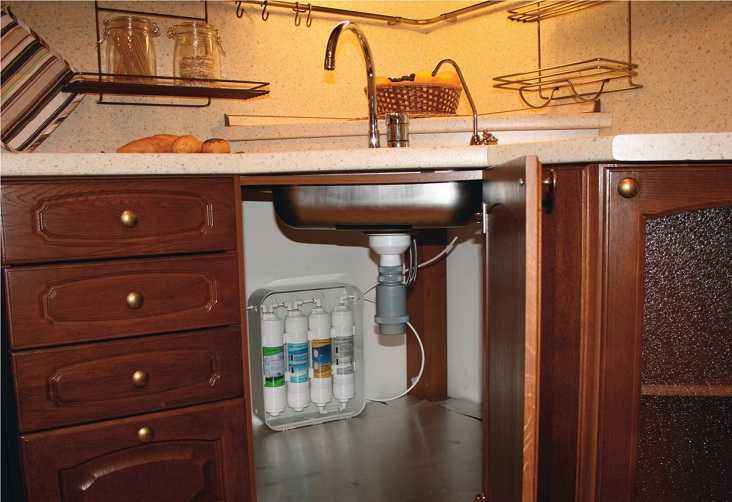
The tap water in our taps is mostly unsuitable for drinking. In order not to buy bottled water, you can purify what you have to the desired state. One way is to install a water filter under the sink. They are usually equipped with a small faucet and mounted simply. Their disadvantage is a decent price and the need to replace the cartridges. But they are good at purifying water that complies with GOST.

Artiklens indhold
Types of filters under the sink
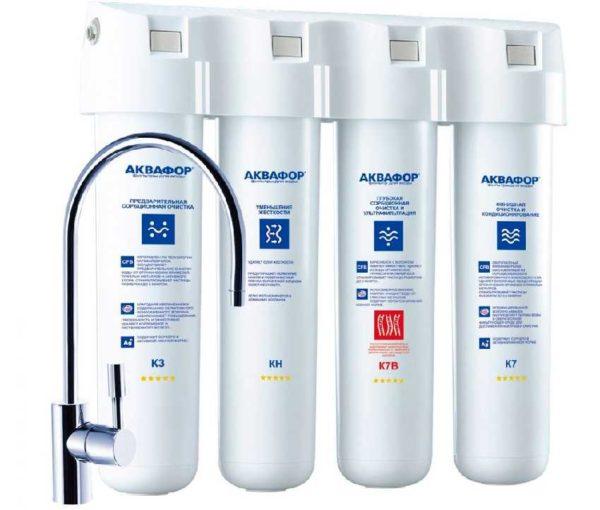
To obtain drinking water at home, there are water filters under the sink of two types – flow-through cartridge and using reverse osmosis technology (reverse osmosis system). These stationary models are externally very similar. They consist of several plastic flask-cases, in which the filter elements are located. Reverse osmosis system has an additional flask with a membrane.

Cartridge and reverse osmosis system – what is the difference?
The main difference between the reverse osmosis system is the use of a special semipermeable membrane. The whole point of this purification is that only water molecules pass through the very small pores of the membrane. Organic and inorganic substances dissolved in it simply do not pass through. Everything down to bacteria and microbes are trapped.
The degree of purification of water reverse osmosis systems – 98-99%. That is, at the output we get almost distilled water that has no taste or odor. Prolonged use of such a liquid leads to the leaching of salts from the body. Therefore, at the output of the reverse osmosis system put mineralizer, in some models it is immediately in the package. This is an additional flask, which contains a backfill of useful minerals. It enriches the composition of water, bringing it to the norm.
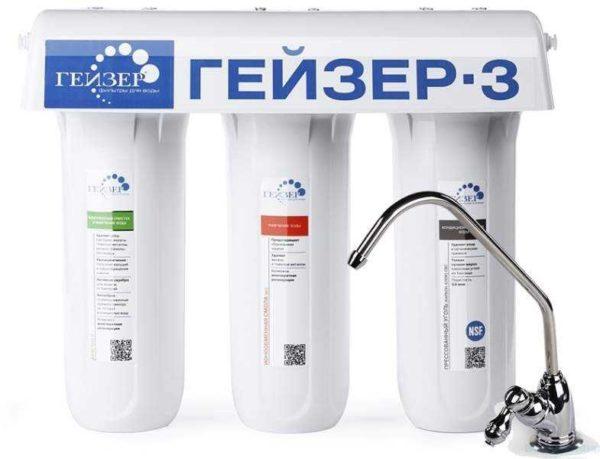

When using stationary flow-through cartridge filters under the sink, you will not get such clean water. Reverse osmosis removes salts, and flow filters (and pitchers too) remove them partially. The difference is clear and tastes good. In addition, after the flow filter, the scale in the kettle remains, but it has a different character, it becomes more friable and is easily removed.
