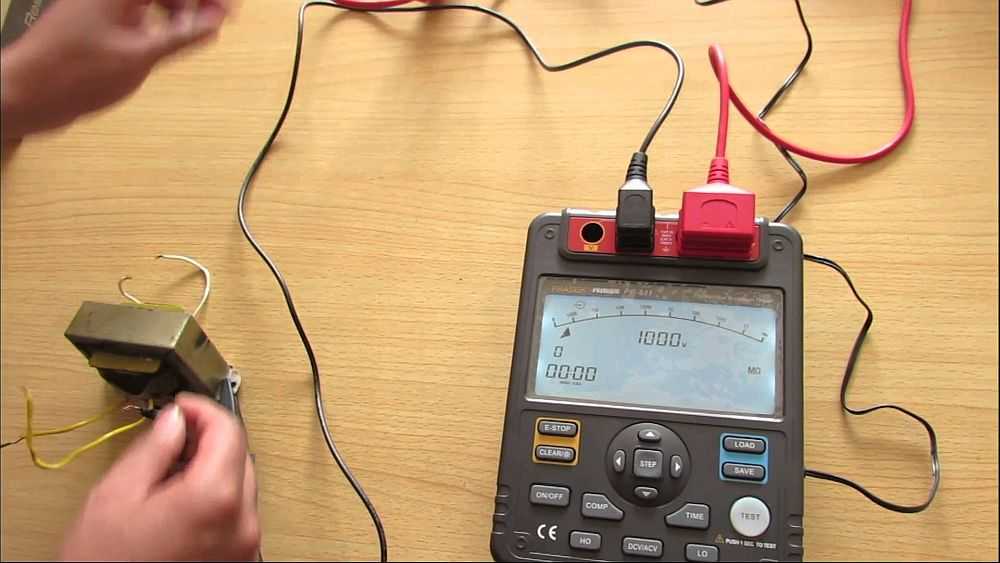
To assess the performance of the cable, wiring, it is necessary to measure the insulation resistance. There is a special device for this purpose – megaohmmeter. It supplies the measured circuit with high voltage, measures the current flowing through it, and displays the results on the screen or scale. How to use a megaohmmeter and consider in this article.
Contenuto dell'articolo
Dispositivo e principio di funzionamento
Megaohmmeter is a device for checking insulation resistance. There are two types of devices – electronic and arrow. Regardless of the type, any megaohmmeter consists of:
In pointer devices, the voltage is generated by a dynamo built into the housing. It is driven by the meter – he turns the knob of the device with a certain frequency (2 revolutions per second). Electronic models take power from the mains, but can also work from batteries.
The operation of a megaohmmeter is based on Ohm’s law: I=U/R. The device measures the current that flows between two connected objects (two cable cores, core-to-ground, etc.). Measurements are made with a calibrated voltage, the value of which is known, knowing the current and voltage, you can find the resistance: R=U/I, which is what the device does.
Before testing, the probes are placed in the appropriate sockets on the instrument and then connected to the object of measurement. During testing, a high voltage is generated in the instrument, which is transmitted to the object under test using the probes. The measurement results are displayed in mega ohms (MOhm) on the scale or screen.
Operating the megohmmeter
During testing, the mega ohmmeter produces very high voltages – 500 V, 1000 V, 2500 V. Due to this fact it is necessary to carry out measurements very carefully. At the enterprises to work with the device are allowed persons who have electrical safety group not lower than the 3rd.
Before making measurements with a megaohmmeter, the circuits to be tested are disconnected from the power supply. If you are going to check the condition of the wiring in the house or apartment, it is necessary to disconnect the switches on the switchboard or unscrew the plugs. After turning off all semiconductor devices.

If you check the socket groups, you remove the plugs of all the devices that are included in them. If you check lighting circuits, unscrew the bulbs. They will not withstand the test voltage. When checking the insulation of motors, they are also completely disconnected from the power supply. After that, grounding is connected to the circuits under test. For this purpose, a multi-core wire in a sheath with a cross-section of at least 1.5 mm2 is attached to the “ground” busbar. This is the so-called portable grounding. For safer work, the free end with a bare conductor is attached to a dry wooden holder. But the bare end of the conductor must be accessible – so that it is possible to touch wires and cables with it.
