The electricity supplied to our homes is not stable. If the frequency is still more or less stable, the voltage fluctuates over a considerable range. The only thing that can be done with this is to put a voltage stabilizer for the house.
A cikk tartalma
Selection by technical characteristics
When choosing a stabilizer, first decide whether you will put it on the whole house / apartment or on a certain device (group of devices). Ideally, when there are problems with voltage, it is better to put a voltage stabilizer for the house at the input, so that all devices were guaranteed normal voltage. But such equipment costs quite a lot of money – at least $500. So the costs are not insignificant. This approach is justified if the throws are significant, then this is the best way out, as the equipment can fail.

If the voltage fluctuates within small limits and most of the equipment works normally, and there are problems only in some part of the more sensitive equipment, it makes sense to put local stabilizers – on specific lines or on individual devices.
By number of phases
Power in the house can be single-phase or three-phase. With single-phase 220 volt networks, everything is clear: you need a single-phase stabilizer. If the house has three phases, there are options:
It is not difficult to choose a voltage stabilizer for a house or dacha on this principle. But it is absolutely necessary to determine.
Choosing the power
Choosing a voltage stabilizer for the house, first you need to calculate its power. The easiest way to determine it is to determine it by the automat, standing in the electrical panel of the house. For example, the input circuit breaker is 40 A. Calculate the power: 40 A * 220 V = 8.8 kW. To ensure that the unit does not work at the limit of possibilities, take a power reserve of 20-30%. For this case, 10-11 KW will be enough.
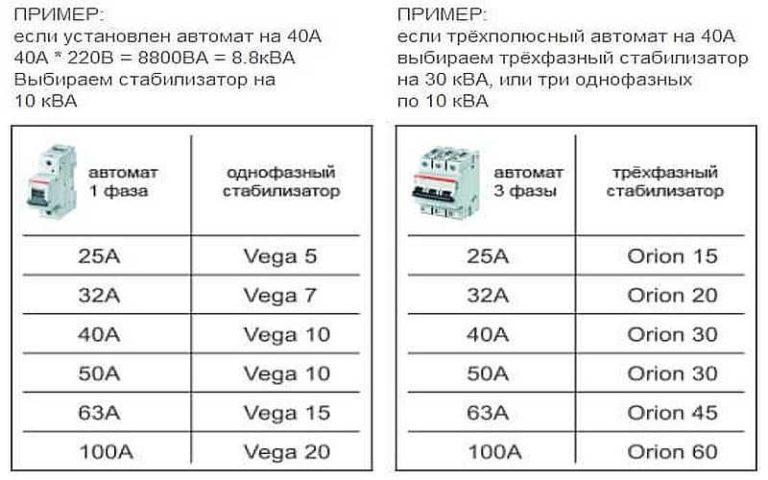
The power of a local stabilizer installed on a separate device is also calculated. In the calculation we take the maximum current consumption indicated in the characteristics. For example, it is 2.5 A. Then count according to the algorithm described above. But if the equipment has a motor (refrigerator, for example), it is necessary to take into account the inrush currents, which are many times higher than the normative ones. In this case, the calculated parameters are multiplied by 2 or 3.
When selecting the capacity, do not confuse kVA with kW. In short, 10 kVA, when there are capacitances and inductances on the load, is not equal to 10 kW. The figure of the real load is less, and how much less – depends on the inductance factor (may also be in the characteristics). For a particular device to calculate everything is simple – you need to multiply by the coefficient, but for the network is more complicated. Just when you see the figure in kVA, take a reserve of about 15-20%. This is approximately the average reactive component.
Stabilization accuracy
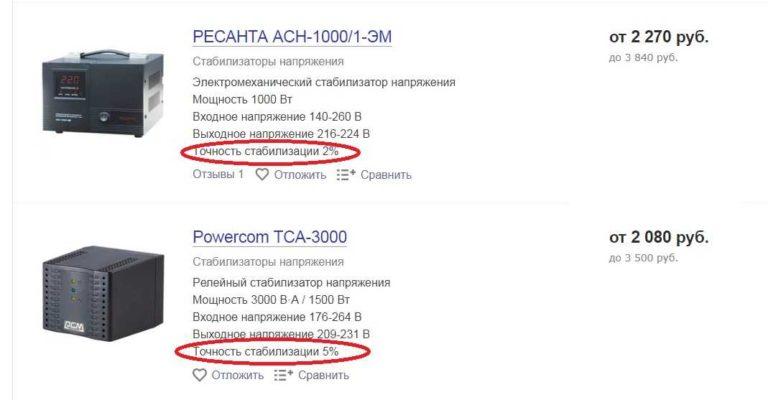
Stabilization accuracy shows how even the output voltage will be. An acceptable level is considered to be 5%. With such a tolerance, domestic equipment works normally, but for imported equipment it is necessary to better stabilize the voltage. So, all stabilizers that have an accuracy of less than 5% – it’s great, everything that is worse is better not to buy.
