Water hardness is one of the most important criteria determining its consumer properties. Forming insoluble mineral deposits on the inner surface of electrical appliances and industrial equipment, it leads to deterioration of their operational characteristics. To assess the quality of water, the permissible limits of the indicator are established.
Obsah článku
How hardness salts are formed
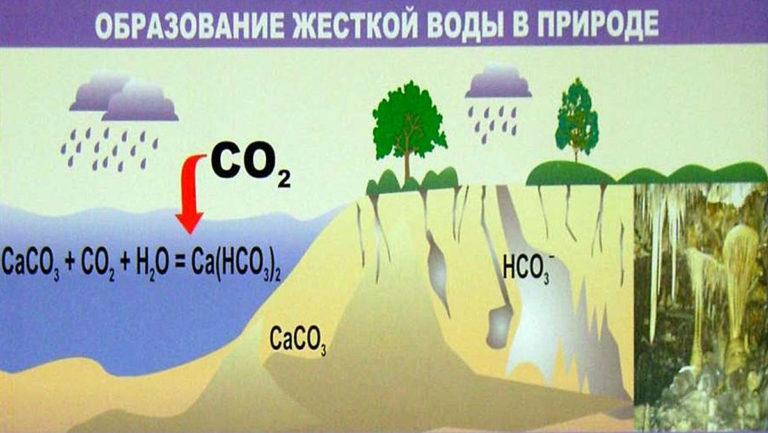
Water is a universal solvent. The composition of natural sources is formed depending on the type of terrain. Water with dissolved carbon dioxide penetrates into the soil, passes through the thickness of geological rocks – gypsum, dolomite, calcite, erodes them, enriching with organic and mineral substances, metal ions. They make up the total mineralization of water(TDS).
Calcium and magnesium cations predominate among them, their total value gives the total hardness of water. It is divided into two types:
- temporary (carbonate);
- permanent (non-carbonate).
The formula for total hardness is as follows:
Zho = [Ca2+] + [Mg2+] = Zhk + Zhnk
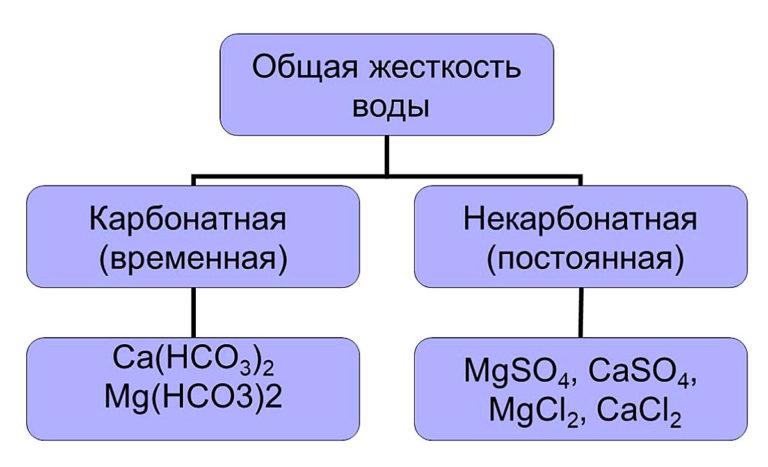
Carbonate hardness is due to the presence of hydrocarbonates Ca(HCO3)2 and Mg(HCO3)2. They are easily removed from solution, forming an insoluble precipitate on boiling. The second type of hardness determines the content of soluble salts in water, which cannot be removed by heating. To eliminate permanent hardness, various methods are used, which will be described later in the article.
Unlike underground sources, surface water contains fewer salts, since it is constantly diluted by precipitation. The level of hardness in them is a variable value. It reaches its maximum values in winter, and during floods it decreases. In groundwater, this indicator is more stable.
