It is not easy to design your own heating system. Even if the installers “plan” it, you need to be aware of many nuances. Firstly, to control their work, and secondly, to assess the need and feasibility of their proposals. For example, in recent years is strongly promoted hydrostrelka for heating. This is a small addition, the installation of which costs a considerable amount of money. In some cases it is very useful, in others you can easily do without it.
Contents of the article
What is a hydrostrelka and where it is installed
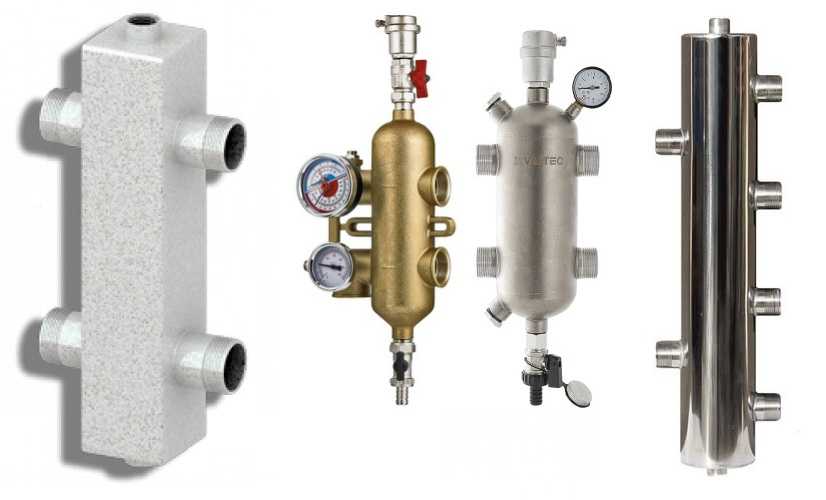
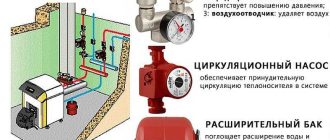
The correct name of this device is a hydraulic arrow or a hydraulic splitter. It is a piece of round or square pipe with welded spigots. Inside, as a rule, there is nothing. In some cases, there may be two screens. One (at the top) for better “escape” of air bubbles, the second (at the bottom) to sift out contaminants.

In the heating system hydrostrelka is placed between the boiler and consumers – heating circuits. It can be located both horizontally and vertically. More often put vertically. With this arrangement in the upper part of the put an automatic air vent, below – a stopcock. Through the faucet periodically drains some of the water with accumulated dirt.
That is, it turns out that the vertically placed hydrodivider, along with the main functions, removes air and makes it possible to remove sludge.
Purpose and principle of operation
A hydrostrelka is needed for branched systems, in which several pumps are installed. It provides the required flow rate for all pumps, regardless of their capacity. That is, in other words, it serves for hydraulic decoupling of the pumps of the heating system. That is why they also call this device – a hydraulic splitter or a hydraulic splitter.
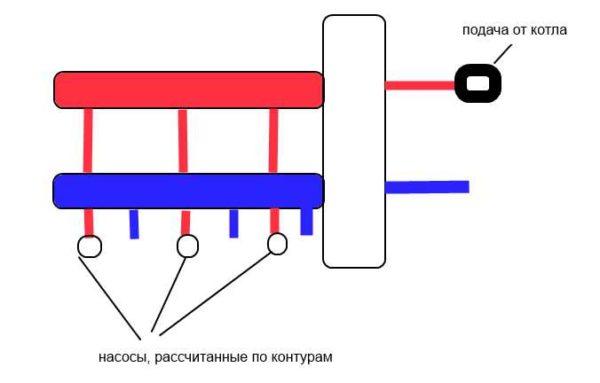
Hydrostrelka put in the case if the system provides several pumps: one on the boiler circuit, the rest on the heating circuits (radiators, water heated floor, boiler indirect heating). For correct operation of their performance is selected so that the boiler pump can pump a little more coolant (10-20%) than is required for the rest of the system.