When using cartridge filters, we can not say that the purification is bad (about 70-80% vs. 95-98% in reverse osmosis), but without the presence of a stage of bacterial purification (there are such filter elements with silver additives), it may be risky to drink it without boiling.
Features of operation
In fact, cartridge systems, and reverse osmosis systems are multistage filters, which implies regular replacement of filter elements. Each such element has a certain resource, which is usually specified in liters, it is how much water it can process without loss of quality. Or often in parallel indicate a time interval of six months, a year, etc. That is, even if the filter has not worked out its resource, it must be changed. Just in them accumulate microorganisms that, if the terms are violated, can get into the water in mass quantities.

There is another situation, the water deteriorates in quality even before the specified time interval and resource. This happens at an increased level of contamination and the filter exhausts its life much faster. There are two ways out: change the filter elements as they become contaminated or put before the installation of an additional stage of purification, which solves this problem.
Features of the choice
The cartridge system is good in that you can select filter elements depending on the composition of water (we are talking about both systems). Therefore, before buying it makes sense to analyze the water, and then select the composition of filters to specifically remove the existing problem. For example, reverse osmosis systems do not work well on water with a high iron content. If you have such a problem, before the installation should be put equipment to remove iron (aeration units or catalytic filters) and only after them you can connect filters with reverse osmosis.
The second point: for normal operation of reverse osmosis requires a decent pressure. Depending on the type of membrane, 1.5 atm (50G) or at least 3 atm (100G) is required. If your water supply does not have such a pressure, it is necessary either to take the installation with a pump (expensive and few), or put a pump in the system, increasing the pressure.
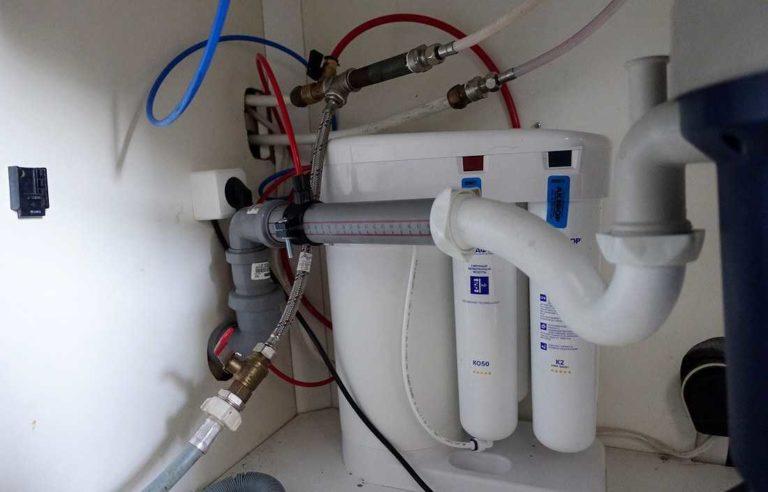
Reverse osmosis is connected to the sewage system. There he drains the concentrate of salts that are removed from the water. If you are planning on installing in a private home and you have a drainage pit or storage tank, you need to keep this in mind. A decent amount of water goes into the sewer, for every liter of purified water, 2-4 liters of concentrate (depending on the hardness) are discharged. Multistage cartridge filter is connected only to the water supply, and all the salts discharged by it remain in the filter.

Since reverse osmosis removes almost all the salts, with prolonged use of such water, the salts are removed from the body. To solve this problem at the output of the filter put mineralizer – a flask with a backfill of mineral salts. It can go in the assembly, and you can put it after the filter. Only it should be said that drinking water without mineralization is more pleasant than “salted”, and the taste of dishes on such water is better. Therefore, many manufacturers provide two modes of operation – with mineralizer or without (switched by the tap).
Here seems to be all the information that can somehow affect your choice between multistage filter purification and reverse osmosis. To say specifically that these water filters installed in the kitchen are good, and these are not, none of the experts will not say. Everyone has their own point of view, and for each better option. And each system has its own advantages.