Input voltage range: limiting and operating range
There are two lines in the characteristics: the limiting range of input voltage and the operating range. These are two different characteristics, reflecting different parameters of the device. The limit range is the upper and lower voltage level at which the device will remain functional.
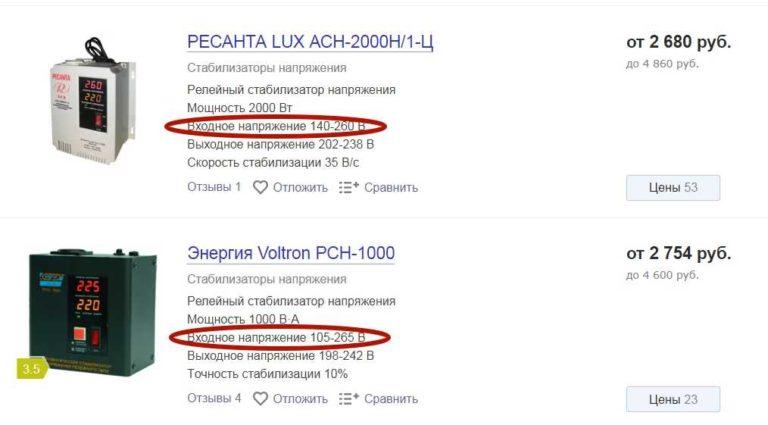
The operating range of the input voltage is the range at which the device should produce the declared parameters (with the same stabilization accuracy).
Load and overload capacity
A very important characteristic that you should pay attention to. Load capacity shows what load can “pull” the voltage stabilizer for the home when working at the lower limit. There are such models that give out the declared power at 220 V. That is, when it is not needed at all. But at the lower limit of 160 V can work only with a half load. The result – working at low voltage, the device can burn out.

The overload capacity is equally important. It shows how long it can work with excessive load. This parameter is important even if you have taken the equipment with a good power reserve. By this parameter you can indirectly determine the quality of parts and the quality of assembly. The higher the overload capacity, the more reliable the equipment.
Types, pros, cons
Voltage stabilizers are of different types, make them from components of different types – electromechanical, electronic. Some of them have electromechanical control, some of them – electronic. To properly select the equipment, you need to have an idea of the advantages and disadvantages.

Electronic (triac)
They are assembled on triacs or thermistors. They have several stages of regulation, which are connected/disconnected depending on the input voltage. Switching can be done by means of an electronic key (works silently, but these are more expensive models) or electronic relay (when triggered there is a sound).
The advantages of electronic stabilizers include high speed of reaction (the time of switching on one stage is about 20 msec). Electronic keys actuate very quickly, connecting the desired number of correction stages or disconnecting them. The second positive point is quiet operation.
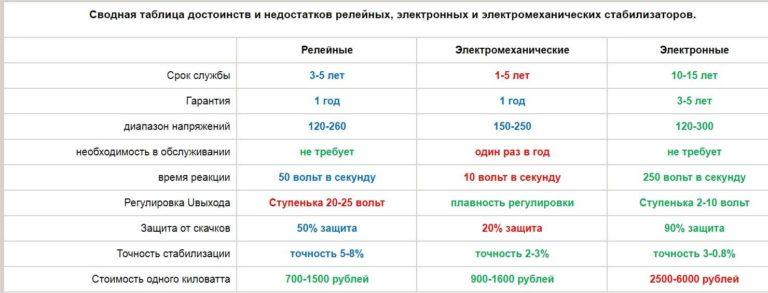
The minuses are also there. The first is the low accuracy of stabilization. In this category, you will not find models that produce voltage with an error of less than 2-3%. This is simply impossible, since the adjustment is stepwise and the error is quite high. The second disadvantage is the high price. Simistors cost a lot, and there are as many of them as there are stages. That is, the more steps and higher the accuracy of regulation, the more expensive the equipment will be.