Requirements for safe working conditions
Even if you want to measure the insulation resistance of a cable at home, before using a megaohmmeter it is worthwhile to familiarize yourself with the safety requirements. The basic rules are several:
- Hold the probes only by the insulated and limited by the stops.
- Before connecting the device, disconnect the voltage, make sure that there are no people nearby (throughout the measured route, if it is a cable).
- Before connecting the probes, remove residual voltage by connecting a portable earth connection. And disconnect it after the probes have been installed.
- After each measurement, remove residual voltage from the probes by connecting their bare parts together.
- After the measurement, connect the portable earth to the measured core, removing any residual charge.
- Work with gloves.
The rules are not very complicated, but your safety depends on their fulfillment.
How to connect the probes
There are usually three probe sockets on the instrument. They are located at the top of the instruments and are signed:
- E- shield;
- L – line;
- Z – ground;
There are also three probes, one of which has two tips on one side. It is used when it is necessary to exclude leakage currents and is attached to the cable shield (if there is one). There is an “E” on the double lug of this probe. The plug that comes from this branch is installed in the corresponding socket. Its second plug is installed in the socket “L” – line. A single probe is always connected to the “ground” socket.
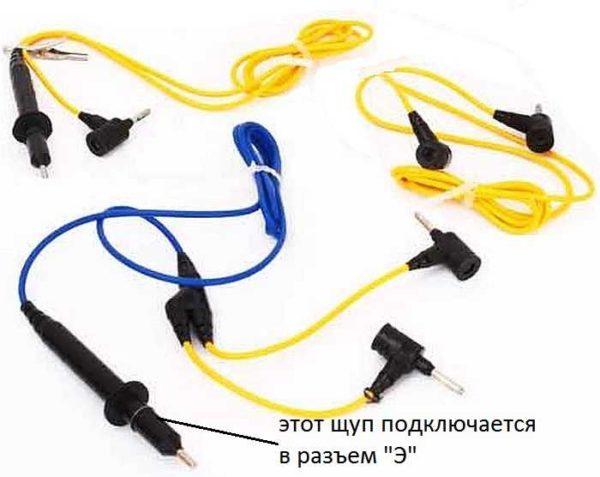

There are stops on the probes. When measuring with your hands, hold them in such a way that your fingers reach these stops. This is a prerequisite for safe operation (remember about high voltage).
If it is necessary to check only the insulation resistance without shielding, two single probes are placed – one in the “Z” terminal and the other in the “L” terminal. Using the crocodile clips on the ends connect the probes:
There are no other combinations. Checked more often insulation and its breakdown, work with the screen is quite rare, as the shielded cables themselves in apartments and private homes are rarely used. Actually, it is not very difficult to use a megaohmmeter. It is only important not to forget about the presence of high voltage and the need to remove the residual charge after each measurement. This is done by touching the ground wire to the newly measured wire. For safety, this wire can be attached to a dry wooden holder.
Measurement process
Set the voltage that the megaohmmeter will output. It is not chosen arbitrarily, but from a table. There are megaohmmeters that work with only one voltage, there are those that work with several. The latter, of course, are more convenient, since they can be used to test various devices and circuits. Switching the test voltage is done by a knob or button on the front panel of the device.
| Element name | Voltage of megaohmmeter | Minimum permissible insulation resistance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical products and apparatuses with voltage up to 50 V | 100 В | Must correspond to the nameplate resistance, but not less than 0.5 megohms. | During measurements semiconductor devices must be shunted |
| same, but with voltage from 50 V to 100 V | 250 В | ||
| same, but with voltage from 100 V to 380 V | 500-1000 В | ||
| above 380 V, but not more than 1000 V | 1000-2500 В | ||
| Switchgears, panels, current conductors | 1000-2500 В | At least 1 megohm | Measure each section of switchgear |
| Electrical wiring, including lighting network | 1000 В | At least 0.5 megohms | In hazardous premises measurements should be made once a year, in other premises – every 3 years. |
| Stationary electric stoves | 1000 В | Not less than 1 megohm | Measurement is carried out on a heated, disconnected stove at least once a year. |
Before using the megaohmmeter, make sure that there is no voltage on the line – with a tester or indicator screwdriver. Then, having prepared the device (set the voltage and on the arrow scale of measurement) and connecting the probes, remove the grounding from the tested cable (if you remember, it is connected before starting work).
