Polycarbonate greenhouses in the trade network are widely represented – for every taste and size. But many people prefer to make them themselves. Because the greenhouse of polycarbonate with their own hands turns out to be many times stronger and more reliable. At the same time, the costs are less or the same.
Съдържание на статията
How to choose a design
If you decide to build a greenhouse from polycarbonate with your own hands, it is desirable to choose a design that allows you to use the main advantage of this material – its ability to bend. These are two types with curved roofs with supports in the form of arcs.
In one design, the arcs come from the ground itself. If they are bent in the form of a radius, a lot of area is lost at the edges, since it is very inconvenient to work there because of the small height.
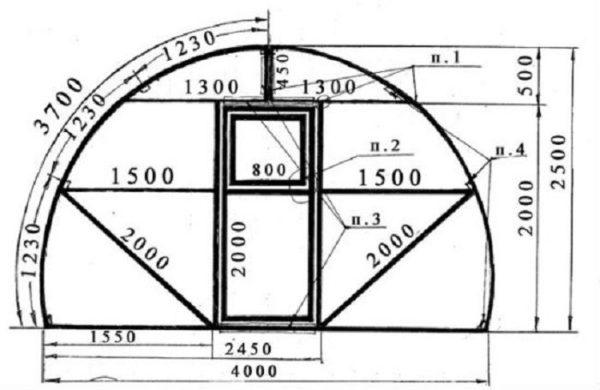
Solves this problem another design – with a composite frame, welded from several pieces. From the ground / from the base come straight posts, which are raised to a height of at least one and a half meters. An arc is welded to them. With this arrangement, the roof is rounded and the walls are straight. Even along the walls you can work without problems, straightening up to your full height.
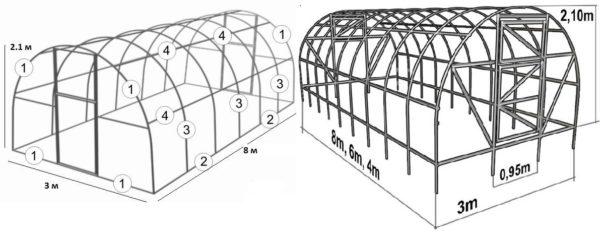
But the rounded roof of the greenhouse has a few disadvantages. First – it is more difficult in it than in a straight one, to make outlets for ventilation. You can solve the problem if you make fanlights in the walls, not in the roof. The second disadvantage of a rounded roof in a polycarbonate greenhouse – snow from it comes down worse than from flat sloping surfaces. If you live in a region with snowy winters, or have to make reinforced trusses, or the roof to make a pitched – with one or two slopes.
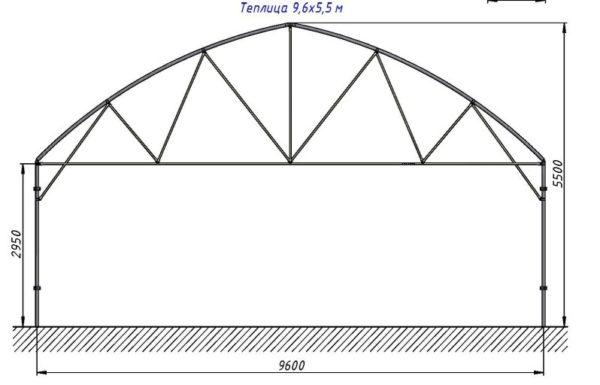
There is a third solution – to make a rounded part of the roof from two arcs welded at an angle, which forms a kind of ridge. With this structure, the snow comes down well and the ridge can be protected with a wide strip of metal. This will improve the descent of snow, and protect the joint from leaks.
Polycarbonate greenhouse with their own hands: material for the frame
The choice of materials for the frame is not very large. Will fit profiled (rectangular) pipes, metal angle and wooden beam. Also use galvanized profiles for drywall.
Wood
Beam is used for small greenhouses, and the design is chosen with a single or double-pitched roof, since it is difficult and time-consuming to bend arcs of wood. The cross-section of the bar depends on the size of the greenhouse and snow/wind loads in the region. The most popular size is 50*50 mm. Such supports are put in the Middle Belt. For greater reliability, the corner posts can be made of a bar of 100*100 mm.
And, to save money, you can not buy a bar, but make a composite – from boards. Take two boards 50 mm wide and 25 mm thick, three boards 15 mm thick. They are folded, nailed together on both sides. The resulting posts are stronger, better tolerate loads, less prone to torsion, as the wood fibers are directed in different directions.
