 30-50%.
Safety group
A safety group is placed on the supply pipe at the boiler outlet. It should control its operation and system parameters. It consists of a pressure gauge, automatic air vent and safety valve.
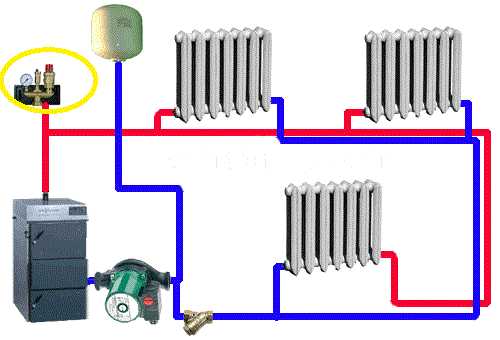
The pressure gauge makes it possible to control the pressure in the system. According to the recommendations it should be within 1,5-3 bar (in one-storey houses it is 1,5-2 bar, in two-storey houses – up to 3 bar). In case of deviation from these parameters it is necessary to take appropriate measures. If the pressure falls below the norm, it is necessary to check for leaks and then add some coolant to the system. In case of increased pressure everything is a bit more complicated: it is necessary to check in what mode the boiler works, whether it has overheated the coolant. Also check the work of the circulation pump, the correctness of the pressure gauge and the safety valve. It is he who should discharge the excess coolant when the pressure threshold is exceeded. A pipe/hose is connected to the free spigot of the safety valve, which is led to the sewer or drainage system. It is better to make it possible to monitor whether the valve is working or not – if water is frequently discharged, it is necessary to look for causes and eliminate them.
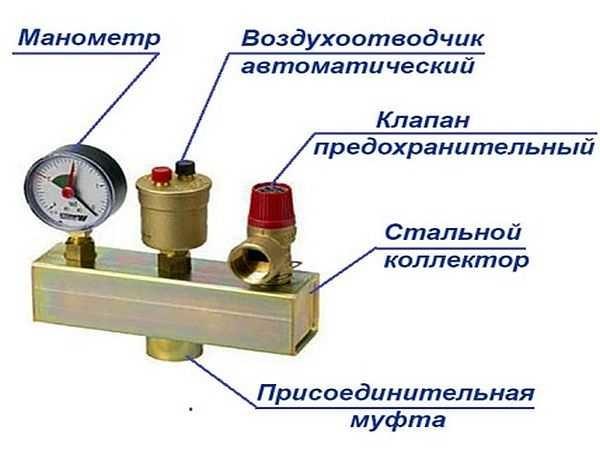
The third element of the group is an automatic air vent. Through it, the air trapped in the system is discharged. A very convenient device that allows you to get rid of the problem of air plugs in the system.
Safety groups are sold assembled (pictured above), or you can buy all the devices separately and connect them using the same pipes that were used to make the system wiring.
Expansion tank for closed heating system
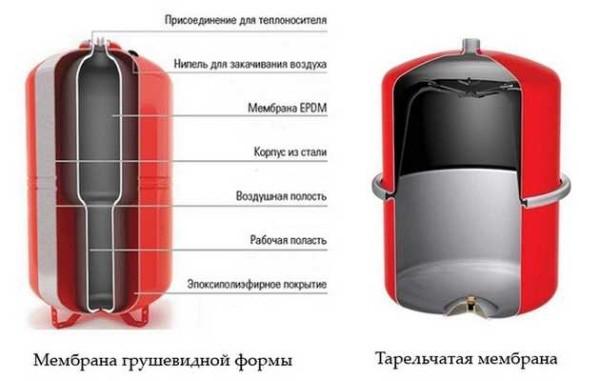
The expansion tank is designed to compensate for the change in the volume of the coolant depending on the temperature. In closed heating systems it is a sealed container, divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. In the upper part there is air or inert gas (in expensive models). As long as the temperature of the coolant is low, the tank remains empty, the membrane is spread out (in the picture on the right).
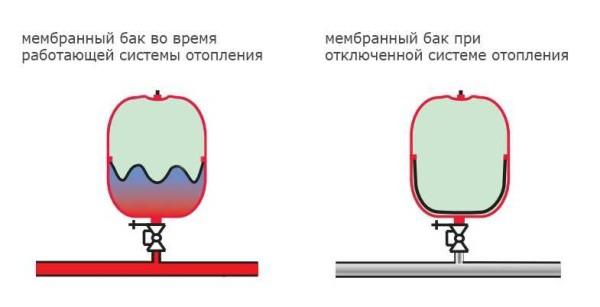
When the coolant is heated, it increases in volume and its excess rises into the tank, pushing back the diaphragm and compressing the gas pumped into the upper part (picture on the left). On the pressure gauge this is shown as an increase in pressure and can serve as a signal to reduce the intensity of combustion. Some models have a safety valve that will release excess air/gas when the pressure threshold is reached.
