It is well known that it is impossible to get a rich harvest without fertile soil. One of the ways to maintain the proper level of nutrients in the soil is the proper application of fertilizers. In this article we will consider the types of fertilizers, their classification, talk about their effect on plants, methods of application and much more.

Hardly any of the modern gardeners or gardeners have a question about what fertilizers are needed for. Without such fertilizers can not do without the care of indoor and garden flowers, or care for your own garden and vegetable garden, or large-scale cultivation of crops. Having an idea of the variety of fertilizers, their composition, you can easily orient yourself in the choice of a suitable fertilizer and improve crop performance.
Съдържание на статията
Why do you need to apply fertilizers
To begin with, let’s try to find out the physiological basis of fertilizer application. It is known that even the most fertile land is depleted over time, the content of nutrients in it decreases, and this invariably affects the quantity and quality of the harvest. In modern conditions there is no possibility to give the land time to rest, during which the lost balance of useful elements is restored. And why wait, because the market offers a wide range of fertilizers that act quickly and bring results. That is why the cultivation of any cultivated plants is difficult to imagine without fertilizers that stimulate their growth and development.
However, in this case it is necessary to adhere to the recommendations, since in the oversaturation of the soil with minerals is as little useful as in their deficiency. In addition to the annual crop rotation (successive change of crops in the same area), it is necessary to observe the timing of fertilizer application, the norms for dosage and the choice of a particular fertilizer for a particular type of plant.
Effect of fertilizers on plants
Trying to understand why it is necessary to constantly apply fertilizers to the soil, let us grasp the fact that fertilizers act in three directions:
- deliver one or more deficient elements needed for plant nutrition;
- form a favorable environment in the ground, which contributes to a better assimilation of useful substances;
- increase soil fertility.
Thanks to this multidirectional action, and it is possible to achieve the desired result – a rich harvest. Thus, the role of fertilizers in the life of plants is very great. It is fertilizers that supply the missing important macro- and microelements in addition to the vital ones – oxygen and carbon, which crops provide themselves independently from air and water.
When nutrients are absorbed from fertilizers, ionic exchange is triggered, as a result of which the lack of components necessary for growth and development is compensated.
Видове
There are several types of systematization of fertilizers on various grounds.
According to the method of production. Fertilizers for plants are divided into industrial and local.
- Industrial are produced at specialized enterprises as a result of chemical or mechanical processes.
- Local – these are fertilizers obtained directly in places of use (in gardens, farms or not far from them). We are talking about manure, slurry, composts, peat, ash, poultry manure, etc.
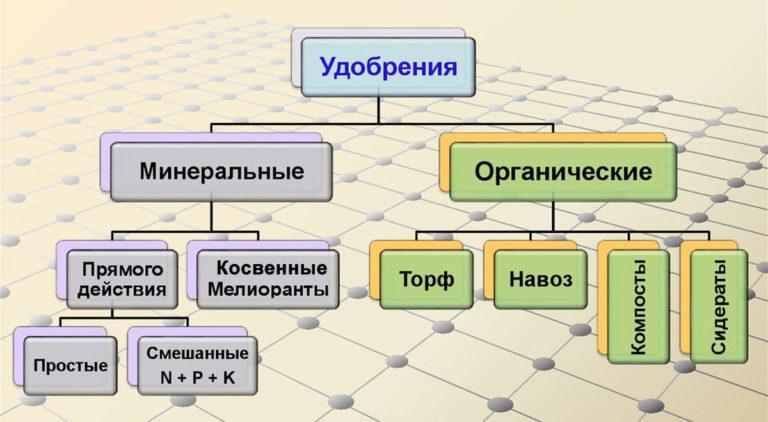
Chemical composition. There are organic and mineral fertilizers, bacterial, as well as growth stimulants. Growth stimulators, as a new type of fertilizer, are gaining popularity today, and we will consider their use in more detail below.
Organic

Organic fertilizers are the absolute leader in the content of nutrients vital for plants. The main source of their production is the natural processing of organic matter. Due to their natural origin and natural renewability, such fertilizers, having the most beneficial effect on the soil, are profitable in economic terms.
Organic fertilizers include:
- Manure. It is solid or liquid animal waste. Its nutritional characteristics depend on the type of animal, the quality of feed consumed by them, and the method of storage. Manure can be with or without bedding. The importance of this fertilizer with a high content of trace elements is enormous. The application of manure on a permanent basis is especially effective. In this case, the organic matter contained in it increases the humus content, improves the absorption capacity and buffering capacity of the soil.