If you build a greenhouse made of polycarbonate with your own hands on a wooden frame, all boards / timber should be treated / impregnated with antiseptics, and such that are designed for the street. The ends that are buried in the ground, treat with compositions for direct contact with the ground. Without such treatment, the wood, firstly, will quickly deteriorate, and secondly, may become a source of plant diseases.
When connecting the posts to the strapping (bottom bar) for greater rigidity and reliability, use steel reinforced mounting angles. They are available in construction stores. To increase the load-bearing capacity of the roof, install additional crosspieces.
Read more about gable roofs here, and about single-pitched roofs here.
Profiled pipes and steel angles
Most of the frames of polycarbonate greenhouses are made of profiled pipe. If there is a welding machine, skills to work with it, it is not difficult to do everything yourself – to weld a square or rectangle is easier than round pipes. Another plus – with the help of a pipe bender it is not difficult to make arcs yourself.
- Profile pipe is good because it has a high rigidity, but it can be bent into an arc
- Such a greenhouse is not afraid even of heavy snowfalls
- Thin-walled pipes, even with doubled arches, often do not survive the winter.
- Large-section posts are interspersed with smaller ones.
The cross-section again depends on the size and natural conditions. Most often they are made of rectangular pipe 20*40 mm. But variants are also possible. For that material, such a parameter as wall thickness is also important. It is desirable that the metal was 2-3 mm. Such a frame endures significant loads.
Steel angle is also a good option, but to bend it – a difficult task, so collect greenhouses in the form of a house – with gable or single-pitched roofs. The size of the shelves – 20-30 mm, the thickness of the metal – from 2 mm.
Galvanized profiles
Polycarbonate greenhouse with its own hands with a framework of profiles – the most unreliable option. It is good in areas with low-snow winters, and even without strong winds. The plus side of this option is that no welding is needed. And the disadvantage – not the greatest load-bearing capacity.
- Try to make the connections as securely as possible
- One of the frames
- Chocks and stops are not superfluous.
The technology used is standard – as for the device of walls and partitions from gypsum board. The only difference is that the frame is covered on one side and attached polycarbonate. It is desirable to make the posts double – splicing two bearing profiles, turning them “back to back” and twisted with self-tapping screws. For greater rigidity of the frame, make tapers, connecting sloping crosspieces neighboring posts. It is desirable to make a pitched roof, not rounded, trusses to strengthen.
Foundation
If you wonder whether or not you need a foundation for a polycarbonate greenhouse, the answer is the same – you need one. And reliable. Very well they fly. Therefore, the foundation should well “anchor” the building.

Tape type
This foundation is for buildings that are planned for more than one year. The most expensive, but also the most thorough option. If it is planned to use the greenhouse all year round, the foundation is made buried – to a depth just below the soil freezing. For seasonal use is suitable concrete and brick or simply from a bar.

Concrete-brick (concrete-brick).
Most often make a concrete-brick option. It is optimal in terms of costs, complexity and duration. Works are carried out in this way:
There are variants of this type of foundation. You can install foundation concrete blocks of small sizes in the prepared trench, the space between them is filled with mortar. They should be installed so that their edge was below the ground level. A layer of concrete is poured on top and leveled. Bookmarks are fixed in the joints.
Empty bottles can be used as a construction material. They are laid in rows, poured with concrete. A very economical and warm foundation is obtained. Its bearing capacity is quite enough for a more serious building.
Brus foundation for a polycarbonate greenhouse
This option is suitable as a temporary solution – it can serve two or three years. This depends on the humidity on the site, the quality of wood and processing. The timber is used with a large cross-section – 100 * 100 or more (you can make a composite, from several boards). It is treated with compositions for wood in contact with the ground. The order of work is as follows:
- Mark the site, dig a trench. Its dimensions should be 7-10 cm deeper and wider than the used bar.
- The bottom and walls are covered with roll waterproofing material (it is better to use “Hydroisol”, it will be enough for a longer period of time).
- Lay the treated timber, connect it in the corners.
- Waterproofing is wrapped around the bar.
- With the help of corners hammered in from both sides, the bar is fixed in place.
- The free space left between the waterproofing and the trench walls is filled with crushed stone if the ground is bubbling and with excavated earth if it is not. The soil is well compacted.
- Next, the strapping timber is attached to this bar. Between them it is worth laying another layer of waterproofing.
This option is suitable only for dry areas with a low location of groundwater. In this case, you can hope that the foundation will live at least a few years.