Units of measurement
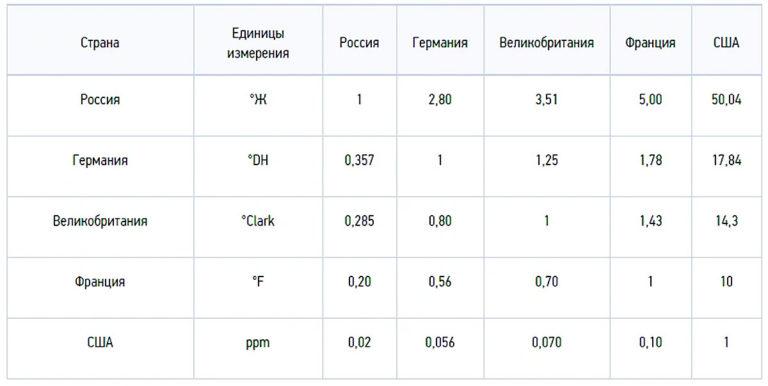
Salt concentration is measured in milligram equivalents per liter: 1 mg-eq/L = 20.04 mg Ca2+ and 12.16 mg Mg2+. In the international SI system, the indicator is numerically expressed in moles per meter3 (mol/m3). In our country, degrees of hardness are used, 1 ºJ = 1 mg-eq/L or 0.5 mmol/L.
Hardness degrees are also used in other countries, but differ in numerical values:
- German hardness degree 1ºdH = 10 mg/L CaO or 7.194 mg/L MgO;
- French 1ºfH = 10 mg/L CaCO3;
- English 1ºClark = 14.254 mg/L CaCO3;
- American 1 gpg = 17.12 mg/L CaCO3.
To convert to other units of measurement, it is more convenient to use another American unit – PPM (PPM), which is equal to 1 mg/L CaCO3. Hence:
- 1ºdH = 17.9 ppm;
- 1ºfH = 10.0 ppm;
- 1ºClark = 14.25 ppm;
- 1º gpg = 17.1 ppm;
- 1ºÆ = 50.05 ppm.
To convert ppm to our convenient ºÆ degrees of hardness, we can use a converter. A scale can be used to convert between degrees:
1 ºJ = 2.804 ºdH = 3.5 ºClark = 5.005 ºfH = 2.924 gpg = 50.05ppm.
Hardness standards
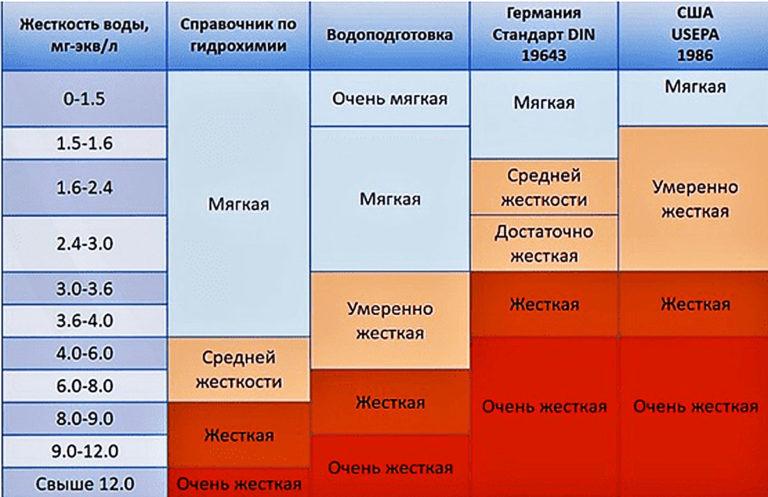
According to the parameter of total hardness, water is distinguished:
- soft – up to 4 ºJ;
- medium hardness – from 4 to 8 ºJ;
- hard water – more than 8 ºJ.
The diversity of natural conditions in Russia makes it impossible to establish uniform hardness standards for all regions. The maximum permissible concentration (MPC) of Ca2+ varies widely depending on local conditions.
However, drinking water standards do not differ much from the WHO (World Health Organization) settings. As a national standard, GOST 31954-2012 has been in force in our country since 01.01.2014. It takes into account the main international norms on water quality and methods of analysis. The standard applies to all underground and surface sources.