As the coolant cools down, the pressure in the upper part of the cistern squeezes the coolant out of the tank into the system, and the pressure gauge readings return to normal. This is the whole principle of operation of the diaphragm-type expansion tank. By the way, membranes are of two types – plate and pear-shaped. The shape of the membrane does not affect the principle of operation.
Volume calculation
According to generally accepted norms, the volume of the expansion tank should be 10% of the total volume of the coolant. This means that you must calculate how much water will fit in the pipes and radiators of your system (there are in the technical data of radiators, and the volume of pipes can be calculated). 1/10th of this figure will be the volume of the expansion tank needed. But this figure is only valid if the coolant is water. If a non-freezing liquid is used, the size of the tank is increased by 50% of the calculated volume.
Here is an example of calculating the volume of a membrane tank for a closed heating system:
- the volume of the heating system is 28 liters;
- the size of the expansion tank for a system filled with water is 2.8 liters;
- the size of the membrane tank for a system with non-freezing liquid is 2.8 + 0.5*2.8 = 4.2 liters.
When buying, choose the nearest larger volume. Do not take the smaller one – it is better to have a small reserve.
What to pay attention to when buying
In stores there are red and blue color cisterns. For heating, red-colored tanks are suitable. Blue are structurally the same, only they are designed for cold water and high temperatures do not tolerate.
What else to pay attention to? There are two types of cisterns – with a replaceable membrane (they are also called flanged) and with an irreplaceable. The second option is cheaper, and significantly, but if the membrane is damaged, you will have to buy the whole thing. In flanged models, only the diaphragm is bought.
Place for installing a diaphragm-type expansion tank
Usually put the expansion tank on the return pipeline before the circulation pump (if you look at the flow of the coolant). A tee is installed in the pipeline, a small section of pipe is connected to one part of it, and the expander is connected to it through fittings. It is better to place it at some distance from the pump, so that pressure drops are not created. An important point is that the piping section of the diaphragm tank should be straight.
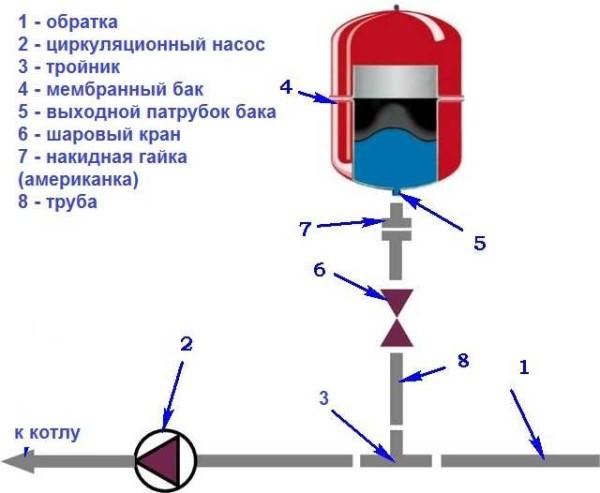
After the tee put a ball valve. It is necessary to be able to remove the tank without draining the coolant. It is more convenient to connect the tank itself with the help of an american (union nut). This again facilitates mounting/dismounting.
Note that some boilers have an expansion tank. If its volume is sufficient, the installation of a second one is not required.
Empty device weighs not so much, but filled with water has a solid mass. Therefore, it is necessary to provide a way of fixing on the wall or additional supports.
- The heating expansion tank can be hung on a bracket
- Make a support platform
- The tank on legs can be installed on the floor
Circulation pump
The circulation pump ensures the performance of a closed heating system. Its capacity depends on many factors: the material and diameter of pipes, the number and type of radiators, the presence of shut-off and thermostatic control valves, the length of pipes, the mode of operation of equipment, etc. In order not to go into the subtleties of calculating the power, the circulation pump can be selected according to the table. You choose the nearest larger value for the heated area or the planned thermal capacity of the system, in the corresponding line in the first columns find the required characteristics.
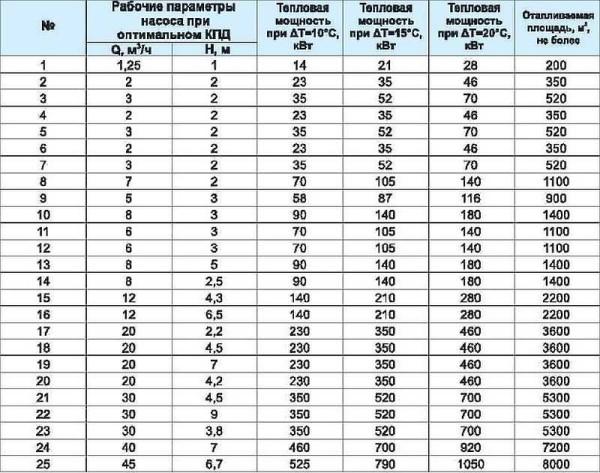
In the second column find the power (what volume of coolant it is able to pump per hour), in the third – the pressure (system resistance), which he is able to overcome.
