One of the most important life support systems in our rather unglamorous climate is heating. There are several different ways to make a heating system. And one of them is steam heating. The system is effective, but it is used very rarely – too many of its disadvantages.
Περιεχόμενα του άρθρου
What it is and how it differs from the usual water systems
Many people believe that steam and water heating is the same. This is a misconception. With steam heating there are also batteries and pipes, there is a boiler. But it is not water that moves through the pipes, but water vapor. The boiler requires a very different kind of boiler. Its task is to vaporize water, not just heat it to a certain temperature, respectively, its power is much higher, as well as requirements for reliability.

System elements
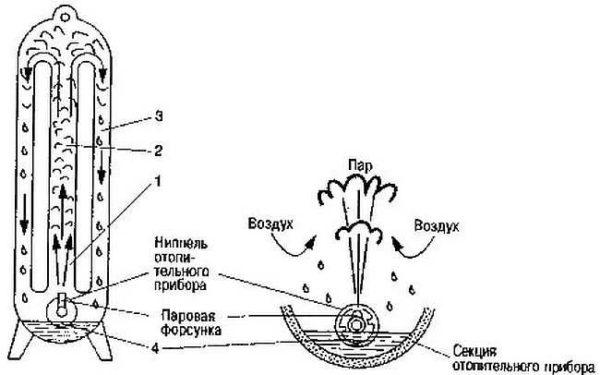
In steam heating, water vapor moves through a pipeline. Its temperature ranges from 130°C to 200°C. Such temperatures impose special requirements on the system elements. Firstly, the pipes. These are only metal pipes – steel or copper. And they must be seamless, with a thick wall.