Why do you need a hydrostrelka for heating? Let’s look at an example. In a heating system with several pumps, they often have different capacities. It often happens that one pump is many times more powerful. To put all pumps have to be next to each other – in the collector unit, where they are hydraulically connected. When the powerful pump is switched on at full capacity, all other circuits are left without coolant. This happens all over the place. To avoid such situations and put in the heating system hydrostrelka. The second way – to spread the pumps over a large distance.
Modes of operation
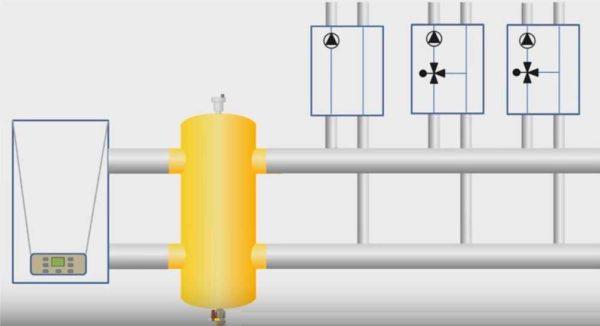
Theoretically, there are three modes of operation of the heating system with a hydrostrelka. They are shown in the figure below. The first – when the boiler pump pumps exactly as much coolant as the entire heating system requires. This is an ideal situation, in real life is very rare. Let us explain why. Modern heating adjusts the work on the temperature of the coolant or on the temperature in the room. Let’s imagine that all perfectly calculated, tweaked the valves and after tuning achieved equality. But after some time the parameters of the boiler or one of the heating circuits will change. The equipment will adjust to the situation, and the equality of performance will be violated. So this mode can exist for a few minutes (or even less).
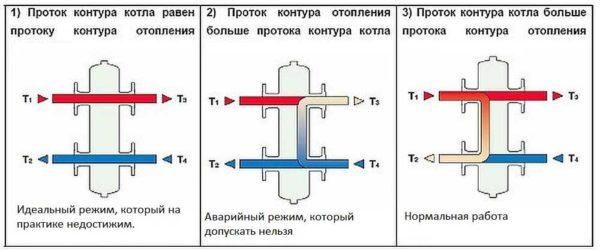
The second mode of operation of the hydrostrelka – when the flow rate of heating circuits is greater than the capacity of the boiler pump (middle figure). This situation is dangerous for the system and should not be allowed. It is possible if the pumps are selected incorrectly. More precisely, the boiler pump has too low a capacity. In this case, in order to ensure the required flow rate, in the circuits together with the heated coolant from the boiler will be supplied from the return. That is, at the boiler outlet, e.g. 80°C, in the circuits after the cold water is fed, e.g. 65°C (the actual temperature depends on the flow deficit). Passing through the heating devices, the temperature of the coolant drops by 20-25°C. That is, the temperature of the coolant supplied to the boiler will be at best 45°C. If we compare it with the output temperature of 80°C, the temperature delta is too large for a normal boiler (not a condensing boiler). This mode of operation is not normal and the boiler will quickly fail.
The third operating mode is when the boiler pump supplies more heated coolant than the heating circuits require (right picture). In this case, part of the heated coolant is returned back to the boiler. As a result, the temperature of the incoming coolant rises and it works in a sparing mode. This is the normal mode of operation of the heating system with a hydrostrelka.
When a hydrostrelka is needed
Hydrostrelka for heating is needed 100% if the system will stand several boilers working in a cascade. And they must work simultaneously (at least most of the time). Here, for the correct operation of the hydrosplitter – the best way out.