- Peat is a plant mass formed under special conditions of high humidity and lack of air. There is a distinction between lowland peat, transitional peat and top peat, which are distinguished by different degrees of mineralization. Most often peat is used to create mixtures.
- Compost is a biological mass formed as a result of decomposition of organic residues under the action of temperature, bacteria and fungi. Composting reduces the loss of nutrients in the mass. Leaves, manure, sawdust and other organic residues decompose at an accelerated rate. The following types of compost are distinguished: peat compost, peat-peat, peat-peat, peat-peat, lignin and manure composts, and garden composts.
- Garden, mixed compost heap
- Compost
- Poultry manure (chicken, duck, goose) is a highly nutritious soil additive. This raw material can be dried and ground. Dry manure contains twice as many useful substances as fresh manure.
- Siderates – plants grown for the purpose of further incorporation into the soil. The method allows you to provide the soil with a full set of nutrients. Most often plow leguminous crops rich in nitrogen and other organic substances.
Inorganic
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers are produced chemically and do not have carbon in their basis. Such fertilizers contain compounds such as oxides, acids and salts. This type of fertilizer is single-component, containing one of the macro- or microelements and complex mixed, consisting of a combination of several substances. These preparations are produced in the form of liquids, suspensions or solid mixtures presented in the form of powders, granules or crystals.
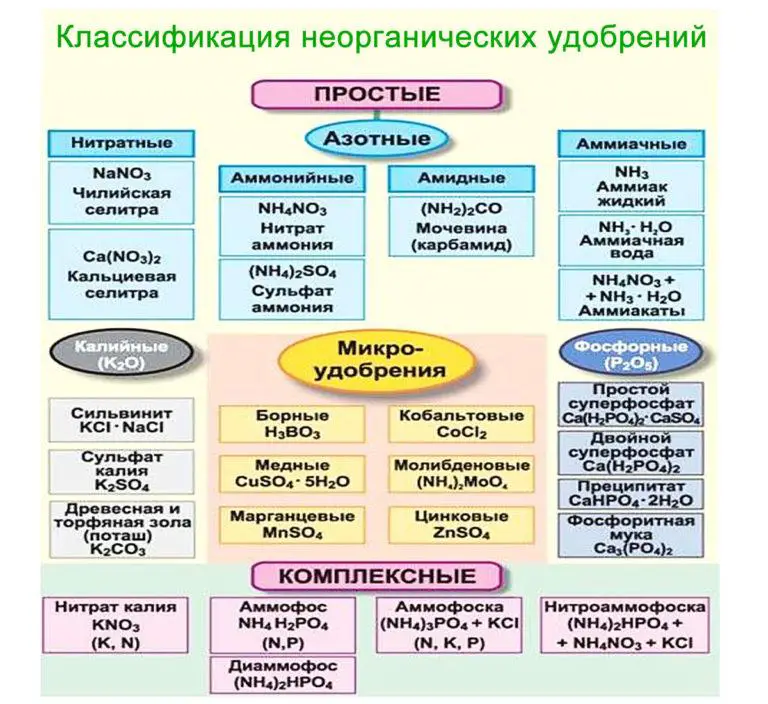
Mineral fertilizers include:
- Nitrogenous. Nitrogen is the most important element in the vital activity of plants, responsible for the assimilation of carbohydrates, accumulation of green mass, increasing yields. The most popular types of nitrogen fertilizers: nitrates, urea and cyanamides. Ammonium nitrate and sodium nitrate are nitrates, reduce the risk of fungal diseases, positively affecting fruiting, but are not recommended for use on alkaline soils. Urea (urea) contains up to 45% nitrogen in its composition and for best results is applied in the soil to avoid evaporation of nitrogen from contact with air. It is successfully used on all soil types and for the vast majority of crops. Calcium cyanamide is indicated for fertilizing alkaline soils. Moreover, nitrogen is not the main element here, but an auxiliary element that supports the action of calcium.