Electromechanical
Assembled on the basis of an adjustable autotransformer. The position of the slider is changed manually using a relay or motor. The plus side of the electromechanical stabilizer is a low price and high accuracy of stabilization. The disadvantage is low performance – the parameters change slowly. The second disadvantage is rather loud operation.
Apparatuses with a motor work quieter, but the adjustment is slow. The average reaction time is 20 V in 0.5 seconds. With sharp spikes, the device simply does not have time to change the voltage. There is another trouble with stabilizers of this type – overvoltage. It occurs in the situation when the previously dropped voltage suddenly comes to normal. Stabilizer does not have time to react, as a result, the output can have a jump to 260 V, and this is disastrous for technology. To avoid this situation, at the output put a voltage protection, cutting off the power supply.
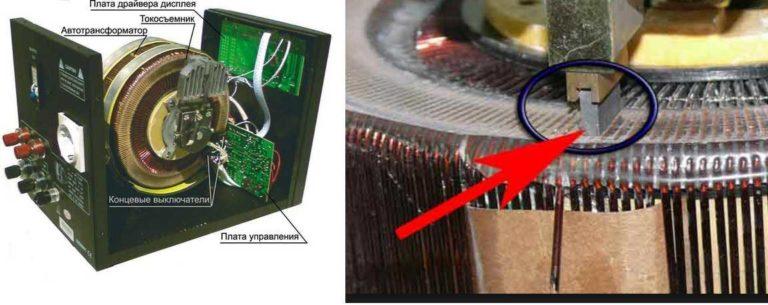
If the electromechanical voltage stabilizer for the house is assembled on the basis of a relay, the response time is shorter, but when working they are noisy, and the adjustment is not smooth, but stepwise. This means that they have a lower accuracy of stabilization. But there is no overvoltage and there is no need to think about additional protection. To avoid confusion, these devices are called relay stabilizers, that’s how they are described in most cases.
There is one more not the most pleasant moment of electromechanical voltage stabilizers for apartments: they wear out faster, they require regular maintenance, about once every six months.
Engineers are constantly improving products, improving the characteristics. Modern models have low noise and acceptable accuracy of stabilization.
A good example is a stabilizer of relay type Resanta ASN 500/1-C. Designed to regulate the input voltage and protect electronic devices from voltage surges with a connected load of up to 0.5 kW. It has noise suppression filters. Microprocessor control allows timely response to voltage changes, and the digital indicator allows you to monitor the parameters of the input voltage on the screen. If the permissible voltage limits are exceeded, the stabilizer will automatically cut off the power supply.
- Packaging Resanta ASN 500/1-C
- On the back of the stabilizer there is a socket for connecting the load and a fuse
- Front panel of the stabilizer Resanta ASN 500/1-Ts with display
- Stabilization voltage at the output of Resanta ASN 500/1-Ts
Resanta ASN 500 can provide stable power supply for such devices as gas boilers, receivers, DVD-players, cash registers and TV sets.
Ferroresonant
These are the most bulky of the stabilizers. They have low response time, high reliability and resistance to interference. The stabilization factor is average (about 3-4%), which is not bad.

But the output voltage has a distorted form (not a sine wave), the work depends on frequency changes in the network, is characterized by a large mass and dimensions. Usually used as the first stage of stabilization, if one device to achieve normal voltage is not possible.
Inverter
This is one of the types of electronic devices, but its operation and internal structure are very different from those described above, so this group is considered separately.
In inverter voltage stabilizers there is a double conversion, first the alternating current is transformed into direct current, then back into alternating current, which is fed to the power factor corrector, where it is stabilized. As a result, at the output we have a perfect sinusoid with stable parameters.
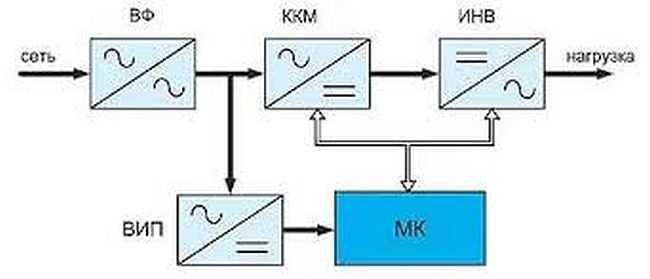
Inverter voltage stabilizer is probably the best choice for today. Here are its advantages:
- A wide operating range of stabilization. The normal range is from 115-290 V.