Choosing a circulation pump in the store, it is desirable not to save money. From its performance depends on the entire system. Therefore, it is better not to save money and choose a proven manufacturer. If you decide to buy unknown equipment, it is necessary to somehow check it for the level of noise. This indicator is especially critical if the heating unit is installed in the living room.
Scheme of tying
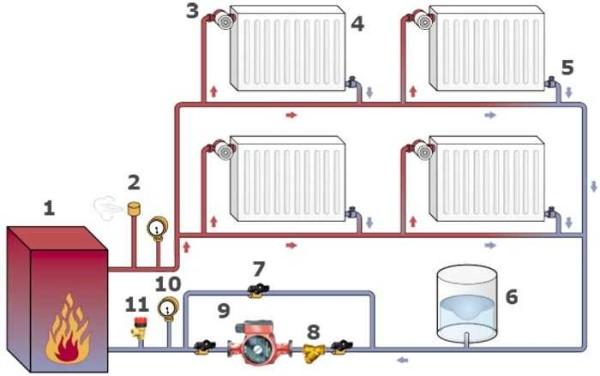
As we have already said before, circulation pumps are put mainly on the return pipeline. In the past, this requirement was mandatory, today it is only a wish. Materials that are used in production can withstand heating up to 90°C, but it is still better not to take risks.
In systems that can also work with natural circulation, the installation should provide for the possibility of removing or replacing the pump without the need to drain the coolant, as well as for the possibility of working without a pump. For this purpose, a bypass is installed – a bypass path through which the coolant can flow if necessary. The scheme for installing a circulation pump in this case is shown in the photo below.

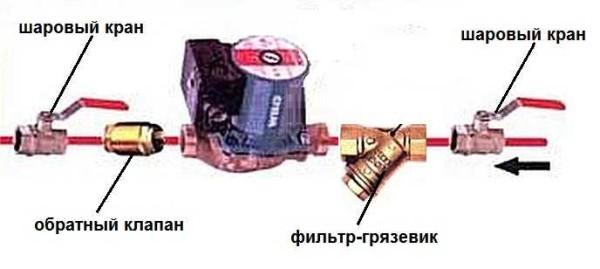
In closed systems with forced circulation, a bypass is not necessary – without a pump it is inoperable. But two ball valves on both sides and a filter at the inlet are necessary. The ball valves make it possible to remove the unit for maintenance, repair or replacement if necessary. A dirt filter prevents clogging. Sometimes, as an additional element of reliability, between the filter and the ball valve put a check valve, which prevents the movement of the coolant in the opposite direction.
How to fill a closed heating system
At the lowest point of the system, usually on the return pipe, to fill/drain the system, an additional valve is installed. In the simplest case, this is a tee installed in the pipeline, to which a ball valve is connected through a small section of pipe.
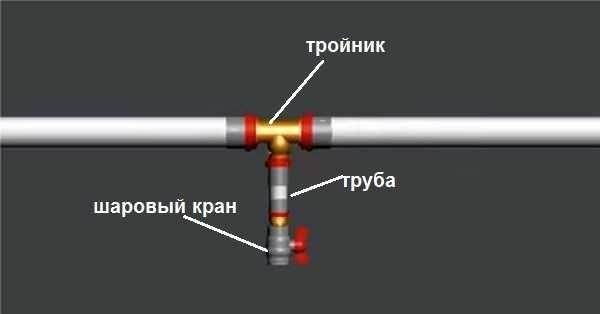
In this case, when draining the system, it is necessary to put a container or connect a hose. When the coolant is poured into the system, the hose of the hand pump is connected to the ball valve. This simple device can be rented from plumbing stores.
There is a second option – when the coolant is just tap water. In this case, the water supply is connected either to a special boiler inlet (in wall-mounted gas boilers), or to a similarly installed on the return ball valve. But in this case, a different point is needed to drain the system. In a two-pipe system it can be one of the last radiators in the branch, to the lower free inlet of which a drain ball valve is installed. Another option is shown in the following diagram. It shows a one-pipe heating system of the closed type.








I recently set up a closed loop heating system in my home, and it’s been a game changer! Super efficient and cozy. Plus, I love how it keeps everything warm without wasting energy. Can’t believe I waited so long to make the switch! Totally recommend it!
So, we just set up closed loop heating in our house, and I’m loving it! Super efficient and cozy. No more cold spots! It’s like having a warm hug all winter. Wish we’d done it sooner—totally worth it! If you’re thinking about it, go for it!