Multistage filters with cartridges
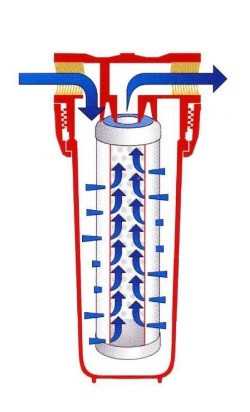
The cartridge itself consists of a housing and a filter element. From what contaminants are cleaned depends on the filter element. The water flows as follows:
Principle of operation of the cartridge:
- enters the inlet pipe;
- flows between the bulb wall and the cartridge;
- as it passes through the cartridge material, it is purified;
- rises through the cavity of the filter element;
- exits the second spigot.
In multi-stage drinking water filters, this transformation takes place sequentially in each of the flasks. To make this possible, they are all united by a common element located in the upper part and connecting the individual housings into a single purification system.
The multistage flow-through water filter works at any pressure that the water movement can provide. The flasks are usually made of plastic, it can be transparent or not. Sometimes there are stainless steel housings, but it is expensive and there are not very many of them.
Parameters and characteristics
The main indicators are performance, service life, and non-critical – pressure loss, maximum operating temperature. Most often when choosing a water filter in the apartment, pay attention to the service life. We have already mentioned it above.
Second, the performance. This is the amount of water that can be purified by the unit for a certain period of time. Usually indicated liters per minute (l/min), but it can also be per hour or per day.
Next, you should pay attention to the size of the filter. There are two standard sizes:
- Big Blue (BB) (in Russian BigBlue) – diameter 185 mm.
- Slim Line (SL) (SlimLine in Russian) – diameter 120-130 mm.
The most common filters of larger format, they are desirable to take, there will be no problems with the replacement of cartridges. There are cases of individual size, but the difficulty here is that in this case you will be tied to the parts of only one company, while the standard filter elements can be taken from other manufacturers. True, not always fits the “head” to the lid, but for these cases there are adapters.
The height of the housing is different. The most common sizes are 10 and 20 inches. If space permits, it is better to take the larger ones. The resource will be increased and it is necessary to change cartridges less often. But in general, when choosing the size, you should be guided by your needs, a small filter is enough for one or two people.
What are the filtering elements
There are a lot of organic and inorganic substances dissolved in water, in addition, there are mechanical impurities in the form of suspension – sand, rust, pieces of winding, etc. In order to obtain normal drinking water, they must be removed and brought to a normal content. For this purpose, different filtering elements – cartridges are used. They come in several types:
- Polypropylene. In multistage purification systems, they are put first. Their task is to remove mechanical impurities. Contaminants accumulate on the surface and in the thickness of the material.
- Coal. Contains activated carbon. They remove chlorine and its compounds, cope well with organic compounds, remove extraneous odors. In such cartridges, the usual activated carbon made from coconut shells (granulated or pressed). Depending on the type of carbon, the efficiency of purification changes (the best – coconut).
- Ion-exchange. Such cartridges contain ion exchange resins. They perfectly cope with water softening, magnesium and calcium salts (hardness salts) are replaced by sodium. Their disadvantage is periodic regeneration, restoring performance. Track the time of regeneration can be traced by the appearance in the scale of the kettle.
- Kombineret. In multistage systems are rarely used, the main application is in single-kettle versions. It contains several types of filter elements. The quality of purification is worse, but if it is necessary to slightly improve several indicators of water at once (slightly out of the norm), you can use and such options.

Cartridges have their own parameters. In addition to the list of contaminants that it removes and physical dimensions, indicate the resource – the number of liters of water that the element can clean. It is usually specified in liters, but often put also a time resource, not more than 3 months, for example.
Popular models of cartridge filters
Filters installed under the sink are most often three-column (three-stage), less often there are models with four bodies. In any case, the first is a mechanical filter, then an ion-exchange filter and the last charcoal filter. If the elements are four, the carbon ones are put two, but with different types of filling. Sometimes on the fourth stage put bioprotection, a new generation of filters with silver for disinfection.
The most popular brands Aquaphor, Geyser, Barrier, not bad have shown themselves products brand Atoll (Atoll). Select the system first of all on the hardness of water, it is divided into normal, hard, very hard. If there are any other problems, such as the need for bacterial purification, look for models that can give you such purification. Then look at the performance and size.
Here is an example of a popular filter – Barrier Expert for installation under the sink. Small size, good performance and high quality water purification – these are the criteria for choosing this model. And the convenience and speed of changing the filter, an additional bonus for the buyer.