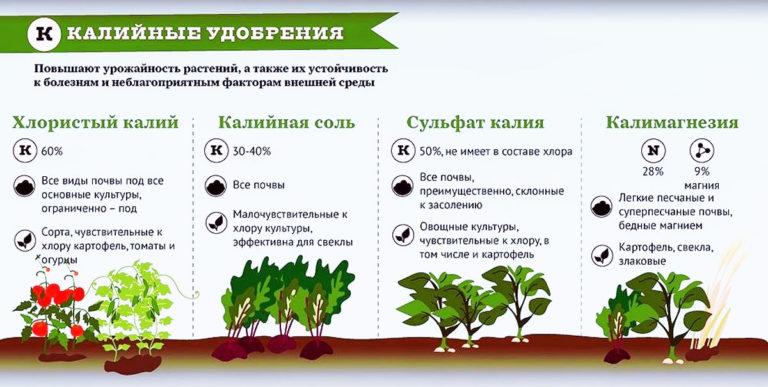
- Potash. This type of fertilizer is necessary to stimulate flowering and fruiting of plants. It supports their immunity and increases resistance to pests. This includes potassium compounds with inorganic substances. For example, potassium chloride is added to the soil before digging for the winter. In this case, chlorine is washed into deeper layers of the soil, and its negative effect is negated. Potassium sulfate is indispensable for many melon crops and is used during the fall digging or regular fertilizing. Potassium is also an integral part of complex fertilizers, such as nitrophosphate (a mixture of phosphate and ammonium nitrate), ammophos (potassium, magnesium, phosphorus) and the popular nitrophos (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium). The use of such combinations allows for more productive enrichment of the soil compared to simple fertilizers.
- Phosphorus. The main element of these fertilizers – phosphorus, is responsible for strengthening the root system and stems, increases resistance to disease, is indispensable for flowering and fruiting plants, improving the brightness of color. This type of fertilizer includes simple and double superphosphate, as well as phosphate flour. Simple superphosphate is a unique additive suitable for all plants and can be used on all soil types. Double superphosphate contains twice as much phosphorus as simple superphosphate. It is used when plants do not require any other elements besides phosphate. Phosphate meal works perfectly on acidic soils, improving immunity and resisting parasites.
- Microfertilizers are an important part of the plant care system. Microelements contained in these compositions – molybdenum, cobalt, zinc, iodine, manganese, copper, etc., provide a full balance of nutrients, being part of vitamins and participating in the formation of enzymes and photosynthesis. The peculiarity of these components is that, unlike macronutrients, they are required in much smaller quantities.
Bacterial
This includes fertilizers that do not contain any nutrients, but there are microorganisms that improve the quality of the soil. At the heart of this group of preparations – a certain pure culture of bacteria, multiplied and released in the form of peat or dry powder. The most popular now is considered to be a bacterial fertilizer “Nitragyn”, containing nodule bacteria found on the roots of leguminous plants.

Growth stimulators
This group of fertilizers includes preparations that improve plant development, leading to increased yields. This occurs by accelerating rooting, improving flowering, increasing ovaries and minimizing fruit drop. The use of growth stimulants provides a clear economic benefit, because the cost of their purchase is recouped many times over through a rich harvest. The most popular preparations that regulate plant growth are Kornevin, Micrassa, Root mixture, Sticks for indoor plants, Bison.
Methods of fertilizing the soil
By the nature of the impact on the soil, fertilizers are distinguished direct and indirect, can be applied simultaneously.
Direct method provides plant nutrition necessary – macro (nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus) and trace elements (molybdenum, zinc, bromine, etc.). Fertilizers can be applied into the soil directly to the root system or in close proximity to it on the surface.
Indirect fertilizers – improve soil properties. Chemical amelioration – gypsum, lime used to reduce increased soil acidity. Bacterial fertilizers that optimize biological processes in the soil.
Methods of fertilizer application
Root fertilization – a method in which the fertilizer is applied at the roots of the plant. It can be carried out superficially and intra-soil. At home, most often, fertilizer is poured on the ground around the roots or in specially made holes. This allows the fertilizer to get into the root system faster and provide the plant with the necessary nutrients.

The main components of root fertilization are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K), which are usually in the form of NPK combination fertilizers. In addition, the root fertilizer may contain trace elements such as iron, copper, manganese, and zinc, which are essential for plant health.
Root fertilizer can be organic or mineral fertilizer. Organic fertilizers are made from natural materials such as manure, humus, compost, bone meal and others. They release nutrients more slowly and can be less concentrated than mineral fertilizers. Inorganic fertilizers are made from synthetic materials with high concentrations of nutrients. Because they are more quickly absorbed by plants, they can be more economical.