The next step is to put the megaohmmeter into operation: on electronic meters we press the Test button, in arrow meters we turn the dynamo knob. In the arrow ones we turn it until the lamp on the case lights up – this means that the necessary voltage in the circuit is created. In digital ones, at some point the value on the screen stabilizes. The numbers on the screen are the insulation resistance. If it is not less than the norm (the average ones are listed in the table, and the exact ones are in the passport to the product), then everything is normal.

After the measurement is over, stop turning the knob of the megaohmmeter or press the end of measurement button on the electronic model. After that, you can disconnect the probe, remove the residual voltage.
In brief, these are all the rules of using a megaohmmeter. Some measurement options will be considered in more detail.
Measuring cable insulation resistance
It is often necessary to measure the insulation resistance of a cable or wire. If you know how to use a megaohmmeter, when checking a single-core cable, it will take no more than a minute, with multicore ones you will have to deal with longer. The exact time depends on the number of cores – you will have to check each one.
Test voltage you choose depending on the voltage of the network with which the wire will work. If you plan to use it for wiring at 250 or 380 V, you can set 1000 V (see table).
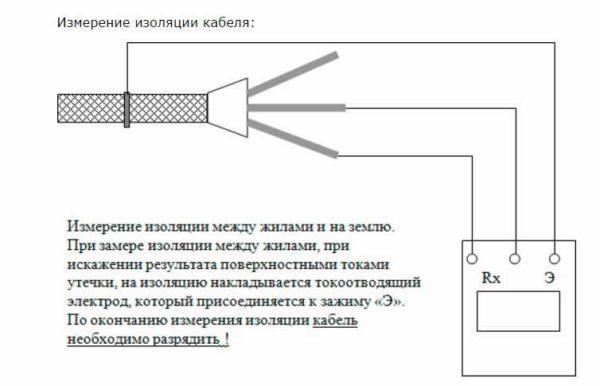
To check the insulation resistance of a single-core cable, one probe is connected to the core, the second – to the armor, apply voltage. If there is no armor, the second probe is attached to the “earth” terminal and also apply test voltage. Look at the readings. If the arrow shows more than 0.5 megohms, everything is normal, the wire can be used. If less – the insulation is broken and it can not be used.
You can test a multi-core cable. Testing is carried out for each conductor separately. All other conductors are twisted into one bundle. If it is necessary to check the breakdown to the “ground”, a wire connected to the corresponding bus is added to the common bundle.
If the cable has a shield, metal sheath or armor, they are also added to the harness. When forming the harness, it is important to ensure good contact.
Measurement of the insulation resistance of socket groups is carried out in the same way. All appliances are switched off from the sockets, and the power is turned off at the switchboard. One probe is installed on the ground terminal, the second – in one of the phases. The test voltage is 1000 V (according to the table). Turn on, check. If the measured resistance is greater than 0.5 megohms, the wiring is normal. Repeat with the second core.
If the wiring is old – there are only phase and zero, testing is carried out between the two conductors. The parameters are similar.
Check the insulation resistance of the electric motor
To carry out measurements, the motor is disconnected from the power supply. It is necessary to get to the winding leads. Asynchronous motors operating at voltages up to 1000 V are tested with a voltage of 500 V.
To check their insulation, one probe is connected to the motor housing, the second is applied to each of the terminals in turn. It is also possible to check the integrity of the winding connection between each other. For this check, the probes should be placed on the winding pairs.