Secondly, radiators. Only cast-iron, registers or pipe with finning are suitable. Cast iron under these conditions are less reliable – in the heated state from contact with cold liquid they can burst. More reliable in this respect are pipe registers, coils or a pipe with fins attached to it – a convector type heater. Steel is more tolerant of cold water hitting its heated surface.
Service life and scope of application
But do not think that the steel steam heating system will serve for a very long time. In it circulates very hot and humid steam, and these are ideal conditions for corrosion of steel. Elements of the system quickly fail. Usually they burst in the most rusty places. With the fact that inside under pressure is pressurized steam with a temperature above one hundred degrees, the danger is obvious.
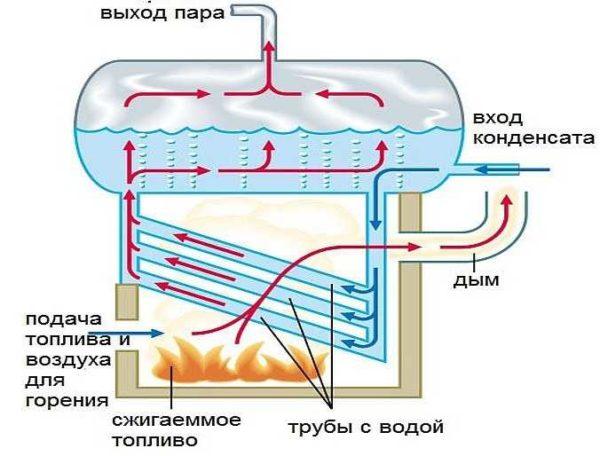
Therefore, steam heating is recognized as dangerous and prohibited for heating public places and apartment buildings. It is still used in some private homes or for heating industrial premises. In production, it is very economical if steam is a derivative of the technological process. In private homes, steam heating is used mainly in houses of seasonal residence – in summer houses. All because of the fact that it normally tolerates freezing – there is little water in the system and it can not harm, as well as because of its economy at the stage of the device (compared to water systems) and high rate of heating the premises.
Advantages and disadvantages
Steam heating is not the most popular, but it has both positive and negative points. And the pluses are quite significant:
- High efficiency of heating. The fact is that the steam in the system does not just heat radiators and pipes to some temperature. Because of the large temperature difference, it condenses. And when condensing 1 liter of steam gives 2300 kJ of heat. Whereas when the same amount of water cools down to 50°C, only 100 kJ of heat is given off. This is why very few radiators are required to heat a room. In some cases, some pipes are sufficient.
- Since steam heating is a small system, it has low inertia. The room starts to heat up just a few minutes after the boiler starts.
The disadvantages of steam heating systems are even more impressive:
- The high temperature of the steam causes all elements of the system to heat up to 100°C or more. This leads to the following consequences:
- very active air circulation in the room, which is uncomfortable and sometimes harmful (in case of dust allergies);
- the air in the room dries out;
- hot elements of the system are traumatic and must be covered, including pipes;
- not all building materials normally tolerate prolonged heating to such temperatures, so the choice of finishing materials is very limited (in fact, it is only cement plaster with subsequent painting with heat-resistant paints).
- Simple steam heating has very limited options for adjusting the heat output. There is only one way to change the temperature – make several parallel branches and turn them on as needed. The second way is to turn off the boiler when it overheats and turn it on after the room cools down. This process is controlled by automation, but this method is far from the most comfortable, since there are constant temperature fluctuations.
- The system is noisy. When moving the steam makes quite a lot of noise. In production shops it does not interfere very much, but in a private house it can be a problem.
As you can see, steam heating is not the best choice, although it is quite inexpensive to arrange.
Types of steam heating systems
According to the method of device distinguish steam heating of two types: with a closed and open loop system. In a closed system, condensate drains into a special receiving pipe, which is led to the corresponding cat inlet. It is laid with a slight slope, so that the condensate moves through the system by gravity.
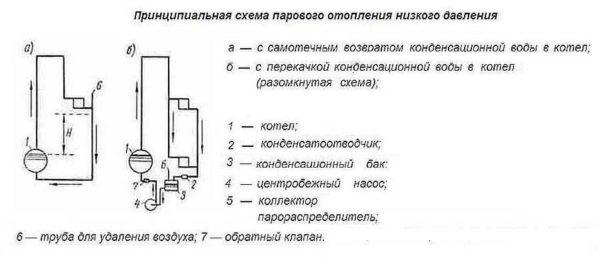
In an open system, condensate is collected in a special tank. When it is filled, it is pumped to the boiler by means of a pump. In addition to the different construction of the system is used and different steam boilers – not all of them can work in closed systems.
In general, there are steam heating systems with a pressure close to atmospheric or even lower. Such systems are called vacuum-steam. What is the appeal of such an installation? Because at low pressure, the boiling point of water is reduced and the system has a more acceptable temperature. But the difficulty in ensuring tightness – air is always sucked in through the connections – has led to the fact that these schemes are practically uncommon.
Low-pressure steam heating is more common. Available domestic steam boilers can create a pressure of no more than 6 atm (at a pressure of more than 7 atm the use of equipment requires permission).
Types of piping
According to the type of wiring steam heating is:
When laying the steam pipeline is made with a slight slope (in 1-2%) in the direction of steam movement, and the condensate pipeline – in the direction of condensate movement.
Boiler selection
Steam boilers can operate on all types of fuel – gas, liquid and solid fuel. In addition to the choice of fuel, it is necessary to correctly select the power of the steam boiler. It is determined depending on the area to be heated:
- up to 200 m2 – 25 kW;
- from 200 m2 to 300 m2 – 30 kW;
- from 300 m2 to 600 m2 – 35-60 kW.
In general, the method of calculation is standard – for 10 square meters take 1 kW of power. This rule is true for houses with a ceiling height of 2.5-2.7 meters. Then follows the choice of a specific model. When buying, pay attention to the presence of a quality certificate – the equipment is dangerous and must be tested.
What pipes to use
Temperatures in steam heating can normally tolerate only metals. The cheapest option – steel. But their connection requires welding. It is also possible to use threaded connections. This option is budget, but not durable: steel in a humid environment quickly corrodes.

Galvanized and stainless steel pipes are more durable, but their price is not modest. But the connection is threaded. Another option – copper pipes. They can only be soldered, they are expensive, but they do not rust. Because of their higher thermal conductivity, they transmit heat even more efficiently. So such a heating system will be super efficient, but also very hot.