Root fertilization is the most effective method of fertilizing plants because it allows nutrients to reach the root system quickly and provide the plant with the nutrients it needs. It can also help improve plant health, reduce the risk of disease and increase yields.
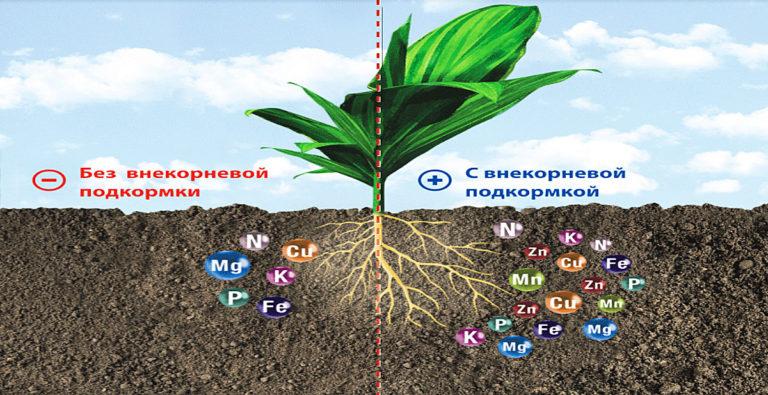
Rootless (foliar) feeding is a method in which fertilizer is applied to the leaves or stems of the plant. It can be used as a supplemental method when the plant needs extra nutrition, or as the main method of fertilization when the root system is damaged or ineffective.
Rootless fertilization can be organic or mineral. Organic foliar fertilizers usually contain plant extracts, whey, and other natural ingredients.
Mineral fertilizers contain synthetic ingredients:
- nitrate salts;
- potassium salts;
- phosphates.
The foliar method has several advantages. It allows fertilizer to enter the plant quickly through leaves, stems, and other surfaces, providing quick results. It can be useful when the root system is damaged. Just like root fertilization, foliar fertilization can help improve plant health, reduce disease risk and increase yields.
However, foliar cannot replace a full root application because it does not provide the plant with the nutrients it needs.

Rules for the use of fertilizers in the household
Even knowing what fertilizers to apply at planting, and what fertilizers to give preference to for regular application, you can make a mistake in some important nuances. Fertilizers need to be applied at a certain time.
- In the dormant period, lasting from November to March, indoor plants do not need fertilizer. But you should not wait until the moment when the heat starts, either. After all, then the plants are actively adapting to the new environmental conditions and forces to assimilate nutrients from fertilizers they do not remain.
- Cultures grown in the open ground, do not fertilize when the sun is at its zenith – this will lead to root burn. The optimal time for fertilizing in this case is cloudy weather or early morning.
- Fertilization of garden crops is not made during the period of disease or parasite attack. To begin with, it is recommended to get rid of the existing problem.
- Plants are not fed on dry soil, this causes root burns.
- It is necessary to comply with the recommended dosage and be sure to monitor the expiration date of fertilizers indicated on the package.
| Fertilizer | Application date |
|---|---|
| Urea | Early spring. Beginning of the growing season. Lack of nitrogen in plant tissues. |
| Ammonium nitrate | Early spring. Beginning of the growing season. Nitrogen deficiency in plant tissues. |
| Superphosphate | Add to the diet of plants during budding, flowering and fruiting. |
| Potassium sulphate | Add to the diet of plants during budding, flowering and fruiting. |
| Nitrofoska | Application during the whole period of cultivation of crops at intervals of at least 3 weeks. |
| Azofoska | Application at least 3 weeks apart during the entire crop growing period. |
| Nitroammophoska | Application at least 3 weeks apart throughout the crop growing period. |
| Cowslip | When preparing beds for planting. In summer as a complex remedy. In spring, scatter over the vegetable garden. |
| Poultry manure | When preparing beds for planting. In summer as a complex remedy. In spring scatter over the vegetable garden. |
| Ash (dry) | Application during the entire period of cultivation of crops at intervals of at least 3 weeks. |
| Ash infusion | Apply at least 3 weeks apart during the entire crop growing period. |
| Yeast solution | Application after transplanting seedlings into the open ground or greenhouse. The optimal time is 4-5 days after the introduction of organic matter. |
| Banana peel | Application during the whole period of cultivation of crops with an interval of at least 3 weeks. |
| Onion peel | Apply at least 3 weeks apart during the entire crop growing period. |
Benefits and harms
Fertilizers have become an integral part of modern agriculture. They increase soil fertility, which increases crop yields. However, in addition to their advantages, fertilizers also have some disadvantages.