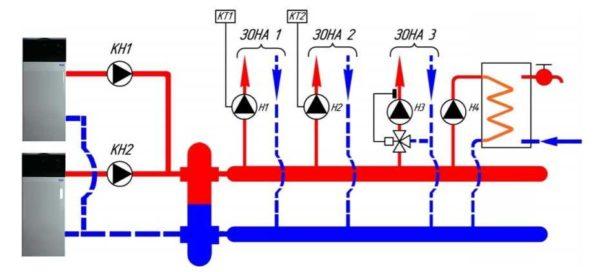
More hydrostrelka for heating can be useful for boilers with cast iron heat exchanger. In the container of the hydrodistributor is constantly mixing warm and cold water. This reduces the temperature delta at the boiler outlet and inlet. For a cast iron heat exchanger, this is a boon. But with the same task will cope bypass with a three-way adjustable valve and it will cost much cheaper. So even for cast iron boilers, standing in small heating systems, with approximately the same flow rate is quite possible to do without connecting the hydrostrelka.
When you can put
If the heating system has only one pump – on the boiler, hydrostrelka is not needed at all. You can do without it if you install one or two pumps on the circuits. Such a system can be balanced with the help of regulating valves. When is the installation of a hydrostrelka justified? When the conditions are as follows:
- There are three or more circuits, all with very different capacities (different circuit volumes, different temperatures required). In this case, even with perfectly accurate selection of pumps and calculation of parameters, there is a possibility of unstable operation of the system. For example, it is often the case that when the underfloor heating pump is switched on, the radiators become cold. In this case we need a hydraulic isolation of pumps and therefore put a hydraulic arrow.
- In addition to radiators, there is a water floor heating, which heats large areas. Yes, it can be connected through a manifold and mixing unit, but it can force the boiler pump to work in extreme mode. If you have frequent pump burns on your heating, you probably need a hydrostrel installation.
- In a medium or large volume system (with two or more pumps) you are going to install automatic control equipment – by coolant temperature or by air temperature. At the same time, you do not want to/can not regulate the system manually (with taps).
In the first case, hydrostrelka is most likely necessary, in the second case, it is worth thinking about its installation. Why only think? Because it is a considerable expense. And it’s not just the cost of the hydrostrelka. It costs about 300$. We will have to put additional equipment. As a minimum, you need manifolds at the inlet and outlet, pumps for each circuit (in a small system without hydrostrelka without them can do without them), as well as the speed control unit pumps, because through the boiler they can no longer be controlled. Together with the fee for installation of equipment, this “extra” is about two thousand dollars. It is really a lot.
Why do they put this equipment? Because with hydrostrelka heating works more stable, does not require constant adjustment of the flow of coolant in the circuits. If you ask the owners of cottages, whose heating is made without a hydrodistributor, you will be told that often have to reconfigure the system – turn valves, adjusting the flow of coolant in the circuits. This is typical if different heating elements are used. For example, a warm floor on the first floor, radiators on two floors, heated utility rooms in which you need to maintain a minimum temperature (garage, for example). If you are supposed to have approximately the same system, and the prospect of “tweaking” you are not satisfied, you can put hydrostrelka for heating. With its presence in each circuit goes to each circuit as much coolant as it requires at the moment and in no way depends on the parameters of operation, working next to the pumps of other circuits.
How to select the parameters
The hydraulic splitter is selected taking into account the maximum possible speed of the coolant flow. The fact is that at high speed of movement of the liquid through the pipes, it begins to make noise. To avoid this effect, the maximum speed is taken equal to 0.2 m/s.
According to the maximum flow of the coolant
To calculate the diameter of the hydrostrelka according to this method, the only thing you need to know is the maximum flow of coolant that is possible in the system and the diameter of the spigots. With spigots, everything is simple – you know what kind of pipe you will do the distribution. We know the maximum flow that the boiler can provide (it is in the technical specifications), and the flow rate of the circuits depends on their size/volume and is determined by the selection of circuit pumps. The flow rate for all circuits is added up and compared with the boiler pump capacity. The higher value is substituted into the formula for calculating the volume of the hydraulic jet.