Table 1. Normative values of calcium and magnesium concentrations in drinking water
| № | Norm. document | Product | Ca, mg/l | Mg, mg/l | Degrees, ºJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | СанПин_2.1.4.1074-01, GN_2.1.5.1315-03 |
Drinking water | Not regulated | Not regulated | 7 |
| 2 | SanPin 2.1.4.1116-02 | Bottled water | 25-130 | 5 – 65 | 1,5-7 |
| 3 | WHO standards | Drinking water | 20-80 | 10 – 30 | Not proposed |
The composition of water is governed by the hardness scale depending on the intended use:
- acceptable value for tap water – 300 ppm or 6 ºJ;
- optimal value for natural water bodies – within 400 ppm or 8 ºJ;
- the maximum allowable hardness level is 500 ppm, 10 ºJ;
- life-threatening salt concentrations – more than 500 ppm, > 10 ºJ.
Particularly strict requirements are imposed on water that is supplied to heating boilers at power plants – the indicator of total hardness cannot exceed 0.05-0.1 mg-eq/l.
How to calculate hardness at home
Increased hardness is not expressed by any external signs – smell, color, consistency. It is evidenced by:
- forming scale on the bottom of the kettle;
- poor foaming of detergents;
- white streaks on the shower head in the bathroom.

The exact composition of water can only be found out with the help of analysis. But at home there is a simple way to determine the hardness of tap water with a small error of 1-2 degrees.
For the experiment you will need: a piece of laundry soap, a small volume of distilled water, electronic scales, a container, a cylindrical glass, a ruler.
- Finely grate 1 g of laundry soap and dissolve it in 3-4 tablespoons of slightly heated distilled water. If you do not have a kitchen scale at hand, you can be guided by eye – half a teaspoon without the top.
- Pour distilled water into the glass with soap solution so that the height of the liquid column corresponds to the percentage of fatty acids indicated on the bar of soap. If 72%, the height of the water column should be 72 mm from the bottom of the beaker, but not from the surface of the table.
- Pour 0.5 liters of tap water into a container and, stirring gently, pour a thin stream of soap solution into it. First, flakes, bubbles will appear in the water, then – a persistent white foam. It indicates that all the salts are already bound.
Calculate the number of centimeters of water column overflowed into the container, you can subtract the height of the remaining soap solution from the original:
hn= hi – ho,
where:
- hn – height of the column of the overflowed solution;
- һi – height of the water column of the initial soap solution;
- ho – height of the column of the residual soap solution.
Each centimeter of solution poured into the container corresponds to 2ºdH. The value coincides with the German unit of hardness. For example, 4.6 centimeters have been poured from a beaker, which corresponds to 9.2 dH.
You can use the table to convert the results obtained into mg-eq/l, and a calculator for exact results.
| № | Degrees dH | Hardness level | Indicator in mg-eq/l |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 – 4 | Very soft | Up to 1.4 |
| 2 | 5 – 11 | Soft | 1,8 – 4,0 |
| 3 | 12 – 22 | Střední | 4,3-8,0 |
| 4 | 22 – 34 | Hard | 8,0-12 |
| 5 | More than 34 | Very stiff | Above 12 |
You can get a more accurate result with electronic testers like the TDS-3. They analyze water for hardness and acidity, displaying the results on the screen as RRM or pH. You can convert the RRM units to ºJ with a calculator.

If you want to get a detailed analysis of water in a well or borehole, you can do it with the “Well-1” kit.