- Low response time – the delay is a few milliseconds.
- High stabilization accuracy: average values in the class of 0.5-1%.
- The output is a perfect sinusoid, which is important for some types of equipment (gas boilers, for example, washing machines of the latest generation).
- Suppression of interference of any nature.
- Small size and weight.
In terms of price, this is not the most expensive equipment – they cost about the same as relay and almost twice as low as electronic ones. At the same time, the quality of conversion in inverter units is much higher.

The disadvantage of this equipment is one: when working, the elements get very warm. For cooling, fans are built in, which emit a soft buzzing sound. Choosing such a voltage stabilizer for an apartment, then put it in the corridor, reducing the noise. In private homes, there are more opportunities to choose the place of installation, so it is quite realistic to find one where the noise will not interfere.
Which stabilizer is better
To say that some type of stabilizer is better and some is worse makes no sense. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, each in a certain situation, for certain requirements – the best choice.
Let’s take a look at typical situations that many people face:
There are actually a lot of situations. But in any case, select the type of voltage stabilizer for the house should be based on their existing problem. Then already in the selected category to choose according to the parameters.
Choice of manufacturer and price
The most difficult to choose a manufacturer. Stazu should say that Chinese units are better not to consider. Even with those that are only half Chinese (with production in the Celestial Empire and head office in another country) you should be very careful. Quality is not always stable.

If you do not care about the external component, pay attention to stabilizers of Russian or Belarusian production. These are Stil and Leader. Quite decent units, with not very good design, but with stable quality.
When you need perfect equipment, look for Italian ORTEA. They have both build quality and appearance at the top. Also, RESANTA has good reviews. Their goods are rated at 4-4.5 on a five-point scale.
Several examples of stabilizers of different types with a capacity of 10-10.5 kW with characteristics and prices are given in the table. See for yourself.
| Név | Típus | Operating input voltage | Stabilization accuracy | Placement type | Ár | User rating on a 5-point scale | Megjegyzések |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUCELF SRWII-12000-L | relay | 140-260 В | 3,5% | wall-mounted | 270$ | 4,0 | |
| RUCELF SRFII-12000-L | relay | 140-260 В | 3,5% | floor standing | 270$ | 5,0 | |
| Energy Hybrid SNVT-10000/1 | hybrid | 144-256 В | 3% | floor standing | 300$ | 4,0 | perfect sine wave at the output, protection against short circuit, against overheating, against overvoltage, against interference |
| Energy Voltron PCH-15000 | relay | 100-260 В | 10% | floor | 300$ | 4,0 | |
| RUCELF SDWII-12000-L | electromechanical | 140-260 В | 1,5% | wall-mounted | 330$ | 4,5 | |
| RESANTA ACH-10000/1-EM | electromechanical | 140-260 В | 2% | floor | 220$ | 5.0 | |
| RESANTA LUX ASN-10000N/1-TS | relay | 140-260 В | 8% | wall-mounted | 150$ | 4,5 | distortion-free sine wave Protection against short circuit, against overheating, against overvoltage, against interference |
| RESANTA ACH-10000/1-TS | relay | 140-260 В | 8% | floor | 170$ | 4.0 | distortion-free sine wave Protection against short circuit, against overheating, against overvoltage, against interference |
| Otea Vega 10-15 / 7-20 | electronic | 187-253 В | 0,5% | floor standing | 1550$ | 5,0 | |
| Stihl R 12000 | electronic | 155-255 В | 5% | floor | 1030$ | 4,5 | |
| Stihl R 12000C | electronic | 155-255 В | 5% | floor | 1140$ | 4.5 | |
| Energy Classic 15000 | electronic | 125-254 В | 5% | wall-mounted | 830$ | 4,5 | |
| Energy Ultra 15000 | electronic | 138-250 В | 3% | wall-mounted | 950$ | 4,5 | |
| SDP-1/1-10-220-T | electronic inverter | 176-276 В | 1% | floor | 1040$ | 5 | distortion-free sine wave |
The price range is wide, but the types of equipment here range from budget relay and electromechanical to ultra-reliable electronic.