Here is an example. Let the maximum flow rate in the system is 7.6 cubic meters per hour. The permissible maximum velocity is taken standard – 0.2 m / s, the diameter of the spigots is 6.3 cm (pipes at 2.5 inches). In this case we get: 18.9 * √ 7.6/0.2 = 18.9 * √38 = 18.9 * 6.16 = 116.424 mm. If we round up, we get that the diameter of the hydraulic shooter should be 116 mm.
According to the maximum boiler output
The second method is the selection of the hydraulic arrow according to the boiler output. The estimate will be approximate, but it can be trusted. You will need the power of the boiler and the temperature difference between the coolant in the supply and return pipelines.

The calculation is also not difficult. Let the maximum power of the boiler – 50 kW, the temperature delta – 10 ° C, the diameters of the branch pipes are the same – 6.3 cm. Substituting the figures, we get – 18,9 * √ 50 / 0,2 * 10 = 18,9 * √ 25 = 18,9 * 5 = 94,5 mm. Rounding off, we get a diameter of 95 mm.
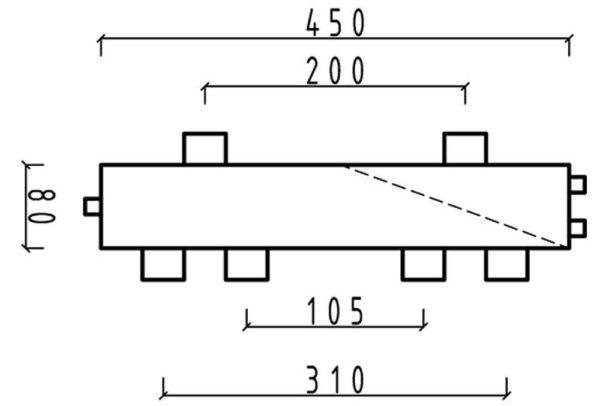
How to find the length of the hydro jet
With the diameter of the hydrosplitter for heating determined, but it is necessary to know the length. It is selected depending on the diameter of the connected branch pipes. There are two types of hydrostrels for heating – with branches located one opposite the other and with alternating spigots (located with a shift one relative to the other).
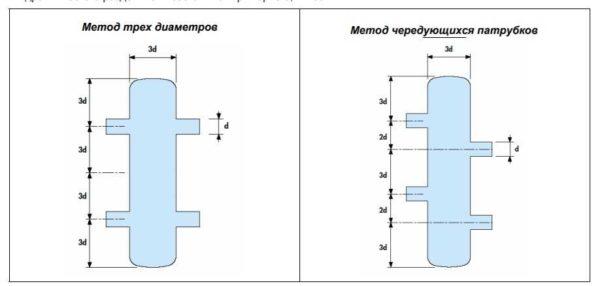
Calculate the length in this case is easy – in the first case it is 12d, in the second – 13d. For medium systems, you can also pick up the diameter depending on the spigots – 3*d. As you can see, nothing complicated. You can calculate it yourself.
Buy or make with your own hands?
As said, ready-made hydrostrelka for heating costs a lot – 200-300$, depending on the manufacturer. To reduce costs, there is a legitimate desire to make it yourself. If you know how to cook, no problem – you bought the materials and made it. But it is necessary to take into account the following points:
- The threads on the bends should be well cut and symmetrical.
- The walls of the bends of the same thickness.

Seems like obvious things. But you’d be surprised how difficult it is to find four normal bends with normally made threads. Further, all welds must be of high quality – the system will work under pressure. The joints are welded strictly perpendicular to the surface, at the right distance. In general, it is not such an easy task.
If you do not know how to use the welding machine yourself, you will have to look for a contractor. Find it is not easy: either expensive ask for services, or the quality of work, to put it mildly, “not very”. In general, many decide to buy hydrostrelka, despite the considerable cost. Especially recently, domestic manufacturers do not do worse, but much cheaper.