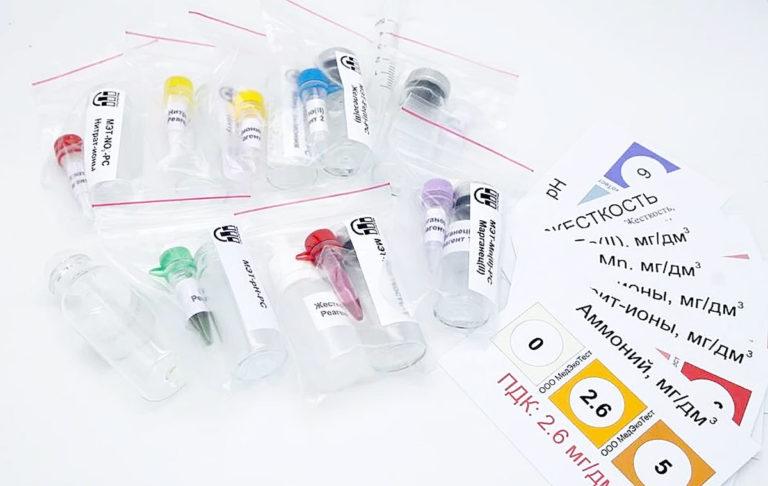
Another simple and inexpensive way to determine the quality of water – test strips.

Effect of water
On the human body
To date, there are no serious studies confirming the harmful effects of hard water on the living organism. But it is known that prolonged consumption of water with an increased level of hardness, contributes to the development of urolithiasis. The body does not have time to eliminate excess trace elements, which leads to the appearance of urinary stones, kidney stones and deposits in the joints.
Water quality is also of hygienic importance. Soap, reacting with calcium and magnesium salts, destroys the protective layer of the skin, causing irritation or allergies. Hair becomes dry and brittle.
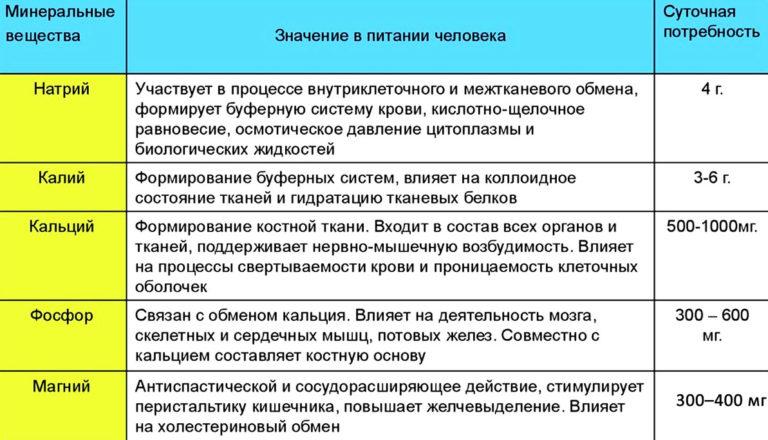
At the same time, calcium and magnesium are important trace elements for human life:
- The daily allowance of calcium is 1000 mg;
- magnesium – 400 mg.
Deficiency of these elements can cause serious disorders in the body. According to studies conducted by WHO noted that the consumption of excessively soft water leads to the leaching of salts from the body and changes in the water-salt balance. In regions where soft water is used:
- an increase in cardiovascular diseases;
- an increase in the number of fractures in children and a decrease in the weight of newborns.
WHO indicates that the presence of salts in water should be considered a prerequisite for the normal vital activity of the body.
On Technique
Hardness salts cause a lot of problems associated with the use of household appliances and industrial equipment:
Too soft water has a negative effect on appliances, increasing the risk of corrosion of pipes due to low alkalinity. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain the correct balance of water-salt composition.
Methods of water softening
There are various ways to reduce hardness. The choice is determined depending on the initial quality of water, its purpose and conditions of use.
Thermal method
Boiling is the simplest and most affordable way to eliminate carbonate hardness. It is suitable for small volumes of water that are used for household needs. However, the method does not eliminate all hardness salts, and dishes will have to be descaled.
Filtration
Not so long ago, a water softening filter represented an impressive installation. Modern technology and materials have made it possible to create compact purification systems that give water softness, easily fitting under the sink in the kitchen. Replacement filter cartridges, in addition to softening water, remove odors and impurities. Proper selection of filters and timely replacement guarantee quality water purification from the water supply, well or borehole. One of the modern complex systems are filters “Barrier”.

Chemical methods
To precipitate hardness salts, special reagents are added to the water – slaked lime, soda, polyphosphates. The method is effective for industrial use. Its main disadvantage is the need for further utilization of waste. Water after such treatment is unsuitable for food purposes.