Many people believe that the use of mineral fertilizers makes vegetables or fruits dangerous for human consumption. This stereotype may be partially true, but not because the chemically created additives are harmful, but because of the excess application rate to the soil.
On a side note. The difference between organic fertilizers and mineral fertilizers is in the speed of their assimilation by plants.
Organics are assimilated by plants slowly, and since mineral compositions have a ready form, they are assimilated immediately after application. Therefore, if you put into the soil an excess of such fertilizers, and did not observe the norm, it leads to an increase in their content in plants. The most common example is nitrates in vegetables.
Harm
It is also worth noting that the use of fertilizers can affect the quality of the grown crop. The carbohydrate content of the plants may decrease, while the amount of crude protein, on the contrary, may increase. In potatoes, for example, the starch content may decrease and in cereals the amino acid composition may change.
One of the main disadvantages is provoking leaching of trace elements such as calcium, magnesium, zinc, copper, manganese from the soil. This can affect the processes of photosynthesis, as well as reduce the resistance of plants to diseases.
Excess fertilizer can lead to soil compaction, increased acidity, groundwater contamination, etc.
Benefits
Despite the above disadvantages, fertilizers also have many advantages. They can significantly increase the yield of crops, improve their appearance and characteristics, as well as make plants more resistant to various pests and diseases.
Thus, it is necessary to apply fertilizers taking into account their benefits and harms in order to achieve maximum effect and preserve the quality of crops.
Safety precautions when working with fertilizers
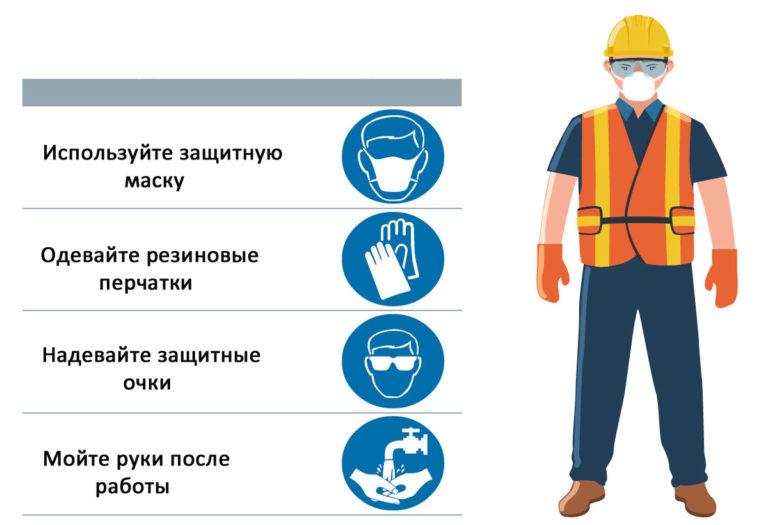
Observe the following safety precautions when handling fertilizers:
- Wear protective clothing including rubber gloves, safety glasses and face mask.
- Avoid contact of fertilizer with skin and eyes. If contact does occur, immediately flush affected areas with water and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Store fertilizers in a separate, closed room, away from children and animals.
- Use fertilizers only for their intended purpose and in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Do not repackage or mix different types of fertilizers without necessary care.
- Wash hands thoroughly and remove protective clothing after finishing work.
- Do not store fertilizers near flammable substances.
- When storing fertilizers, keep an eye on the expiration date and do not use expired products.
Заключение
Experienced agrarians and gardeners confirm that the use of fertilizers can significantly improve the quality and appearance of agricultural products, as well as positively affect the condition of the soil. If it is not possible to purchase ready-made means, then prepare them yourself.
There are many different fertilizers and forms of feeding, allowing you to choose the best solution for specific crops and season. The final choice is left to each gardener. The right choice of fertilizers guarantees a rich and high-quality harvest.
To understand fertilizers, with a serious approach to the matter, is not so difficult. In conclusion, watch the video with an explanation of the expert about the types of existing fertilizers and their use:








I remember when I first tried organic fertilizer in my garden. It really boosted my plants! Just had to make sure not to overdo it. Balancing is key, right? I learned that using the right method makes a big difference. Definitely worth the effort!