Pile and bedrock
Another type of foundation that will not protect from frost. But it is reliable and will serve for a long time. Read here for a full description of the technology of making a pile-rostver foundation, and we will give a short list of works.
Next, you can attach the strapping, and you can add a couple of rows of bricks and only after that install the frame. After this we can say that the greenhouse from polycarbonate with their own hands is almost ready. It remains to fix the polycarbonate.
What polycarbonate to choose
How long the polycarbonate greenhouse will last, bought or built with your own hands, how well it will “work”, depends on the parameters and quality of polycarbonate. To his choice should be treated responsibly – the amount is not insignificant.

Types of polycarbonate
There are three types of this material:
- Monolithic. In appearance similar to glass, but better transmits light, two to four times lighter, many times (and 100-200) stronger. Thickness – from 0.75 mm to 40 mm. Disadvantage – high price. Apply this material if there is a risk of damage – often hail, the greenhouse stands so that icicles can fall on it, snow can come down. There is a multilayer monolithic polycarbonate. Sheets can be up to 3-5 pieces, they can have different properties. For example, for greenhouses is usually used double – the first layer is characterized by increased strength, the second – does not pass ultraviolet.
- Fluted (profiled). Appeared relatively recently. It is formed from a monolithic sheet, on which the relief is formed. There are types similar to corrugated steel, slate. The thickness of this type of polycarbonate is 0,8-1,2 mm. With such a small thickness, it withstands hail strikes up to 20 mm in diameter, bends well, normally tolerates frosts up to -50 ° C.
- Cellular (honeycomb, structured). Consists of two (or more) sheets of polycarbonate, connected by lintels. The shape, size, thickness of the lintels – all this affects the qualities and performance characteristics. The thickness of cellular polycarbonate – 4, 6, 8, 10, 16, 20, 24 and 32 mm. For greenhouses, it is better to take no thinner than 10 mm, multilayer.
What kind of polycarbonate is better to use for the construction of greenhouses? Depends on the mode of operation of the greenhouse. If it will be heated, you need honeycomb. If it is a variant exclusively for the warm season, more suitable fluted (or monolithic). Monolithic is also not bad, but corrugated has greater rigidity. For greenhouses that are planned to be used from early spring or throughout the winter, put honeycomb polycarbonate. Due to its structure, it has bol% vs. its high thermal insulation characteristics – better retains heat, although worse transmits light (86% vs. 95%).
Choosing cellular polycarbonate
It is not difficult to choose fluted or monolithic – we are guided by the stated characteristics. It is important only that there was protection from ultraviolet light. There are no other pitfalls. But with cellular there are many nuances. It is necessary to pay attention to the following:
The easiest way to check the quality of cellular polycarbonate is to try to squeeze it between your fingers. If it is not squeezed, even if you make a significant effort – you can take. If squeezed easily – look for another.
Peculiarities of installation
According to the technology, polycarbonate is mounted with the help of starting and connecting profiles. First, profiles are installed on the frame, a sheet of cellular polycarbonate is inserted into them, which is fixed to self-tapping screws with special press washers, which at the same time protect the place of attachment from leaks. Profiles, in addition to holding in place the sheets, also protect the cuts from getting into the bottom of dust, dirt. The system has a neat look, works well, but all the components cost a decent amount of money.
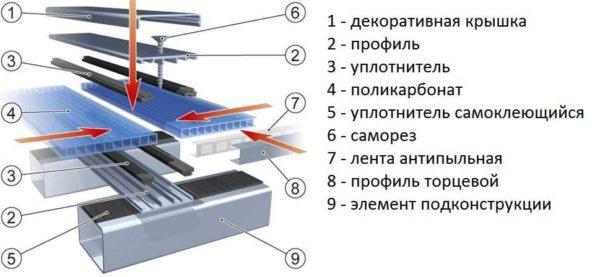
Aesthetics for a greenhouse – not the most necessary property, therefore, if you need to save money, prefer to fasten in a simple way, without profiles and press washers. This is how they do it:
This is what concerns the direct attachment of cellular polycarbonate. There is another point, which became clear in the process of operation of greenhouses made of polycarbonate. Polycarbonate should not be located close to the ground. It is desirable that it starts at least half a meter from the surface. Why? Because firstly, it is still contaminated and through it almost no light passes, so it does not affect the overall illumination. Secondly, it starts to deteriorate – blackening, delaminating. It is not clear what causes this reaction, but it is common. So developing a layout of a polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands, provide for half-meter walls of other material – brick, building blocks. It does not matter.