- Popular filter Barrier Expert Ion Exchange
- Barrier Expert filter assembled under the sink
- Three cartridges for the filter
| Navn | Præstation | Purified water temperature | Working pressure | Antal oprensningstrin | Til hvilken slags vand | Pris | Fremstillingsland |
| Barrier “Expert Standard” | 2 l/min | from +5°C to + 35°C | up to 7 atm | 3 | Normal hardness | 40$ | Rusland |
| Barrier “Expert Complex” | 2 l/min | from +5 ° C to + 35 ° C | up to 7 atm | 3 | For hard water with high iron content | 95$ | Rusland |
| Barrier “Expert Ferrum” | 2 l/min | from +5 ° C to + 35 ° C | up to 7 atm | 3 | For water of normal hardness with high iron content | 62$ | Rusland |
| Geyser 2PK Lux | 2.5 l/min | up to +40°C | at least 0.5 atm | 2 | Normal hardness (without mechanical filter) | 33$ | Rusland |
| Geyser 2IVZh Lux | 2.5 l/min | up to +40°C | at least 0.5 atm | 2 | Hard (without mechanical filter) | 35$ | Rusland |
| Geyser 3 IVJ lux | 3 l/min | up to +40°C | from 0.5 atm to 7 atm | 3 | For hard water | 53$ | Rusland |
| AQUAPHOR CRYSTAL A | 2.5 l/min | from +5°C to + 40°C | from 0.63 atm to 6.3 atm | 3 | For water of medium hardness | 40$ | Rusland |
| AQUAFOR Crystal KVADRO NNV | 2.5 l/min | from +5°C to + 40°C | from 0.63 atm to 6.3 atm | 3 | For very hard water | 103$ | Rusland |
| AQUAFOR Trio Fe | 2.5 l/min | from +5°C to + 40°C | from 0.63 atm to 6.3 atm | 3 | For water with high iron content | 60$ | Rusland |
| Crystal ECO | 2.5 l/min | from +5°C to + 40°C | from 0.63 atm to 6.3 atm | 3 | For water disinfection | 75$ | Rusland |
| Praktic EU200 | 1-2 l/min | from +5°C to + 35°C | 1.4 atm to 7.9 atm | 3 | For hard water | 35$ | Germany |
| Praktic EU312 | 1-2 l/min | from +5°C to + 35°C | 1.4 atm to 7.9 atm | 4 | For water with high iron content | 85$ | Germany |
| Praktic EU320 | 1-2 l/min | from +5°C to + 35°C | 1.4 atm to 7.9 atm | 4 | For hard water, ultrafiltration | 100$ | Germany |
| Atoll A-211E g/D-21s STD | from +5°C to + 40°C | up to 6 atm | 2 | For additional treatment of drinking water | 98$ | ||
| Atoll A-211E g/D-21s STD | from +5°C to + 40°C | up to 6 atm | 3 | For hard water | 125$ |
To say that any of these manufacturers is better is impossible, all of them have about the same number of positive and negative reviews. The manufacturers of Barrier filters have a very poorly developed service, although the products themselves are not bad. We can not say that Geyser is ideal in this regard, but things are a little better. In general, Russian manufacturers can not yet please quality service, so that all the problems will have to deal with themselves.

Another tip that may be useful when choosing a filter, look not only at the cost of the set. Much more important is the cost of consumables (cartridges) and their standard sizes, connection methods. The convenience of maintenance is also important, filters will have to be changed, so easy replacement is a plus.
Omvendt osmose-systemer
Under the sink in the kitchen you can put multistage water purification filters working on the principle of reverse osmosis. They are ideal if the water has too many deviations from the norm. When installing a conventional multi-stage filter, it is very difficult to achieve the required water quality, most likely, it will be necessary to add a few more single units to the system, which will allow you to achieve water of normal quality. Reverse osmosis in any case copes with the task, the difference is simply in the amount of water that will be discharged with the removed salts into the sewer (the more hard and polluted water, the more concentrate is discharged).
Principle of operation
A reverse osmosis system consists of membranes with very small pore sizes. Almost all substances in the water, including microorganisms, bacteria and microflora, have molecule sizes larger than water molecules. And the pores in the membrane are so small that only water passes through them. There are very few foreign substances penetrating through the membrane – no more than 0.5-2% of the total amount of water.