Výměna iontů
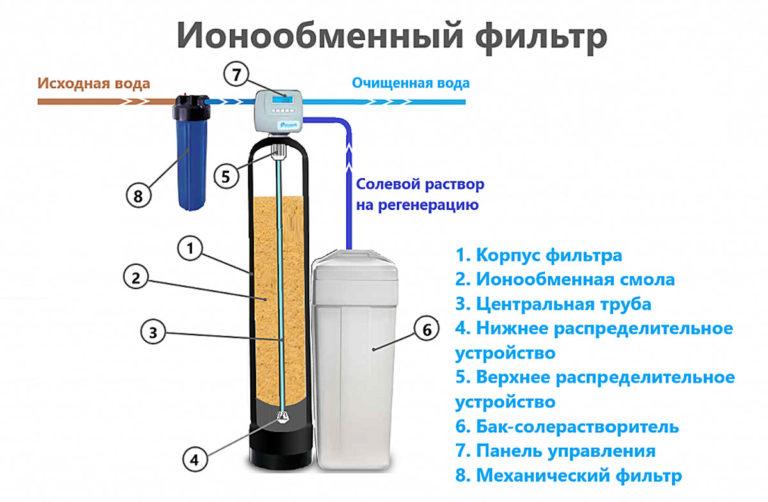
Filtration through ion exchange resins is successfully used in industry. The principle is based on the replacement of alkaline earth metal cations by sodium and hydrogen ions in a column with fine-grained backfill. A solution of table salt is used to regenerate the spent resin. If the water hardness level changes, manual adjustment of the settings is necessary.
Physical methods
These methods are based on the processes of electrodialysis, ultrasound action, electromagnetic pulses. Hardness salts are converted into a modified state in which they do not crystallize into a solid precipitate, but form unstable compounds. The use of ultrasonic and electromagnetic waves additionally promotes the detachment of already existing scale.
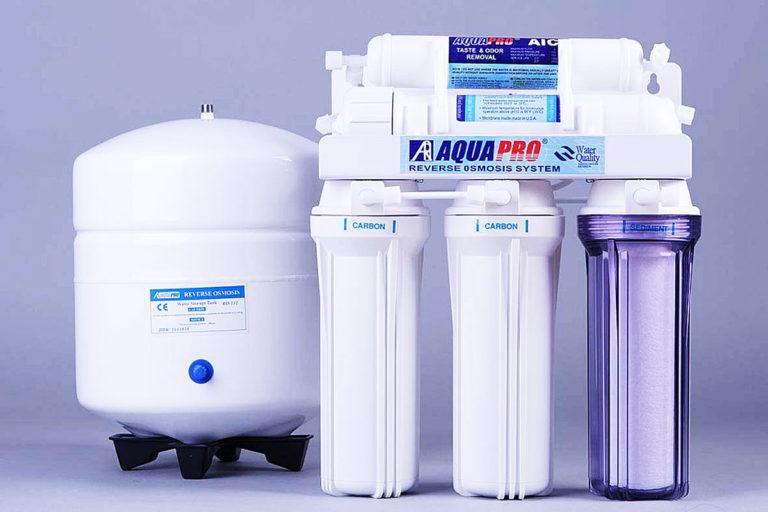
Membrane method
This method of purification has another name – reverse osmosis. Water under high pressure is passed through a filter with microscopic cells and is completely purified from chemical impurities, suspended particles, bacteria. The quality of the obtained water is close to distilled water. Additional mineralization is required for its use. The disadvantage of the method is its high cost.

Podtrženo, sečteno
When assessing the quality of water, it is important to consider not only the level of hardness and the likelihood of scale formation, but also the corrosivity. Proper assessment will allow you to choose an effective set of measures for water treatment.







Man, I didn’t know water hardness could mess with appliances! I once had scale buildup in my coffee maker and thought it was toast. After some research, I got a water softener, and now my machines run smooth. Good to know there are ways to tackle this!