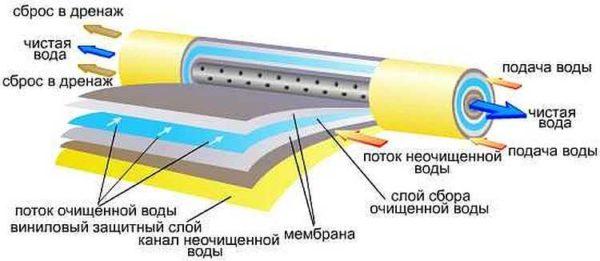
On the other hand, all salts remain on the surface of the membrane. So that they do not contaminate it, they are removed by the flow of water into the sewer.
Features of operation
The size of the membrane for the cartridge is standard. Only specific characteristics of membranes are added. They come in two types by capacity:
- 50G with a capacity of up to 196 liters / day (about 130 ml / min);
- 100G – water purification rate of about 400 l/d (280 ml/min).
The first type of membranes is cheaper, the second is more expensive. To ensure their work requires a certain pressure, for 50G you need at least 1.5 atm, for 100G at least 3 atm. If there is no such pressure in the system, you can find a unit with a built-in pump, you can put it yourself, matching the parameters of the system.
One more thing: water filters under the sink with reverse osmosis do not like too chlorinated or iron water. In principle, before the membrane are pre-filters that eliminate this problem, but pay attention to what type of water is designed for this system.
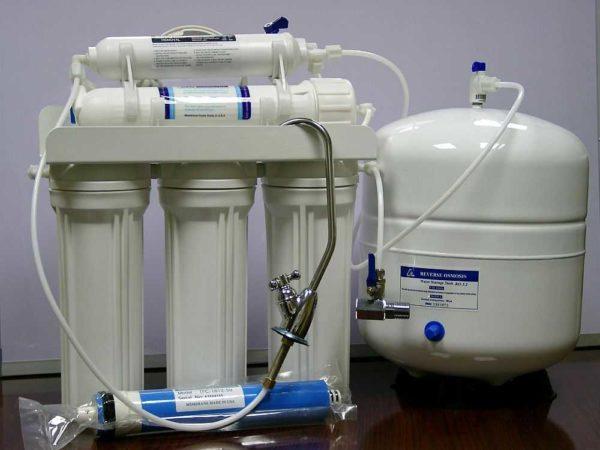

Another nuance: such purification systems work quite slowly, a glass or half in a minute, it’s not much. Therefore, the kit often comes with a tank for storing purified water. This is not just a tank, but a membrane-type tank, which maintains a certain pressure inside. Therefore, purified water can be used even when there is no pressure in the water supply. Just remember that the characteristics indicate the total volume of the tank. In reality, the stock of water in it is about 2 times less.
Some popular models
Since the systems are very similar, they are produced by the same companies as the usual cartridge water purification and softening systems, so new names are rare. In descending order of popularity: Geyser, Aquaphor, Atoll, Barrier. Characteristics of some models are summarized in the table. According to it you can get a general idea of the order of prices and the difference in characteristics, but each model usually has several modifications, usually for water of different hardness or with different additional problems (increased iron content, bacterial contamination, etc.).
| Navn | Kapacitet | Working pressure | Antal oprensningstrin | Water temperature | Water tank | Pris |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atoll A-550 Patriot | 120 l/day | 2,8 – 6,0 bar | 5 | 4°C – 38°C | er | 130$ |
| Atoll A-575E (Russian-made) | 195 l/day | 2,8 – 6,0 bar | 5 | 4°C – 38°C | er | 200$ |
| Aquaphor DWM-101S Morion (with mineralizer) | 187 l / day | 2 – 6.5 atm | 6 | 5°C – 38°C | 5 liter tank | 120$ |
| Aquaphor Crystal Eco H (bacterial protection for hard water) |
60 l/day | 2 – 6,5 atm | 4 | 5°C – 38°C | no | 90$ |
| Geyser Prestige-P with pump | 270 l/day | from 1.5 atm | 5 | 5°C – 38°C | 12 l tank | 180$ |
| Geyser Prestige-M (with mineralizer) | 200 l/day | from 3 atm | 6 | 5°C – 38°C | 12 l tank | 130$ |
| Barriere Profi Osmo 100 | 228 l/day | 3 – 7 atm | 5 | 5°C – 35°C | 8 liter tank | 140$ |
| Barrier K-OSMOS (with pump) | 200 l/day | 3 – 7 atm | 4 | 5°C – 35°C | back 8 liters | 120$ |
What else you need to know about reverse osmosis systems, they must be operated continuously. Long interruptions are very undesirable.